An overview of Coq
... What is Coq? • A functional programming language with rich type sys. • Define inductive data types and write algorithms manipulating them. • All programs must terminate. ...
... What is Coq? • A functional programming language with rich type sys. • Define inductive data types and write algorithms manipulating them. • All programs must terminate. ...
Local search algorithms - Computer Science, Stony Brook University
... Local search: algorithms that perform local search in the state space, evaluating and modifying one or more current states rather than systematically exploring paths from an initial state. ♦ Operate using a single (or few) current node and gererally move only to neighbors of the node. ♦ Paths follow ...
... Local search: algorithms that perform local search in the state space, evaluating and modifying one or more current states rather than systematically exploring paths from an initial state. ♦ Operate using a single (or few) current node and gererally move only to neighbors of the node. ♦ Paths follow ...
... The course covers the fundamentals of data structures and object-oriented programming. They are two sides of the same coin: – As a programmer becomes more proficient, they realize that how well and efficiently a problem can be solved often depends on how the data are stored. Some of the ideas are qu ...
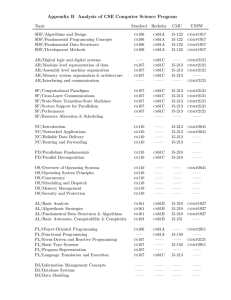
Appendix B Analysis of CSE Computer Science Program
... process and concepts needed to go from high-level descriptions of algorithms to correct imperative implementations, with specific application to basic data structures and algorithms. Much of the course will be conducted in a subset of C amenable to verification, with a transition to full C near the ...
... process and concepts needed to go from high-level descriptions of algorithms to correct imperative implementations, with specific application to basic data structures and algorithms. Much of the course will be conducted in a subset of C amenable to verification, with a transition to full C near the ...
MATHEMATICAL IN COMPUTER SCIENCE
... According to Mollenhoff in 1988 “Atanasoff: Forgotten Father of the Computer” published by Iowa State University Press. [2] To understand the role of mathematics in computer science, there are some questions arise about the relationship between the two fields. 1. What is Computer Science? One defini ...
... According to Mollenhoff in 1988 “Atanasoff: Forgotten Father of the Computer” published by Iowa State University Press. [2] To understand the role of mathematics in computer science, there are some questions arise about the relationship between the two fields. 1. What is Computer Science? One defini ...
An Algorithm For Finding the Optimal Embedding of
... derived [9] by exploiting the structure of the stationary points we only need to find a point on the Stiefel manifold that attains this value. In section 3 we introduce the second problem and show by means of the derivations arising in the first problem that the second problem is equivalent to a con ...
... derived [9] by exploiting the structure of the stationary points we only need to find a point on the Stiefel manifold that attains this value. In section 3 we introduce the second problem and show by means of the derivations arising in the first problem that the second problem is equivalent to a con ...
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm (/ˈælɡərɪðəm/ AL-gə-ri-dhəm) is a self-contained step-by-step set of operations to be performed. Algorithms exist that perform calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning.An algorithm is an effective method that can be expressed within a finite amount of space and time and in a well-defined formal language for calculating a function. Starting from an initial state and initial input (perhaps empty), the instructions describe a computation that, when executed, proceeds through a finite number of well-defined successive states, eventually producing ""output"" and terminating at a final ending state. The transition from one state to the next is not necessarily deterministic; some algorithms, known as randomized algorithms, incorporate random input.The concept of algorithm has existed for centuries, however a partial formalization of what would become the modern algorithm began with attempts to solve the Entscheidungsproblem (the ""decision problem"") posed by David Hilbert in 1928. Subsequent formalizations were framed as attempts to define ""effective calculability"" or ""effective method""; those formalizations included the Gödel–Herbrand–Kleene recursive functions of 1930, 1934 and 1935, Alonzo Church's lambda calculus of 1936, Emil Post's ""Formulation 1"" of 1936, and Alan Turing's Turing machines of 1936–7 and 1939. Giving a formal definition of algorithms, corresponding to the intuitive notion, remains a challenging problem.