OUTDOOR SCIENCE SCHOOL VOC (#1 – Test)
... 8. (Pg 195; 10) OXYGEN [O] – is a colorless, odorless, gaseous element found in our atmosphere (a) 21% of the gas making up our air is oxygen [O] (b) O2 allows aerobic (oxygenated environment) organisms to efficiently convert food into energy (through cellular respiration) (c) O2 is a chemical agent ...
... 8. (Pg 195; 10) OXYGEN [O] – is a colorless, odorless, gaseous element found in our atmosphere (a) 21% of the gas making up our air is oxygen [O] (b) O2 allows aerobic (oxygenated environment) organisms to efficiently convert food into energy (through cellular respiration) (c) O2 is a chemical agent ...
1st Semester Study Guide
... a. When water carries nutrients down to lower layers in the soil b. Rock that has tiny connected air spaces, and lets water run through it. c. The organic material in soil d. Soild, unweathered rock e. Twigs, leaves, and other organic matter on top of the ...
... a. When water carries nutrients down to lower layers in the soil b. Rock that has tiny connected air spaces, and lets water run through it. c. The organic material in soil d. Soild, unweathered rock e. Twigs, leaves, and other organic matter on top of the ...
Earth Science Quiz-1 Please answer the following multiple choice
... a. A tentative explanation of a body of data is called a hypothesis b. A theory is less likely to be correct than hypotheses. c. A hypothesis is strengthened if it successfully predicts the outcomes of new experiments. d. If new evidence indicates that a theory is wrong, the theory may be modified d ...
... a. A tentative explanation of a body of data is called a hypothesis b. A theory is less likely to be correct than hypotheses. c. A hypothesis is strengthened if it successfully predicts the outcomes of new experiments. d. If new evidence indicates that a theory is wrong, the theory may be modified d ...
Use of natural U/Th concentration ratio for estimation of
... sediments, respectively, were almost the same [1-4]. However, applications of phosphatic fertilizers, which are known to contain high U (10-300 times higher than uncontaminated soils) but low in Th [5-7], might increase U concentrations in agricultural field. It is difficult to estimate the excess a ...
... sediments, respectively, were almost the same [1-4]. However, applications of phosphatic fertilizers, which are known to contain high U (10-300 times higher than uncontaminated soils) but low in Th [5-7], might increase U concentrations in agricultural field. It is difficult to estimate the excess a ...
English
... Grape fruitfulness Fruitfulness=potential of vine to yield fruit Two main factors influence fruitfulness ...
... Grape fruitfulness Fruitfulness=potential of vine to yield fruit Two main factors influence fruitfulness ...
Impacts of air pollution on terrestrial and aquatic ecosystem on
... Impacts of air pollution on terrestrial and aquatic ecosystem on southern Baffin Island ...
... Impacts of air pollution on terrestrial and aquatic ecosystem on southern Baffin Island ...
Earth Science Quiz-1 Please answer the following multiple choice
... a. A tentative explanation of a body of data is called a hypothesis b. A theory is less likely to be correct than hypotheses. c. A hypothesis is strengthened if it successfully predicts the outcomes of new experiments. d. If new evidence indicates that a theory is wrong, the theory may be modified d ...
... a. A tentative explanation of a body of data is called a hypothesis b. A theory is less likely to be correct than hypotheses. c. A hypothesis is strengthened if it successfully predicts the outcomes of new experiments. d. If new evidence indicates that a theory is wrong, the theory may be modified d ...
Reproduction and Heredity
... Plantlet produced at the end of stolons, or runners (slender stems that grow along the soil surface, or in this case, hang from the main plant body) ...
... Plantlet produced at the end of stolons, or runners (slender stems that grow along the soil surface, or in this case, hang from the main plant body) ...
Seismic Behavior of RCC Frame Structure Considering Soil
... typically designed as two independent systems, and the superstructure is fixed at the bottom. The calculated seismic response of the building is generally dependent on the structure above ground level i.e., superstructure. This method is generally simple and convenient, but the energetic characteris ...
... typically designed as two independent systems, and the superstructure is fixed at the bottom. The calculated seismic response of the building is generally dependent on the structure above ground level i.e., superstructure. This method is generally simple and convenient, but the energetic characteris ...
Foundation Maintenance and Footing Performance
... Brickwork will resist cracking where it can. It will attempt to span areas that lose support because of subsided foundations or raised points. It is therefore usual to see cracking at weak points, such as openings for windows or doors. In the event of construction settlement, cracking will usually r ...
... Brickwork will resist cracking where it can. It will attempt to span areas that lose support because of subsided foundations or raised points. It is therefore usual to see cracking at weak points, such as openings for windows or doors. In the event of construction settlement, cracking will usually r ...
Slideshow Review for Midterm
... Which element makes up greatest percent by volume in: 1. Earth’s Crust 2. Earth’s Atmosphere 3. Earth’s Hydrosphere Define: 4. Lithosphere, Atmosphere, Hydrosphere ...
... Which element makes up greatest percent by volume in: 1. Earth’s Crust 2. Earth’s Atmosphere 3. Earth’s Hydrosphere Define: 4. Lithosphere, Atmosphere, Hydrosphere ...
Constructive & Destructive Forces
... Mechanical Weathering: • Caused by…(Agents) – Freezing and Thawing – Release of Pressure – Growth of Plants – Abrasion – Grinding away of rock by other rock particles that are carried by water, ice, wind, or gravity ...
... Mechanical Weathering: • Caused by…(Agents) – Freezing and Thawing – Release of Pressure – Growth of Plants – Abrasion – Grinding away of rock by other rock particles that are carried by water, ice, wind, or gravity ...
Ground Cover Plants for Missouri Gardens
... Select plants that are well-suited to the light exposure, soil type and drainage. See Table 1 below for suggested plants for various ground cover locations. Consider planting North American native plants as ground covers. They require less maintenance and less fertilizer. The table below also includ ...
... Select plants that are well-suited to the light exposure, soil type and drainage. See Table 1 below for suggested plants for various ground cover locations. Consider planting North American native plants as ground covers. They require less maintenance and less fertilizer. The table below also includ ...
2-1 Classroom Investigations, 5th Grade
... Weathering of earth materials is the process by which forces and materials change the physical and chemical character of rocks near the surface of the Earth. The processes can be classified as: 1. Mechanical weathering – breaking down or crushing of rocks into smaller pieces (e.g., freezing and thaw ...
... Weathering of earth materials is the process by which forces and materials change the physical and chemical character of rocks near the surface of the Earth. The processes can be classified as: 1. Mechanical weathering – breaking down or crushing of rocks into smaller pieces (e.g., freezing and thaw ...
IOSR Journal of Environmental Science, Toxicology and Food Technology (IOSR-JESTFT)
... Land quality is the capacity of land to support highest biological productivity, conserve environmental quality and increase land and animals health [8]. In such a case several indicator has been used to assess land quality. The common indicators are encompasses physical, chemical and biological ind ...
... Land quality is the capacity of land to support highest biological productivity, conserve environmental quality and increase land and animals health [8]. In such a case several indicator has been used to assess land quality. The common indicators are encompasses physical, chemical and biological ind ...
soil calculative questions.ANSWERS
... 1 metric ton/hectare/year divided by 13 metric tons/mm/hectare = 0.0769 mm / year 2 cm * 10 mm / cm = 20 mm 20 mm divided by 0.0769 mm / year = 260 years ...
... 1 metric ton/hectare/year divided by 13 metric tons/mm/hectare = 0.0769 mm / year 2 cm * 10 mm / cm = 20 mm 20 mm divided by 0.0769 mm / year = 260 years ...
UNIT 5 PLANET EARTH
... TOPIC 2 ROCKS AND THE ROCK CYCLE Igneous rock- formed from hot magma or lava Magma- melted rock found in earth Intrusive rock- rock formed very deep and slowly in Earth’s crust Lava- when magma breaks through Earth’s crust from an volcanic eruption Extrusive rock- rock formed when lava cools on Eart ...
... TOPIC 2 ROCKS AND THE ROCK CYCLE Igneous rock- formed from hot magma or lava Magma- melted rock found in earth Intrusive rock- rock formed very deep and slowly in Earth’s crust Lava- when magma breaks through Earth’s crust from an volcanic eruption Extrusive rock- rock formed when lava cools on Eart ...
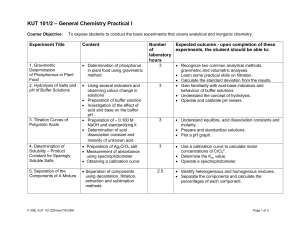
KUT 101/2 – General Chemistry Practical I
... • Preparation of Na2S2O3 solution and standardizing it • Determination of the oxidizing capacity of an unknown liquid bleach • Preparation of Cu(NO)3 and performing basic laboratory procedures • Reduction of copper with zinc • Preparation of ∼ 0.100 M NaOH and standardizing it. • Analysis of an unkn ...
... • Preparation of Na2S2O3 solution and standardizing it • Determination of the oxidizing capacity of an unknown liquid bleach • Preparation of Cu(NO)3 and performing basic laboratory procedures • Reduction of copper with zinc • Preparation of ∼ 0.100 M NaOH and standardizing it. • Analysis of an unkn ...
Printer-friendly Version
... It was pointed out by Schlesinger et al. (2009), however, that the numbers don’t add up. To sequester that much carbon an unrealistic amount of biomass should have been produced. Likewise, if the carbon was sequestered as pedogenic CaCO3 an unrealistic amount of calcium would be needed from chemical ...
... It was pointed out by Schlesinger et al. (2009), however, that the numbers don’t add up. To sequester that much carbon an unrealistic amount of biomass should have been produced. Likewise, if the carbon was sequestered as pedogenic CaCO3 an unrealistic amount of calcium would be needed from chemical ...
Degradation pattern of illicit drugs in soil
... Illicit drugs are those whose nonmedical use is prohibited by the international law and mainly belongs to the class of opiates, cocaine, cannabis, amphetamines type substances (ATSs), etc. (Hall et al. 2008; UNODC 2007). ATS comprise two groups of compounds: [1] the amphetamines group (e.g., ampheta ...
... Illicit drugs are those whose nonmedical use is prohibited by the international law and mainly belongs to the class of opiates, cocaine, cannabis, amphetamines type substances (ATSs), etc. (Hall et al. 2008; UNODC 2007). ATS comprise two groups of compounds: [1] the amphetamines group (e.g., ampheta ...
Getting to Know: Erosion by Water
... The Grand Canyon is one of the most breathtaking places in the world. As you look over the rim of the canyon, it is possible to see rock layers that are more than one billion years old! The Colorado River started eroding those rocks 5 to 6 million years ago. Today, the Grand Canyon is vast and yet t ...
... The Grand Canyon is one of the most breathtaking places in the world. As you look over the rim of the canyon, it is possible to see rock layers that are more than one billion years old! The Colorado River started eroding those rocks 5 to 6 million years ago. Today, the Grand Canyon is vast and yet t ...
Earth Science Final Exam Study Guide
... 1. What does the theory of plate tectonics state about the earth? 2. What do magnetic stripes on the ocean floor represent? 3. What are the three types of plate boundaries & what features can be found at each? 4. What is Pangaea? 5. What evidence is used to support the theory of continental drift? 6 ...
... 1. What does the theory of plate tectonics state about the earth? 2. What do magnetic stripes on the ocean floor represent? 3. What are the three types of plate boundaries & what features can be found at each? 4. What is Pangaea? 5. What evidence is used to support the theory of continental drift? 6 ...
Microbial Activity in Arsenic Contaminated Soil
... Will soil previously contaminated with CCA contain microbes that show more resilience to prolonged exposure to CCA wood than microbes in an uncontaminated soil? ...
... Will soil previously contaminated with CCA contain microbes that show more resilience to prolonged exposure to CCA wood than microbes in an uncontaminated soil? ...
Geomorphic Processes: Endogenic and Exogenic
... Disintegration and decay of rocks via weather elements: high temperatures, extreme cold and freeze-thaw cycles No change in chemical composition of rocks • Exfoliation – due to thermal expansion/contraction and/or release of pressure when buried rocks are uplifted and exposed e.g., Exfoliation D ...
... Disintegration and decay of rocks via weather elements: high temperatures, extreme cold and freeze-thaw cycles No change in chemical composition of rocks • Exfoliation – due to thermal expansion/contraction and/or release of pressure when buried rocks are uplifted and exposed e.g., Exfoliation D ...
Deconstruction LT 5-LS2-1
... parts and animals) and therefore operate as “decomposers.” Decomposition eventually restores (recycles) some materials back to the soil. Organisms can survive only in environments in which their particular needs are met. A healthy ecosystem is one in which multiple species of different types are eac ...
... parts and animals) and therefore operate as “decomposers.” Decomposition eventually restores (recycles) some materials back to the soil. Organisms can survive only in environments in which their particular needs are met. A healthy ecosystem is one in which multiple species of different types are eac ...