Solving Equations with Decimals
... undo multiplication by dividing both sides of the equation by 4. ...
... undo multiplication by dividing both sides of the equation by 4. ...
Methods of Solving Quadratic Equations
... term and is based on the fact that if (expression) 2 = k , where k is a constant, then expression = ± k . Examples: Solve (a) 9x 2 = 25 , (b) x 2 " 7 = 0 , (c) 3(x " 5) 2 = 2 Solving by Completing the Square ...
... term and is based on the fact that if (expression) 2 = k , where k is a constant, then expression = ± k . Examples: Solve (a) 9x 2 = 25 , (b) x 2 " 7 = 0 , (c) 3(x " 5) 2 = 2 Solving by Completing the Square ...
Abstract
... THE RARE INTERACTION LIMIT IN A FAST-SLOW MECHANICAL SYSTEM DOMOKOS SZÁSZ BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY A BSTRACT. Gaspard and Gilbert(2008) suggested a two-step strategy to derive the ’macroscopic’ heat equation from the ’microscopic’ kinetic equation. Their model consisted of a chain of local ...
... THE RARE INTERACTION LIMIT IN A FAST-SLOW MECHANICAL SYSTEM DOMOKOS SZÁSZ BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY A BSTRACT. Gaspard and Gilbert(2008) suggested a two-step strategy to derive the ’macroscopic’ heat equation from the ’microscopic’ kinetic equation. Their model consisted of a chain of local ...
Separation of the hydrogen atom Schrödinger equation
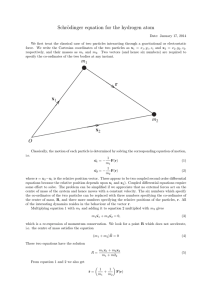
... where r = x2 −x1 is the relative position vector. These appear to be two coupled second order differential equations because the relative position depends upon x1 and x2 ). Coupled differential equations require some effort to solve. The problem can be simplified if we appreciate that no external fo ...
... where r = x2 −x1 is the relative position vector. These appear to be two coupled second order differential equations because the relative position depends upon x1 and x2 ). Coupled differential equations require some effort to solve. The problem can be simplified if we appreciate that no external fo ...