Environmental Chemistry
... Under surface conditions rocks disintegrate by a process of weathering – Forms sediments and soil – May be physical (freeze/thaw, wet/dry, growth of roots, etc.) or chemical ...
... Under surface conditions rocks disintegrate by a process of weathering – Forms sediments and soil – May be physical (freeze/thaw, wet/dry, growth of roots, etc.) or chemical ...
chemical and isotopic evidence for the in situ origin of marine humic
... similar results, The majority of samples fell in the range C ‘v 52-56%, H N 5.06.1%, and C: H N 8.4-10. It is therefore apparent that these two elements are not useful for establishing criteria to differentiate marine from nonmarinc humic acids, contrary to the previous report by Bordovskiy ( 1965). ...
... similar results, The majority of samples fell in the range C ‘v 52-56%, H N 5.06.1%, and C: H N 8.4-10. It is therefore apparent that these two elements are not useful for establishing criteria to differentiate marine from nonmarinc humic acids, contrary to the previous report by Bordovskiy ( 1965). ...
chem equation Pkt Student2
... 1) Which side of the yields arrow do you find reactants? ______________________________ 2) Which side of the yields arrow do you find products? _______________________________ 3) In a chemical equation, what do the coefficients represent? ______________________________ 4) In a chemical equation, wha ...
... 1) Which side of the yields arrow do you find reactants? ______________________________ 2) Which side of the yields arrow do you find products? _______________________________ 3) In a chemical equation, what do the coefficients represent? ______________________________ 4) In a chemical equation, wha ...
CHEMISTRY 123-07 Midterm #1 – Answer key October 14, 2010
... 32. Ions that contain atoms of more than one element are called polyatomic ions. 33. Proton donors are known as Brønsted acids. 34. A compound that forms between a non-metal and a non-metal is a molecular compound. 35. Stoichiometric coefficients found in a balanced equation can be used to derive mo ...
... 32. Ions that contain atoms of more than one element are called polyatomic ions. 33. Proton donors are known as Brønsted acids. 34. A compound that forms between a non-metal and a non-metal is a molecular compound. 35. Stoichiometric coefficients found in a balanced equation can be used to derive mo ...
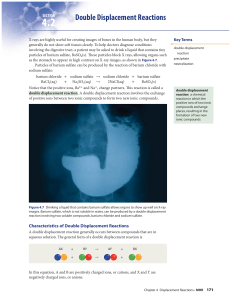
Double Displacement Reactions
... 1. The hydrogen ion, ammonium ion, and all Group 1 (alkali metal) ions form soluble compounds with nearly all anions. 2. Nitrate and acetate ions form soluble compounds with nearly all cations. 3. Chloride, bromide, and iodide ions form compounds that have low solubility with silver, lead(II), mercu ...
... 1. The hydrogen ion, ammonium ion, and all Group 1 (alkali metal) ions form soluble compounds with nearly all anions. 2. Nitrate and acetate ions form soluble compounds with nearly all cations. 3. Chloride, bromide, and iodide ions form compounds that have low solubility with silver, lead(II), mercu ...
Topic 4 - Lloyd Crosby
... f. Oxidizing agent Causes oxidation, so it must accept electrons from the species its oxidizes, and therefore, is reduced g. Reducing agent Causes reduction, so it must donate electrons to the species it reduces, and therefore, is oxidized h. Disproportionation Is a reaction in which the same specie ...
... f. Oxidizing agent Causes oxidation, so it must accept electrons from the species its oxidizes, and therefore, is reduced g. Reducing agent Causes reduction, so it must donate electrons to the species it reduces, and therefore, is oxidized h. Disproportionation Is a reaction in which the same specie ...
Acid Base Equilibria
... Weak acid: one that only partially dissociates in aqueous solution and therefore exists in the solution as a mixture of acid molecules component ions: For example, HF dissociates in water to give H+ and F-. It is a weak acid with a dissociation equation that is HF (aq) ↔ H+ (aq) + F-(aq) Note the us ...
... Weak acid: one that only partially dissociates in aqueous solution and therefore exists in the solution as a mixture of acid molecules component ions: For example, HF dissociates in water to give H+ and F-. It is a weak acid with a dissociation equation that is HF (aq) ↔ H+ (aq) + F-(aq) Note the us ...
Metamorphic Rocks
... occurs along convergent plate boundaries Example 1: Continent-Continent Collisions Compressional stresses deforms plate edge ...
... occurs along convergent plate boundaries Example 1: Continent-Continent Collisions Compressional stresses deforms plate edge ...
09_Lecture
... • Blood is buffered by the bicarbonate buffer system. • Dissolved CO2 produced during cellular respiration travels through the bloodstream to the lungs. • This dissolved CO2 is rapidly equilibrated through carbonic acid into bicarbonate ions. ...
... • Blood is buffered by the bicarbonate buffer system. • Dissolved CO2 produced during cellular respiration travels through the bloodstream to the lungs. • This dissolved CO2 is rapidly equilibrated through carbonic acid into bicarbonate ions. ...
GG 101 Objectives Chapter Links
... Chapter 10. Volcanism 1. Recognize the importance of volcanic activity to the science of geology 2. Describe how volcanism relates to the origin of the atmosphere and affects Earth's climate 3. Contrast the beneficial and catastrophic effects of volcanism on humans. 4. Indicate the factors that cont ...
... Chapter 10. Volcanism 1. Recognize the importance of volcanic activity to the science of geology 2. Describe how volcanism relates to the origin of the atmosphere and affects Earth's climate 3. Contrast the beneficial and catastrophic effects of volcanism on humans. 4. Indicate the factors that cont ...
Chapter 4 Solution Chemistry
... solution. For example, Ag+ can be added to a solution of Cl- to precipitate all of the Cl- in the form of insoluble AgCl. The concentration of the Cl- is determined by weighing the AgCl and using the stoichiometry of the reaction. To determine the concentration of chloride ion in a 100.0 mL sample o ...
... solution. For example, Ag+ can be added to a solution of Cl- to precipitate all of the Cl- in the form of insoluble AgCl. The concentration of the Cl- is determined by weighing the AgCl and using the stoichiometry of the reaction. To determine the concentration of chloride ion in a 100.0 mL sample o ...
Chapter 4: Solution Chemistry: The Hydrosphere
... 4.1 SOLUTIONS ON EARTH AND OTHER PLACES aqueous solution: a solution where water is the dissolving medium (the solvent) – For example, when table salt (NaCl) is dissolved in water, it results in an aqueous solution of sodium chloride, NaCl(aq), with Na+ and Cl- ions dissolved in water. – Note: The p ...
... 4.1 SOLUTIONS ON EARTH AND OTHER PLACES aqueous solution: a solution where water is the dissolving medium (the solvent) – For example, when table salt (NaCl) is dissolved in water, it results in an aqueous solution of sodium chloride, NaCl(aq), with Na+ and Cl- ions dissolved in water. – Note: The p ...
12 Point Buck Perennial
... Spring Plot is an annual mix of forage oats, producing green foliage with an erect growth habit. Buckwheat grows well in almost any soil, produces clusters of small white flowers forming triangular shaped black seeds that shatter easily giving access for seed and stalk feeding. Forage peas offer lea ...
... Spring Plot is an annual mix of forage oats, producing green foliage with an erect growth habit. Buckwheat grows well in almost any soil, produces clusters of small white flowers forming triangular shaped black seeds that shatter easily giving access for seed and stalk feeding. Forage peas offer lea ...
Titan
... C. about 3 times more massive than Jupiter D. about 3 times less massive than Jupiter E. neither of the above ...
... C. about 3 times more massive than Jupiter D. about 3 times less massive than Jupiter E. neither of the above ...
Rocks and Minerals
... Geologist group rocks into three categories based upon how they form. The three types of rock are Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic. Igneous rocks are volcanic in origin. When magma rises through fissures in the Earth’s crust, it cools as it moves away from the heat of the mantle and forms an ig ...
... Geologist group rocks into three categories based upon how they form. The three types of rock are Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic. Igneous rocks are volcanic in origin. When magma rises through fissures in the Earth’s crust, it cools as it moves away from the heat of the mantle and forms an ig ...
Comparative studies on the digestive enzymes in the gut of
... simple compounds. The digestive enzymes of earthworms are responsible for the decomposition and humification of organic matter. These enzymes are active at a very narrow pH range and efficiently maintain the highly non-linear pH parameters3. Organic wastes, broken down and fragmented rapidly by eart ...
... simple compounds. The digestive enzymes of earthworms are responsible for the decomposition and humification of organic matter. These enzymes are active at a very narrow pH range and efficiently maintain the highly non-linear pH parameters3. Organic wastes, broken down and fragmented rapidly by eart ...
Redox
... Oxidation Numbers • An oxidation number describes the “electrical state” of an atom or ion. Particles can either be neutral (+p = e-), positive (+p > e-) or negatively (+p < e-) charged. ...
... Oxidation Numbers • An oxidation number describes the “electrical state” of an atom or ion. Particles can either be neutral (+p = e-), positive (+p > e-) or negatively (+p < e-) charged. ...
Descriptive Chemistry for Midterm Exam #2
... Occurrence: found in more compounds than any other element on earth. It is the most abundant element in universe. Oxidation states: 0 in H2, +1 in compounds with other non-metals, −1 in metal hydrides. Industrial Preparation of H2: This is carried out through the reduction of +1 oxidation state in H ...
... Occurrence: found in more compounds than any other element on earth. It is the most abundant element in universe. Oxidation states: 0 in H2, +1 in compounds with other non-metals, −1 in metal hydrides. Industrial Preparation of H2: This is carried out through the reduction of +1 oxidation state in H ...
chem 100 class notes - Louisiana Tech University
... Classification of compounds as acids, bases and salts Most of the chemical compounds can be classified either as an acid, a base or a salt. Acids: Acids are compounds that increase the hydrogen ion concentration when dissolved in water. They usually have at least one removable hydrogen atom attached ...
... Classification of compounds as acids, bases and salts Most of the chemical compounds can be classified either as an acid, a base or a salt. Acids: Acids are compounds that increase the hydrogen ion concentration when dissolved in water. They usually have at least one removable hydrogen atom attached ...
GEOLOGY FOR MINING ENGINEERS
... kilometers of the Earth’s surface, but a few traces remain even 10,000 kilometers above the surface. THE BIOSPHERE The biosphere is the thin zone near the Earth’s surface that is inhabited by life. It includes the uppermost solid Earth, the hydrosphere, and the lower parts of the atmosphere. Land ...
... kilometers of the Earth’s surface, but a few traces remain even 10,000 kilometers above the surface. THE BIOSPHERE The biosphere is the thin zone near the Earth’s surface that is inhabited by life. It includes the uppermost solid Earth, the hydrosphere, and the lower parts of the atmosphere. Land ...
articles - Geoscience Research Institute
... direction when water was heated in the lower sphere. The mixture passed through the electrodes and was liquefied within a condenser below the sparking chamber. The products formed were then washed down into water and captured within a trap. After one week of sparking, the products were removed from ...
... direction when water was heated in the lower sphere. The mixture passed through the electrodes and was liquefied within a condenser below the sparking chamber. The products formed were then washed down into water and captured within a trap. After one week of sparking, the products were removed from ...
Semester 1 Course Review
... 3. How does the outer core produce the Earth’s magnetic field? 4. How is heat transferred from the core to the crust? 5. Who contributed to the theory of plate tectonics and what does the theory state? 6. How does the development of the Theory of Plate Tectonics demonstrate the scientific process? 7 ...
... 3. How does the outer core produce the Earth’s magnetic field? 4. How is heat transferred from the core to the crust? 5. Who contributed to the theory of plate tectonics and what does the theory state? 6. How does the development of the Theory of Plate Tectonics demonstrate the scientific process? 7 ...
Chemical Monitoring and Management by Ahmad Shah Idil
... Hence, collaboration between chemists is essential for solving chemical issues, or when dealing with large amounts of data being collected, as the chemists provide input and expertise from their own particular field, for a common goal. ...
... Hence, collaboration between chemists is essential for solving chemical issues, or when dealing with large amounts of data being collected, as the chemists provide input and expertise from their own particular field, for a common goal. ...