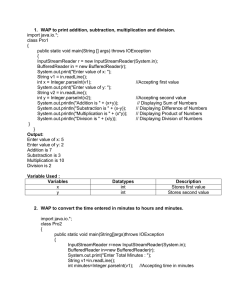
NUMBER SYSTEM
... Determine the number of digits after the decimal point which do not have bar on them. Let there be n digits without bar just after the decimal point. Multiply both sides of x by such power of 10, so that only repeating decimals are remaining on the right side of the decimal point. Use the method of ...
... Determine the number of digits after the decimal point which do not have bar on them. Let there be n digits without bar just after the decimal point. Multiply both sides of x by such power of 10, so that only repeating decimals are remaining on the right side of the decimal point. Use the method of ...
APSC 174J Lecture Notes
... since E and G do not have exactly the same elements; in particular, we can see that 7 ∈ G whereas 7 ∈ / E, and this shows that the elements of E and G are not exactly the same. Writing down the elements of a set explicitly is sometimes plainly impossible. Let B for example be the set of all integers ...
... since E and G do not have exactly the same elements; in particular, we can see that 7 ∈ G whereas 7 ∈ / E, and this shows that the elements of E and G are not exactly the same. Writing down the elements of a set explicitly is sometimes plainly impossible. Let B for example be the set of all integers ...
HS Glossary
... algebra (A) The branch of mathematics that uses letters and/or symbols, to represent numbers and express mathematical relationships. algebraic equation (A) A mathematical statement that is written using one or more variables and constants which contains an equal sign. Examples: ...
... algebra (A) The branch of mathematics that uses letters and/or symbols, to represent numbers and express mathematical relationships. algebraic equation (A) A mathematical statement that is written using one or more variables and constants which contains an equal sign. Examples: ...