File - Mr. McCarthy
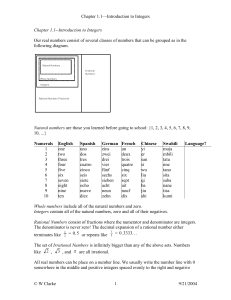
... negative result. A simple way to think about the Real “Imaginary" numbers can seem Numbers is: any point anywhere on the impossible, but they are still useful! number line (not just the whole Examples: √(-9) (=3i), 6i, -5.2i numbers). The "unit" imaginary numbers is √(Examples: 1.5, -12.3, 99, √2, π ...
... negative result. A simple way to think about the Real “Imaginary" numbers can seem Numbers is: any point anywhere on the impossible, but they are still useful! number line (not just the whole Examples: √(-9) (=3i), 6i, -5.2i numbers). The "unit" imaginary numbers is √(Examples: 1.5, -12.3, 99, √2, π ...
Full text
... (0, 0, • • • , 0) and are in one-to-one correspondence with the sequences of the subscript set. All the sequences of a q-set contain even numbers only. Next, divide all integers of a q - s e t by two. It is seen that the set of sequences so p r o duced a r e the h and l e s s part partitions of (h q ...
... (0, 0, • • • , 0) and are in one-to-one correspondence with the sequences of the subscript set. All the sequences of a q-set contain even numbers only. Next, divide all integers of a q - s e t by two. It is seen that the set of sequences so p r o duced a r e the h and l e s s part partitions of (h q ...
Notes for Lesson 1-6: Multiplying and Dividing Real Numbers
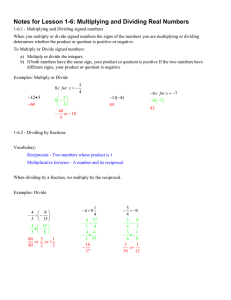
... Multiplication by Zero - The product of any number and zero will always be zero Division by Zero - When the divisor is zero, the answer is undefined Zero divided by a number - When zero is your divisor, the answer is always zero Examples: Multiply or Divide ...
... Multiplication by Zero - The product of any number and zero will always be zero Division by Zero - When the divisor is zero, the answer is undefined Zero divided by a number - When zero is your divisor, the answer is always zero Examples: Multiply or Divide ...
Full text
... Very recently, G. A. Moore [2] considered, among other things, the limiting behavior of the maximal real roots of Gn(x) defined by (1), and with G0(x) = - 1 , Gl(x) = x-l. Let gn denote the maximal real root of Gn(x) which may be called "the generalized golden numbers" following [1]. G. Moore confir ...
... Very recently, G. A. Moore [2] considered, among other things, the limiting behavior of the maximal real roots of Gn(x) defined by (1), and with G0(x) = - 1 , Gl(x) = x-l. Let gn denote the maximal real root of Gn(x) which may be called "the generalized golden numbers" following [1]. G. Moore confir ...
Full text
... a2 in order of decreasing magnitude to form P(a ls a 2 ) . The number pair (a19 a 2 ) may be replaced by a rectangle (ax . a 2 ) of sides a1 and a 2 . In such a case9 £(#1 • a2) 9 C(a1 . a 2 ) 9 and L(ax . a 2 ) may be defined as above9 but by replacing the comma with a dot. £(#1 . a2) and C(a1 . a ...
... a2 in order of decreasing magnitude to form P(a ls a 2 ) . The number pair (a19 a 2 ) may be replaced by a rectangle (ax . a 2 ) of sides a1 and a 2 . In such a case9 £(#1 • a2) 9 C(a1 . a 2 ) 9 and L(ax . a 2 ) may be defined as above9 but by replacing the comma with a dot. £(#1 . a2) and C(a1 . a ...
Integers, Rational, and Real Numbers
... The size of an integer, or the distance from zero of that integer along a number line is called the absolute value of that integer. | 1 | = 1 because 1 is one unit away from zero on a number line, but | -1 | = 1 also, because -1 is also one unit away from zero on a number line! In fact, 1 and -1 ar ...
... The size of an integer, or the distance from zero of that integer along a number line is called the absolute value of that integer. | 1 | = 1 because 1 is one unit away from zero on a number line, but | -1 | = 1 also, because -1 is also one unit away from zero on a number line! In fact, 1 and -1 ar ...
1 Sequences, Series, how to decide if a series in convergent
... errors come confusing series with sequence, so train yourself to always ask “is this a statement about a series or is it a statement about a sequence?” The series a1 +a2 +· · · is called an infinite series because it is formed from an infinite sequence. It has nothing to do with whether the sum a1 + ...
... errors come confusing series with sequence, so train yourself to always ask “is this a statement about a series or is it a statement about a sequence?” The series a1 +a2 +· · · is called an infinite series because it is formed from an infinite sequence. It has nothing to do with whether the sum a1 + ...
Notes - Cornell Computer Science
... to prove their Proposition 2.3 showing that the arithmetic operations produce regular sequences. In Proposition 2.6 they show that the algebraic operations form a field. This is an easy result. ...
... to prove their Proposition 2.3 showing that the arithmetic operations produce regular sequences. In Proposition 2.6 they show that the algebraic operations form a field. This is an easy result. ...
















![[Part 3]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008795885_1-d87cc86e59aaf2f47366e1db501c3b95-300x300.png)




