Patterns and Sequences
... Patterns refer to usual types of procedures or rules that can be followed. Patterns are useful to predict what came before or what might come after a set a numbers that are arranged in a particular order. This arrangement of numbers is called a sequence. For example: 3,6,9,12 and 15 are numbers that ...
... Patterns refer to usual types of procedures or rules that can be followed. Patterns are useful to predict what came before or what might come after a set a numbers that are arranged in a particular order. This arrangement of numbers is called a sequence. For example: 3,6,9,12 and 15 are numbers that ...
Algebra 1 and 2 - Superceded eRiding website
... c) Count on and back in steps of 0.4, 0.75, 3/4… d) Round numbers, including to one or two decimal places. e) Know and use squares, cubes, roots and index notation. f) Know or derive quickly prime numbers less than 30 and factor pairs for a given number. g) Convert between fractions, decimals and pe ...
... c) Count on and back in steps of 0.4, 0.75, 3/4… d) Round numbers, including to one or two decimal places. e) Know and use squares, cubes, roots and index notation. f) Know or derive quickly prime numbers less than 30 and factor pairs for a given number. g) Convert between fractions, decimals and pe ...
Fibonacci sequence
... but each month thereafter produced one new pair of rabbits. If each new pair thus produced reproduces in the same manner, how many pairs of rabbits will there be at the end of one year? ...
... but each month thereafter produced one new pair of rabbits. If each new pair thus produced reproduces in the same manner, how many pairs of rabbits will there be at the end of one year? ...
Introduction to Discrete Mathematics
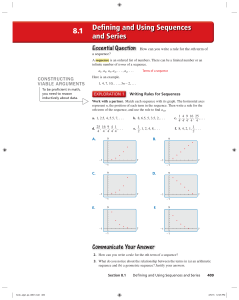
... Number Sequences In general a number sequence is just a sequence of numbers a1, a2, a3, …, an (it is an infinite sequence if n goes to infinity). We will study sequences that have interesting patterns. ...
... Number Sequences In general a number sequence is just a sequence of numbers a1, a2, a3, …, an (it is an infinite sequence if n goes to infinity). We will study sequences that have interesting patterns. ...
Full text
... Also, it is apparent that jf [ satisfying (1) implies that j - f j satisfies (1) and it is convenient to associate a sequence with its negative. ...
... Also, it is apparent that jf [ satisfying (1) implies that j - f j satisfies (1) and it is convenient to associate a sequence with its negative. ...
Sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an ordered collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed. Like a set, it contains members (also called elements, or terms). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is called the length of the sequence. Unlike a set, order matters, and exactly the same elements can appear multiple times at different positions in the sequence. Formally, a sequence can be defined as a function whose domain is a countable totally ordered set, such as the natural numbers.For example, (M, A, R, Y) is a sequence of letters with the letter 'M' first and 'Y' last. This sequence differs from (A, R, M, Y). Also, the sequence (1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8), which contains the number 1 at two different positions, is a valid sequence. Sequences can be finite, as in these examples, or infinite, such as the sequence of all even positive integers (2, 4, 6,...). In computing and computer science, finite sequences are sometimes called strings, words or lists, the different names commonly corresponding to different ways to represent them into computer memory; infinite sequences are also called streams. The empty sequence ( ) is included in most notions of sequence, but may be excluded depending on the context.