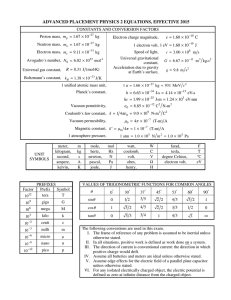
Basics of density functional perturbation theory
... susceptibility, Born effective charge tensors, piezoelectricity, internal strains non-linear dielectric susceptibility, phonon-phonon interaction, Grüneisen parameters, ... ...
... susceptibility, Born effective charge tensors, piezoelectricity, internal strains non-linear dielectric susceptibility, phonon-phonon interaction, Grüneisen parameters, ... ...
Source Location of the Wedge-like Dispersed Ring Current in the
... overlap between the low energy component and high energy component at their high latitude parts. The difference between Figure 2b (3 LT, non-storm time) and Figure 2c (6 LT, storm time) is just the strength of the dispersion, which strongly depends on the drift distance and the electric field streng ...
... overlap between the low energy component and high energy component at their high latitude parts. The difference between Figure 2b (3 LT, non-storm time) and Figure 2c (6 LT, storm time) is just the strength of the dispersion, which strongly depends on the drift distance and the electric field streng ...
Development of Micromegas-like gaseous detectors using a
... where h is the Plank constant. When a particle is accelerated, its wavelength can be reduced to the typical size of an atom or below. The particle can hence be used to probe the structure of matter at very small scales. In practice, this is realized by directing a beam of high energy particles towar ...
... where h is the Plank constant. When a particle is accelerated, its wavelength can be reduced to the typical size of an atom or below. The particle can hence be used to probe the structure of matter at very small scales. In practice, this is realized by directing a beam of high energy particles towar ...
Super-hot (T > 30 MK) Thermal Plasma in Solar Flares
... above the photosphere. (Image credit: NASA)..........................................................................3 Figure 1.3 – Rotation rate versus depth from the photosphere (as a fraction of the solar radius), cut across various latitudes; the tachocline is at ~0.66 R☉ (Image credit: NSF/NSO) ...
... above the photosphere. (Image credit: NASA)..........................................................................3 Figure 1.3 – Rotation rate versus depth from the photosphere (as a fraction of the solar radius), cut across various latitudes; the tachocline is at ~0.66 R☉ (Image credit: NSF/NSO) ...
Microwave Conductivity of Magnetic Field Induced Insulating Phase of Bilayer Hole Systems
... lB = ~/eB. As B is increased, the carrier is more tightly confined, and the zeropoint motion, which favors the gaseous phase, is suppressed. The quantum Hall effects (QHE) exhibited by 2DS have received much attention. The integer quantum Hall effect (IQHE) [von Klitzing et al., 1980] observed aroun ...
... lB = ~/eB. As B is increased, the carrier is more tightly confined, and the zeropoint motion, which favors the gaseous phase, is suppressed. The quantum Hall effects (QHE) exhibited by 2DS have received much attention. The integer quantum Hall effect (IQHE) [von Klitzing et al., 1980] observed aroun ...
Nanoscale Thermoelectric Energy Conversion - Kim Lab
... ABSTRACT Nanoscale Thermoelectric Energy Conversion Yuri M. Zuev In the last two decades numerous novel nanoscale materials have been synthesized. Electronic characterization is essential for the integration of these materials into current semiconductor devices. The investigation of thermoelectric ...
... ABSTRACT Nanoscale Thermoelectric Energy Conversion Yuri M. Zuev In the last two decades numerous novel nanoscale materials have been synthesized. Electronic characterization is essential for the integration of these materials into current semiconductor devices. The investigation of thermoelectric ...
Transverse electric plasmons in bilayer graphene
... As a consequence, the departure of the dispersion curve from the light line in bilayer graphene is much faster for μ > γ /2 than for μ < γ /2, and it is faster than in monolayer graphene as well [note the two orders of magnitude difference between the abscissa scales in Figs. 3(a) and 3(b)]. Thus, w ...
... As a consequence, the departure of the dispersion curve from the light line in bilayer graphene is much faster for μ > γ /2 than for μ < γ /2, and it is faster than in monolayer graphene as well [note the two orders of magnitude difference between the abscissa scales in Figs. 3(a) and 3(b)]. Thus, w ...
Lecture 45
... • “Photonic crystals are composed of periodic dielectric or metallo-dielectric nanostructures that affect the propagation of electromagnetic waves (EM) in the same way as the periodic potential in a crystal affects the electron motion by defining allowed and forbidden electronic energy bands. Photon ...
... • “Photonic crystals are composed of periodic dielectric or metallo-dielectric nanostructures that affect the propagation of electromagnetic waves (EM) in the same way as the periodic potential in a crystal affects the electron motion by defining allowed and forbidden electronic energy bands. Photon ...
Simulation of coherent interactions between Rydberg atoms * F. Robicheaux, J. V. Hernández,
... the atoms will hardly move over the important time. But, unlike previous work where the atoms are at random positions inside the gas, we imagine the atoms have been prepared to have spatial correlation. The simplest case we investigated is when the atoms are positioned to be exactly on a cubic latti ...
... the atoms will hardly move over the important time. But, unlike previous work where the atoms are at random positions inside the gas, we imagine the atoms have been prepared to have spatial correlation. The simplest case we investigated is when the atoms are positioned to be exactly on a cubic latti ...
Density of states
In solid-state and condensed matter physics, the density of states (DOS) of a system describes the number of states per interval of energy at each energy level that are available to be occupied. Unlike isolated systems, like atoms or molecules in gas phase, the density distributions are not discrete like a spectral density but continuous. A high DOS at a specific energy level means that there are many states available for occupation. A DOS of zero means that no states can be occupied at that energy level. In general a DOS is an average over the space and time domains occupied by the system. Localvariations, most often due to distortions of the original system, are often called local density of states (LDOS). If the DOS of an undisturbedsystem is zero, the LDOS can locally be non-zero due to the presence of a local potential.