Transport Characteristics of Gated Core
... 1. Introduction Recent development of nanotechnology enables to fabricate the semiconductor nanowires (NW) with the coremultishell structure (CMS) for which the outer diameter is less than 30 nm [1]. Such nanostructures find an application in the quantum electronics because of their transport proper ...
... 1. Introduction Recent development of nanotechnology enables to fabricate the semiconductor nanowires (NW) with the coremultishell structure (CMS) for which the outer diameter is less than 30 nm [1]. Such nanostructures find an application in the quantum electronics because of their transport proper ...
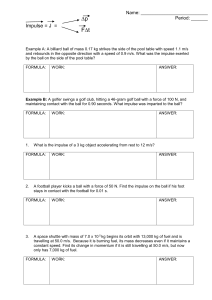
Worksheet 9 - Impulse
... A tennis player, remembering her coach’s emphasis on “follow-through,” kept her racket in contact with the tennis ball for 0.75 s to achieve an impulse of 74 Ns. What was the average force exerted by the racket on the ball? ...
... A tennis player, remembering her coach’s emphasis on “follow-through,” kept her racket in contact with the tennis ball for 0.75 s to achieve an impulse of 74 Ns. What was the average force exerted by the racket on the ball? ...
January 2009 - University of Michigan
... 1. (Quantum Mechanics) Eight electrons are placed in a 3-d infinite square well (cube) with each side having length = L. Neglect interactions between the electrons. What is the minimum energy of this system? ...
... 1. (Quantum Mechanics) Eight electrons are placed in a 3-d infinite square well (cube) with each side having length = L. Neglect interactions between the electrons. What is the minimum energy of this system? ...
Atomic Structure
... • Implicit in the solutions for the resulting orbital equations (wavefunctions) are three quantum numbers (n, l, and ml). A fourth quantum number, ms accounts for the magnetic moment of the electron. • Examine Table 2-2 and discuss. – n the primary indicator of energy of the atomic orbital. – l dete ...
... • Implicit in the solutions for the resulting orbital equations (wavefunctions) are three quantum numbers (n, l, and ml). A fourth quantum number, ms accounts for the magnetic moment of the electron. • Examine Table 2-2 and discuss. – n the primary indicator of energy of the atomic orbital. – l dete ...
Practice problems - Phenix at Vanderbilt
... levels in this nucleus are not precisely the same as though in the Bohr formula since the electrons are not only affected by the Z=2 nucleus, but they are also affected by each other. However, if one of the electrons from a He atom is removed, this positively charged ion (a 42 He nucleus plus only O ...
... levels in this nucleus are not precisely the same as though in the Bohr formula since the electrons are not only affected by the Z=2 nucleus, but they are also affected by each other. However, if one of the electrons from a He atom is removed, this positively charged ion (a 42 He nucleus plus only O ...
Density of states
In solid-state and condensed matter physics, the density of states (DOS) of a system describes the number of states per interval of energy at each energy level that are available to be occupied. Unlike isolated systems, like atoms or molecules in gas phase, the density distributions are not discrete like a spectral density but continuous. A high DOS at a specific energy level means that there are many states available for occupation. A DOS of zero means that no states can be occupied at that energy level. In general a DOS is an average over the space and time domains occupied by the system. Localvariations, most often due to distortions of the original system, are often called local density of states (LDOS). If the DOS of an undisturbedsystem is zero, the LDOS can locally be non-zero due to the presence of a local potential.