No Slide Title
... There are many programming languages available today. These vary in complexity and how close they are to human speech. As a general rule, the closer a language is to English, the further away it gets from the native language of the computer – binary. As languages move further and further away from ...
... There are many programming languages available today. These vary in complexity and how close they are to human speech. As a general rule, the closer a language is to English, the further away it gets from the native language of the computer – binary. As languages move further and further away from ...
PPT
... Concept of type was formalized Names could have any length Arrays could have any number of subscripts Parameters were separated by mode (in & out) Subscripts were placed in brackets Compound statements (begin ... end) Semicolon as a statement separator Assignment operator was := if had an else-if cl ...
... Concept of type was formalized Names could have any length Arrays could have any number of subscripts Parameters were separated by mode (in & out) Subscripts were placed in brackets Compound statements (begin ... end) Semicolon as a statement separator Assignment operator was := if had an else-if cl ...
Programming Languages
... Programming languages are important for students in all disciplines of computer science because they are the primary tools of the central activity of computer science : programming. There is an idea: the structure of language defines the boundaries of thought. ...
... Programming languages are important for students in all disciplines of computer science because they are the primary tools of the central activity of computer science : programming. There is an idea: the structure of language defines the boundaries of thought. ...
N4Less27.pps
... Early programmers allowed control to pass from one part of a program to another by using goto statements. Control would "go to" a different part of the program when conditions allowed. ...
... Early programmers allowed control to pass from one part of a program to another by using goto statements. Control would "go to" a different part of the program when conditions allowed. ...
Information in the Digital Domain
... Higher level languages allow programmers to express a process in a more abstract form (closer to the actual problem domain) The software development cycle consists of: Analyze and understand the problem Devise a plan to solve the problem Create an executable program that implements the plan ...
... Higher level languages allow programmers to express a process in a more abstract form (closer to the actual problem domain) The software development cycle consists of: Analyze and understand the problem Devise a plan to solve the problem Create an executable program that implements the plan ...
1351
... Construct a basic Java program using Sun’s Java Development Toolkit (JDK) Students will be able to create a Java program using a simple text editor. Students can compile programs through a command prompt window creating Java bytecode using Sun’s JDK. Programs can be debugged using errors displayed i ...
... Construct a basic Java program using Sun’s Java Development Toolkit (JDK) Students will be able to create a Java program using a simple text editor. Students can compile programs through a command prompt window creating Java bytecode using Sun’s JDK. Programs can be debugged using errors displayed i ...
Formalizing the Dynamic Semantics of Java
... A PL’s semantics is concerned with the meaning of (wellformed) programs: how a program may be expected to behave when executed on a computer. A PL’s pragmatics is concerned with the way in which the PL is intended to be used in practice. Pragmatics include the paradigm(s) supported by the PL. ...
... A PL’s semantics is concerned with the meaning of (wellformed) programs: how a program may be expected to behave when executed on a computer. A PL’s pragmatics is concerned with the way in which the PL is intended to be used in practice. Pragmatics include the paradigm(s) supported by the PL. ...
CCL in Programming
... The Certificate of Completion (CCL) in Programming is designed to prepare the student to work in the programming field. Courses focus on programming theory, Java programming, Visual Basic programming, and web programming. ...
... The Certificate of Completion (CCL) in Programming is designed to prepare the student to work in the programming field. Courses focus on programming theory, Java programming, Visual Basic programming, and web programming. ...
Basic Concepts of Programming
... Assembly languages use mnemonic symbols to represent instructions & data. Programs are translated by assembler and loaded and run using a loader. Assembly language is more programmer friendly, but still tedious. Like machine language, it is not portable as each computer has its own unique language. ...
... Assembly languages use mnemonic symbols to represent instructions & data. Programs are translated by assembler and loaded and run using a loader. Assembly language is more programmer friendly, but still tedious. Like machine language, it is not portable as each computer has its own unique language. ...
Computer Science A, 1
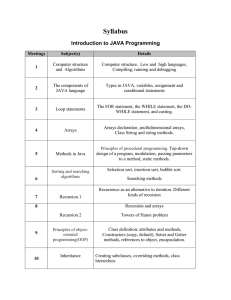
... Course plan • Introduction to programming • Basic concepts of typical programming languages. • Tools: compiler, editor, integrated editor, libraries. • A bit about software engineering – methods used in constructing programs. • A bit about graphics ...
... Course plan • Introduction to programming • Basic concepts of typical programming languages. • Tools: compiler, editor, integrated editor, libraries. • A bit about software engineering – methods used in constructing programs. • A bit about graphics ...
Introduction, Course Overview, and Language Specification
... Disadvantages • Different hardware requires a completely different program (not just a port) ...
... Disadvantages • Different hardware requires a completely different program (not just a port) ...
COMP205 Comparative Programming Languages
... “unit” meaning. When outputting text it is often desirable to include punctuation, where these are also used (within the language) as separators we must precede the punctuation character with what is called an escape character (usually a backslash ‘\’). ...
... “unit” meaning. When outputting text it is often desirable to include punctuation, where these are also used (within the language) as separators we must precede the punctuation character with what is called an escape character (usually a backslash ‘\’). ...
2. Comparative Programming Languages I
... “unit” meaning. When outputting text it is often desirable to include punctuation, where these are also used (within the language) as separators we must precede the punctuation character with what is called an escape character (usually a backslash ‘\’). ...
... “unit” meaning. When outputting text it is often desirable to include punctuation, where these are also used (within the language) as separators we must precede the punctuation character with what is called an escape character (usually a backslash ‘\’). ...
Open Sources
... • Computers can not understand human languages • It can deal only with 0’s & 1’s • Compilers can convert programming languages to machine language (0’s&1’s) ...
... • Computers can not understand human languages • It can deal only with 0’s & 1’s • Compilers can convert programming languages to machine language (0’s&1’s) ...
Why study programming languages?
... Programming Language Design and Implementation (4th Edition) by T. Pratt and M. Zelkowitz Prentice Hall, 2001 ...
... Programming Language Design and Implementation (4th Edition) by T. Pratt and M. Zelkowitz Prentice Hall, 2001 ...
Review1_etzelcz_Abbreviated_Review_Zach_Etzel_
... Abbreviated Review October 2, 2007 What have we discussed about languages so far this semester? some historical information o Pascal language is named after mathematician Pascal by Niklaus Wirth created as a teaching language. Early compilers translated it to P-code o FORTRAN was intended to perfo ...
... Abbreviated Review October 2, 2007 What have we discussed about languages so far this semester? some historical information o Pascal language is named after mathematician Pascal by Niklaus Wirth created as a teaching language. Early compilers translated it to P-code o FORTRAN was intended to perfo ...