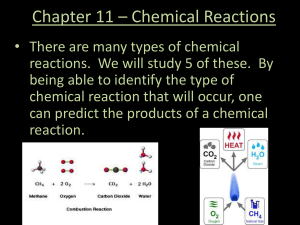
Types of Chemical Reactions
... Convert the grams of each element into the moles of each element with their molar mass. Divide the smallest number of moles of an element into the moles of each element present. Convert the fractional ratios for each element into whole numbers by multiplying all the ratios by the same ...
... Convert the grams of each element into the moles of each element with their molar mass. Divide the smallest number of moles of an element into the moles of each element present. Convert the fractional ratios for each element into whole numbers by multiplying all the ratios by the same ...
nutrient disorder management in groundnut
... pH) and excess of Mn with acid soils (below 4.5 pH). In India since groundnut is mostly grown in the soils having pH more than 7.5 there is high incidence of Mn deficiency. The main symptom of manganese deficiency is chlorosis or yellowing between the veins of new leaves. There may also be a disting ...
... pH) and excess of Mn with acid soils (below 4.5 pH). In India since groundnut is mostly grown in the soils having pH more than 7.5 there is high incidence of Mn deficiency. The main symptom of manganese deficiency is chlorosis or yellowing between the veins of new leaves. There may also be a disting ...
Chapter 11 * Chemical Reactions
... participate in the formation of the nonaqueous product are written. General Equation: Na2SO4 (aq) + Ba(NO3)2 (aq 2NaNO3 (aq) + BaSO4 (s) Ionic Equation: 2Na+1 (aq) + SO4-2 (aq) + Ba+2 (aq) + 2NO3-1 (aq) 2Na+1 (aq) + 2 NO3-1 (aq) + BaSO4 (s) Net Ionic Equation: Ba+2 (aq) + SO4-2 (aq) BaSO4 (s) ...
... participate in the formation of the nonaqueous product are written. General Equation: Na2SO4 (aq) + Ba(NO3)2 (aq 2NaNO3 (aq) + BaSO4 (s) Ionic Equation: 2Na+1 (aq) + SO4-2 (aq) + Ba+2 (aq) + 2NO3-1 (aq) 2Na+1 (aq) + 2 NO3-1 (aq) + BaSO4 (s) Net Ionic Equation: Ba+2 (aq) + SO4-2 (aq) BaSO4 (s) ...
Chemical change is a process that involves recombining atoms and
... as aqueous when it is dissolved in water. An ionic compound that is slightly soluble is usually shown as solid, even when it’s in water. Molecular compounds are very difficult to predict. The smaller the molecules are, the more they tend to be gases. The larger they are, the more they tend to be l ...
... as aqueous when it is dissolved in water. An ionic compound that is slightly soluble is usually shown as solid, even when it’s in water. Molecular compounds are very difficult to predict. The smaller the molecules are, the more they tend to be gases. The larger they are, the more they tend to be l ...
Chapter 4. Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... We sometimes have a problem with the arbitrary difference between strong and weak electrolytes. We often think that nonelectrolytes produce no ions in aqueous solution at all. We sometimes cannot tell the difference between dissolution and dissociation. The symbols (equilibrium) and (resonance) ...
... We sometimes have a problem with the arbitrary difference between strong and weak electrolytes. We often think that nonelectrolytes produce no ions in aqueous solution at all. We sometimes cannot tell the difference between dissolution and dissociation. The symbols (equilibrium) and (resonance) ...
Chemical Technology - Engineers Institute of India
... 2. Chemical Industry plays important role in every part of life. For example foods, drugs, petroleum, and fertilizer industry 3. Chemical Industry is different than other industry as in chemical Industry we start from raw material and end up with consumer product through series of physical and chemi ...
... 2. Chemical Industry plays important role in every part of life. For example foods, drugs, petroleum, and fertilizer industry 3. Chemical Industry is different than other industry as in chemical Industry we start from raw material and end up with consumer product through series of physical and chemi ...
PPT: Chemical Reactions Review
... (CO3)2-: What is the oxidation # of C? O is -2, and the overall charge is -2 So C + 3(O) = -2 or C + 3(-2) = -2 C = +4 The oxidation # of ions = charge of ions Mn3+ has an oxidation # of +3 S2- has an oxidation # of -2 ...
... (CO3)2-: What is the oxidation # of C? O is -2, and the overall charge is -2 So C + 3(O) = -2 or C + 3(-2) = -2 C = +4 The oxidation # of ions = charge of ions Mn3+ has an oxidation # of +3 S2- has an oxidation # of -2 ...
OXIDATION NUMBERS
... The oxidation number is used to express the oxidation state of an element, whether as the uncombined element or when combined in a compound; it consists of a + or – sign followed by a number, or it is zero. Atoms of elements have no overall charge and are therefore given an oxidation number of zero. ...
... The oxidation number is used to express the oxidation state of an element, whether as the uncombined element or when combined in a compound; it consists of a + or – sign followed by a number, or it is zero. Atoms of elements have no overall charge and are therefore given an oxidation number of zero. ...
Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks and Plutons
... out at the surface by some unknown forces acting in a manner like the squeezing of toothpaste from a tube. Fact: Magma bodies rise and intrude in response to the simple pull of gravity. Liquid rock— magma—has a lower specific gravity than solid rock. This causes the magma to rise and perhaps, over t ...
... out at the surface by some unknown forces acting in a manner like the squeezing of toothpaste from a tube. Fact: Magma bodies rise and intrude in response to the simple pull of gravity. Liquid rock— magma—has a lower specific gravity than solid rock. This causes the magma to rise and perhaps, over t ...
Return-flow prediction and buffer designation in two rainforest
... Many studies conducted in temperate regions have shown mismatches between the topographic index and soil moisture or capillary potential patterns (e.g., Burt and Butcher, 1985; Crave and Gascuel-Odoux, 1997). Our study may show similar findings, but for tropical soils. This would not be a disappoint ...
... Many studies conducted in temperate regions have shown mismatches between the topographic index and soil moisture or capillary potential patterns (e.g., Burt and Butcher, 1985; Crave and Gascuel-Odoux, 1997). Our study may show similar findings, but for tropical soils. This would not be a disappoint ...
Net ionic equation
... Steps to write net ionic equations: 1. Write a balanced complete equation. 2. Dissociate any and only strong electrolytes. ...
... Steps to write net ionic equations: 1. Write a balanced complete equation. 2. Dissociate any and only strong electrolytes. ...
experimental study on use of cemented materials for
... surface roads have been compacted by human and animal traffic and the tracks were developed as a natural result of the movement of traffic. These road surfaces were widened and covered with rock and gravel, and thus made suitable to tackle the traffic better. However, these road surfaces were transf ...
... surface roads have been compacted by human and animal traffic and the tracks were developed as a natural result of the movement of traffic. These road surfaces were widened and covered with rock and gravel, and thus made suitable to tackle the traffic better. However, these road surfaces were transf ...
BC Science 10 Workbook Answers
... bacteria, using a series of chemical reactions, convert nitrate back into nitrogen gas. 8. Eutrophication is the process by which excess nutrients result in increased plant production and decay in aquatic ecosystems. Interpreting Illustrations ...
... bacteria, using a series of chemical reactions, convert nitrate back into nitrogen gas. 8. Eutrophication is the process by which excess nutrients result in increased plant production and decay in aquatic ecosystems. Interpreting Illustrations ...
Horticulture Herbaceous Ornamentals #315 Summer Bulbs
... resembling the flowers of gladiolus in shape; flowers are fragrant; foliage strap-like Bloom time: late summer into early autumn Planting: Plant 3-4” deep; space corms about 6” apart Culture: Full sun; keep soil evenly moist, but not wet; protect from wind; staking may be needed Lifting and storing: ...
... resembling the flowers of gladiolus in shape; flowers are fragrant; foliage strap-like Bloom time: late summer into early autumn Planting: Plant 3-4” deep; space corms about 6” apart Culture: Full sun; keep soil evenly moist, but not wet; protect from wind; staking may be needed Lifting and storing: ...
The impact of structural Fe(III) reduction by bacteria on
... Abstract—Although clay mineral reduction is thought to occur primarily as a result of the activity of indigenous microorganisms in soil, most research has focused on chemical mechanisms of Fe reduction within clay minerals. Here we show that bacteria isolated from soils and sediments catalyze the ra ...
... Abstract—Although clay mineral reduction is thought to occur primarily as a result of the activity of indigenous microorganisms in soil, most research has focused on chemical mechanisms of Fe reduction within clay minerals. Here we show that bacteria isolated from soils and sediments catalyze the ra ...
Balancing and Predicting Chemical Reactions:
... 2. Aqueous nitric acid and calcium hydroxide solutions react to form water and aqueous calcium nitrate Word equation: nitric acid(aq) + calcium hydroxide(aq) water(l) + calcium nitrate(aq) Skeleton formula equation: HNO3(aq) + Ca(OH)2(aq) H2O(l) + Ca(NO3)2(aq) ...
... 2. Aqueous nitric acid and calcium hydroxide solutions react to form water and aqueous calcium nitrate Word equation: nitric acid(aq) + calcium hydroxide(aq) water(l) + calcium nitrate(aq) Skeleton formula equation: HNO3(aq) + Ca(OH)2(aq) H2O(l) + Ca(NO3)2(aq) ...
classifying rocks
... Sedimentary rocks have characteristics unique to how they form. Forces on Earth’s surface can break down rocks. This process is called weathering. Rocks can be broken down through physical weathering or chemical weathering. Physical weathering breaks down rocks into smaller pieces through physical p ...
... Sedimentary rocks have characteristics unique to how they form. Forces on Earth’s surface can break down rocks. This process is called weathering. Rocks can be broken down through physical weathering or chemical weathering. Physical weathering breaks down rocks into smaller pieces through physical p ...
Aqueous Reactions
... dissociate into separate ions in water. However, not all electrolytes behave the same way. Some are strong electrolytes, and dissociate completely, so no ions are left bonded together. Others are weak electrolytes- they only partly dissociate, and many of their ions are still bonded to each other. O ...
... dissociate into separate ions in water. However, not all electrolytes behave the same way. Some are strong electrolytes, and dissociate completely, so no ions are left bonded together. Others are weak electrolytes- they only partly dissociate, and many of their ions are still bonded to each other. O ...
Planet Earth
... • Your presentation should outline the location/s, elements (soil, landforms, climate, flora and fauna,) human impacts/threats, and conservation measures being undertaken. • Try to make your presentation interesting for your audience • Include some form of audience participation if possible • Give y ...
... • Your presentation should outline the location/s, elements (soil, landforms, climate, flora and fauna,) human impacts/threats, and conservation measures being undertaken. • Try to make your presentation interesting for your audience • Include some form of audience participation if possible • Give y ...
Week 7: Igneous Rocks - Elderslie High School
... 4. Rocks formed by fast cooling magma are called v_________________ or e_________________ rocks. Examples of these types of rock are: b________________ and o______________________. ...
... 4. Rocks formed by fast cooling magma are called v_________________ or e_________________ rocks. Examples of these types of rock are: b________________ and o______________________. ...
here
... colonies were isolated from vermicompost using serial dilutions and plated onto general growth media. The amplification and sequence analysis of the 16S rDNA gene from 39 isolates showed a high percentage (79%) of Actinobacteria sp., especially Arthrobacter sp. (54%) and Streptomyces sp. (15%). Prot ...
... colonies were isolated from vermicompost using serial dilutions and plated onto general growth media. The amplification and sequence analysis of the 16S rDNA gene from 39 isolates showed a high percentage (79%) of Actinobacteria sp., especially Arthrobacter sp. (54%) and Streptomyces sp. (15%). Prot ...
CH 4 Notes
... When a substance loses electrons, it undergoes oxidation: Ca (s) + 2 H1+ (aq) ---> Ca2+ (aq) + H2 (g) The neutral Ca has lost two electrons to 2 H1+ to become Ca2+ We say Ca has been oxidized to Ca2+ When a substance gains electrons, it undergoes reduction: 2 Ca (s) + O2 (g) ---> 2 CaO (s) ...
... When a substance loses electrons, it undergoes oxidation: Ca (s) + 2 H1+ (aq) ---> Ca2+ (aq) + H2 (g) The neutral Ca has lost two electrons to 2 H1+ to become Ca2+ We say Ca has been oxidized to Ca2+ When a substance gains electrons, it undergoes reduction: 2 Ca (s) + O2 (g) ---> 2 CaO (s) ...
Chapter 12 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
... oxidized nor reduced. • The oxidation number of oxygen is −2 on both sides of the equation, so oxygen is neither oxidized nor reduced. • The only remaining atoms are nitrogen atoms. Nitrogen atoms are found in two different compounds among the products, and the nitrogen atoms in these compounds have ...
... oxidized nor reduced. • The oxidation number of oxygen is −2 on both sides of the equation, so oxygen is neither oxidized nor reduced. • The only remaining atoms are nitrogen atoms. Nitrogen atoms are found in two different compounds among the products, and the nitrogen atoms in these compounds have ...
by John Mu
... Indicators were identified with the observation that the colour of some flowers depends on soil composition .............16 While we usually think of the air around us as neutral, the atmosphere naturally contains acidic oxides of carbon, nitrogen and sulfur. The concentrations of these acidic oxide ...
... Indicators were identified with the observation that the colour of some flowers depends on soil composition .............16 While we usually think of the air around us as neutral, the atmosphere naturally contains acidic oxides of carbon, nitrogen and sulfur. The concentrations of these acidic oxide ...
Lectures on Chapter 4, Part 2 Powerpoint 97 Document
... Silver is reclaimed from ores by extraction using basic Cyanide ion. OH Ag(s) + CN (aq) + O2 (g) Ag(CN)2-(aq) Oxidation: CN-(aq) + Ag(s) Ag(CN)2-(aq) Since we need two cyanide ions to form the complex, add two to the reactant side of the equation. Silver is also oxidized, so it looses an electron, s ...
... Silver is reclaimed from ores by extraction using basic Cyanide ion. OH Ag(s) + CN (aq) + O2 (g) Ag(CN)2-(aq) Oxidation: CN-(aq) + Ag(s) Ag(CN)2-(aq) Since we need two cyanide ions to form the complex, add two to the reactant side of the equation. Silver is also oxidized, so it looses an electron, s ...