Kimberly M. Dreaden, Aurelien Desaunay, and Jeffrey L. Ullman
... In the U.S., waterborne pathogens cause 19.5 million illnesses per year, and are the number one cause of water quality impairment (Bridge, 2010; EPA, 2013). The Southeast has 4,227 waterbodies that fail to meet bacterial water quality standards. Agriculture is the primary source of pathogen loading ...
... In the U.S., waterborne pathogens cause 19.5 million illnesses per year, and are the number one cause of water quality impairment (Bridge, 2010; EPA, 2013). The Southeast has 4,227 waterbodies that fail to meet bacterial water quality standards. Agriculture is the primary source of pathogen loading ...
Weathering and Erosion
... Roots force their way soil and rocks causing rocks to split apart Roots force their way under rocks pushing them to the surface and apart from one ...
... Roots force their way soil and rocks causing rocks to split apart Roots force their way under rocks pushing them to the surface and apart from one ...
Four main kinds of changes affect the Earth`s surface: (1) weathering
... Four main kinds of changes affect the Earth's surface: (1) weathering, (2) erosion, (3) mass movement, and (4) changes in the Earth's crust. Weathering is the breaking up of rocks by such agents as water, ice, chemicals, growing plants, and changing temperature. Soil is an important product of weath ...
... Four main kinds of changes affect the Earth's surface: (1) weathering, (2) erosion, (3) mass movement, and (4) changes in the Earth's crust. Weathering is the breaking up of rocks by such agents as water, ice, chemicals, growing plants, and changing temperature. Soil is an important product of weath ...
6thGrScience
... Igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary rocks have unique characteristics that can be used for identification and/or classification. a. ________Most rocks are composed of one or more minerals, but there are a few types of sedimentary rocks that contain organic material, such as coal. The composition of ...
... Igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary rocks have unique characteristics that can be used for identification and/or classification. a. ________Most rocks are composed of one or more minerals, but there are a few types of sedimentary rocks that contain organic material, such as coal. The composition of ...
Links4Soils - Alpine Space
... Spatial planning: minimising soil sealing, sustainable urban planning, the mitigation of soil contamination, smart use and protection of the best soils; Management and preservation of ecosystem functions: the buffering and filtering capacity of soils, water purification, and the preservation of soil ...
... Spatial planning: minimising soil sealing, sustainable urban planning, the mitigation of soil contamination, smart use and protection of the best soils; Management and preservation of ecosystem functions: the buffering and filtering capacity of soils, water purification, and the preservation of soil ...
Spheres of the Earth
... • Lithosphere is Greek for “rocky sphere” • The solid, outermost shell of a rocky planet • In Earth, the Lithosphere includes the crust and upper mantle ...
... • Lithosphere is Greek for “rocky sphere” • The solid, outermost shell of a rocky planet • In Earth, the Lithosphere includes the crust and upper mantle ...
11_chapter 5
... Further, in the present investigation, under in vitro conditions all the chosen bacteria grew readily in the presence of rock powders as a trace nutrient source. XRD analysis revealed a decrease in the concentration of microcline, albite and removal of biotite from biotite granite and removal of al ...
... Further, in the present investigation, under in vitro conditions all the chosen bacteria grew readily in the presence of rock powders as a trace nutrient source. XRD analysis revealed a decrease in the concentration of microcline, albite and removal of biotite from biotite granite and removal of al ...
Succession - Renton School District
... community over time. When you have a blank ecosystem what species come colonize first, second, third and finally balance out the system. ...
... community over time. When you have a blank ecosystem what species come colonize first, second, third and finally balance out the system. ...
Power Point for Lab 1
... Marine sediments refer to sediments carried by fresh water but deposited in salt water. Marine sediments can build up over long periods of time until eventually they are quite deep. http://www.mo15.nrcs.usda.gov/ features/gallery/bonneau.jpg ...
... Marine sediments refer to sediments carried by fresh water but deposited in salt water. Marine sediments can build up over long periods of time until eventually they are quite deep. http://www.mo15.nrcs.usda.gov/ features/gallery/bonneau.jpg ...
Chapter 13 Soil and Its Uses
... Concept: Distinct horizontal layers in the soil that differ in chemical composition, physical properties, particle size, and amount of organic matter. Each recognizable layer is known as a horizon. Composition: 1. The top layer: (见 fig.13.9 p295) a) A horizon(A 层), or topsoil(表土层)which consists of s ...
... Concept: Distinct horizontal layers in the soil that differ in chemical composition, physical properties, particle size, and amount of organic matter. Each recognizable layer is known as a horizon. Composition: 1. The top layer: (见 fig.13.9 p295) a) A horizon(A 层), or topsoil(表土层)which consists of s ...
CommercialFoundations
... • Build base of foundation below frost depth or • Provide frost protection for foundation ...
... • Build base of foundation below frost depth or • Provide frost protection for foundation ...
Diagnostic Tool
... theories and technology area within the earth’s crust unit. Students are surprised to know that the continents are still moving, approximately 2cm every year. Students may mix up the terms “earthquake proof” and “earthquake resistant.” It can be difficult for students to understand shock-absorbing p ...
... theories and technology area within the earth’s crust unit. Students are surprised to know that the continents are still moving, approximately 2cm every year. Students may mix up the terms “earthquake proof” and “earthquake resistant.” It can be difficult for students to understand shock-absorbing p ...
Blue Grama and Buffalograss Installation for Urban Landscapes
... Spray with glyphosate, leave dead grass in place, heavily core aerate before seeding Use a sod cutter Soil Preparation Till to break up soil compaction. Buffalograss and blue grama do not require high levels of organic matter in the soil. Adding organic soil amendments (compost, manure, etc.) is gen ...
... Spray with glyphosate, leave dead grass in place, heavily core aerate before seeding Use a sod cutter Soil Preparation Till to break up soil compaction. Buffalograss and blue grama do not require high levels of organic matter in the soil. Adding organic soil amendments (compost, manure, etc.) is gen ...
kourtney`s biomes
... They eat large fish and small fish and birds and leaves and berries. Polar bears have a creamy-white coat. Polar bears are fast and outrun a caribou in a short distance. Polar .A little of 1 to 4 young is born after a gestation of about 9 months, After the young polar bear are born the stay with the ...
... They eat large fish and small fish and birds and leaves and berries. Polar bears have a creamy-white coat. Polar bears are fast and outrun a caribou in a short distance. Polar .A little of 1 to 4 young is born after a gestation of about 9 months, After the young polar bear are born the stay with the ...
Chemical Weathering
... concentrations. Kaolinite deposits are important examples of such deposits. Kaolinite is a type of clay mineral used in manufacture of ceramics and paper. A Gossan is a yellow to red deposit made up mostly of sulfide minerals such as pyrite (FeS2). The dissolution of pyrite and other sulfides forme ...
... concentrations. Kaolinite deposits are important examples of such deposits. Kaolinite is a type of clay mineral used in manufacture of ceramics and paper. A Gossan is a yellow to red deposit made up mostly of sulfide minerals such as pyrite (FeS2). The dissolution of pyrite and other sulfides forme ...
Soil Texture
... Let’s walk through this in more detail trying to identify a loam soil. The black dot highlights a spot inside this area that would be classified as this type of soil. The dashed horizontal line moving towards our dot comes from the percent clay side means that this type of soil has 20% clay. The das ...
... Let’s walk through this in more detail trying to identify a loam soil. The black dot highlights a spot inside this area that would be classified as this type of soil. The dashed horizontal line moving towards our dot comes from the percent clay side means that this type of soil has 20% clay. The das ...
Introduction On many rainfed, higher-altitude agricultural fields in the
... of the field. The geology of the fields is the same, so we do not expect major differences in parent material. The texture patterns and to some extent the patterns on the timeslices show a consistent pattern on both sides of the road. The redder colours on the texture map indicate a higher concentra ...
... of the field. The geology of the fields is the same, so we do not expect major differences in parent material. The texture patterns and to some extent the patterns on the timeslices show a consistent pattern on both sides of the road. The redder colours on the texture map indicate a higher concentra ...
Unit 13 - Electrochemistry
... the relationship between electric forces and chemical reactions. Voltage: The potential difference or electromotive force, measured in volts; it represents the amount of work that moving an electric charge between two points would take. Electrode: A conductor used to establish electrical contact wit ...
... the relationship between electric forces and chemical reactions. Voltage: The potential difference or electromotive force, measured in volts; it represents the amount of work that moving an electric charge between two points would take. Electrode: A conductor used to establish electrical contact wit ...
Diversity of Organisms in Compost and Soil
... • The hypothesis was rejected, the Simpson’s Index showing soil had a greater diversity than compost. • The compost had low species evenness, dominated by two species; Species A and earthworm • The soil had species evenness where no one species was dominant over another. • One possible explanation i ...
... • The hypothesis was rejected, the Simpson’s Index showing soil had a greater diversity than compost. • The compost had low species evenness, dominated by two species; Species A and earthworm • The soil had species evenness where no one species was dominant over another. • One possible explanation i ...
Earth*s Changing Surface
... The lithosphere floats on top of the convection currents. The center of the Earth is called the core. The inner core is solid. The outer core is liquid. The currents of the outer core make the Earth’s magnetic field. ...
... The lithosphere floats on top of the convection currents. The center of the Earth is called the core. The inner core is solid. The outer core is liquid. The currents of the outer core make the Earth’s magnetic field. ...
Appendix A—Treatments To Manage Factors Limiting Restoration
... Favor species found growing on similar disturbances. Increase plant cover. Favor species with a variety of root forms (fibrous roots, taproots, spreading roots). Favor plants with lots of root biomass. Avoid plants with dense root mats. ...
... Favor species found growing on similar disturbances. Increase plant cover. Favor species with a variety of root forms (fibrous roots, taproots, spreading roots). Favor plants with lots of root biomass. Avoid plants with dense root mats. ...
How Often and How Long to Water
... It’s not easy to determine a plant’s exact water needs because many factors influence the amount of water a plant requires—plant type, maturity, soils, weather, location and root depth. Although many desert-adapted plants can survive on rainfall (e.g. plants labeled with one drop), supplemental irri ...
... It’s not easy to determine a plant’s exact water needs because many factors influence the amount of water a plant requires—plant type, maturity, soils, weather, location and root depth. Although many desert-adapted plants can survive on rainfall (e.g. plants labeled with one drop), supplemental irri ...
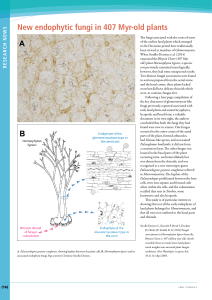
Research News
... and the basal corms; these plants lacked roots but did have delicate rhizoids which were, in contrast, fungus-free. Following a four-page compilation of the key characters of glomeromycete-like fungi previously reported associated with early land plants and extant bryophytes, lycopods, and basal fer ...
... and the basal corms; these plants lacked roots but did have delicate rhizoids which were, in contrast, fungus-free. Following a four-page compilation of the key characters of glomeromycete-like fungi previously reported associated with early land plants and extant bryophytes, lycopods, and basal fer ...
weathering - Duplin County Schools
... Exfoliation and Abrasion are also types of physical weathering. ...
... Exfoliation and Abrasion are also types of physical weathering. ...
Understand the effect of rock type and climate upon the rate, degree
... Frost action: freezing and thawing in cracks and pores in rocks, enlarging the cracks and pores— eventually, pieces of rock (called scree) break off altogether. Exfoliation (“onion skin weathering”): 1. During the day the sun heats up the surface of the rock causing the rock to expand. 2. During ...
... Frost action: freezing and thawing in cracks and pores in rocks, enlarging the cracks and pores— eventually, pieces of rock (called scree) break off altogether. Exfoliation (“onion skin weathering”): 1. During the day the sun heats up the surface of the rock causing the rock to expand. 2. During ...