Ch 15 Notes: The Autonomic Nervous System 2012
... Structurally, the ANS includes autonomic sensory neurons, integrating centers in the CNS, and autonomic motor neurons. Functionally, the ANS usually operates without conscious control. The ANS is regulated by centers in the brain, mainly the hypothalamus and medulla oblongata, which receive input fr ...
... Structurally, the ANS includes autonomic sensory neurons, integrating centers in the CNS, and autonomic motor neurons. Functionally, the ANS usually operates without conscious control. The ANS is regulated by centers in the brain, mainly the hypothalamus and medulla oblongata, which receive input fr ...
pdf
... (Lefaucheur, 2006). For a better language recovery the left hemisphere may be more important, as patients with better recovery have been observed to have higher activation in the left hemisphere (Heiss & Thiel, 2006). An increasing number of studies have demonstrated that low frequency (1 Hz) repeti ...
... (Lefaucheur, 2006). For a better language recovery the left hemisphere may be more important, as patients with better recovery have been observed to have higher activation in the left hemisphere (Heiss & Thiel, 2006). An increasing number of studies have demonstrated that low frequency (1 Hz) repeti ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... – Reflex in response to stimulation of the outer portion of the sole of the foot (make a ‘J’ from the heel along the lateral edge through the ball of the foot) – Infant (to 1 ½ yrs): extension and fanning of toes ...
... – Reflex in response to stimulation of the outer portion of the sole of the foot (make a ‘J’ from the heel along the lateral edge through the ball of the foot) – Infant (to 1 ½ yrs): extension and fanning of toes ...
21-Spinal Cord Tracts I
... with pain and thermal sensations (lateral tract) and also non- discriminative touch and pressure (medial tract) Fibers of the two tracts are intermingled to some extent In brain stem, constitute the spinal lemniscus Fibers are highly somatotopically arranged, with those Information is sent to the fo ...
... with pain and thermal sensations (lateral tract) and also non- discriminative touch and pressure (medial tract) Fibers of the two tracts are intermingled to some extent In brain stem, constitute the spinal lemniscus Fibers are highly somatotopically arranged, with those Information is sent to the fo ...
The nervous tissue is made up of
... The anterior spinal artery is derived by the union of the anterior spinal artery from each vertebral artery. It runs in a midline groove (Ventral median fissure) on the ventral aspect of the spinal cord. Each posterior spinal artery is a branch the vertebral artery or the posterior inferior cerebell ...
... The anterior spinal artery is derived by the union of the anterior spinal artery from each vertebral artery. It runs in a midline groove (Ventral median fissure) on the ventral aspect of the spinal cord. Each posterior spinal artery is a branch the vertebral artery or the posterior inferior cerebell ...
Head, Spine and Chest Trauma
... The damage primarily is caused by increased pressure inside the skull that compresses the brain. Whenever a patient starts deteriorating following a closed head injury, you should suspect brain swelling (cerebral edema). Elaboration - Intracerebral, Subdural and Epidural Hematoma Depending on the lo ...
... The damage primarily is caused by increased pressure inside the skull that compresses the brain. Whenever a patient starts deteriorating following a closed head injury, you should suspect brain swelling (cerebral edema). Elaboration - Intracerebral, Subdural and Epidural Hematoma Depending on the lo ...
3680Lecture13 - U of L Class Index
... The Feed-Forward Sweep • Hierarchy can be defined more functionaly • The feed-forward sweep is the initial response of each visual area “in turn” as information is passed to it from a “lower” area • Consider the latencies of the first responses in various areas ...
... The Feed-Forward Sweep • Hierarchy can be defined more functionaly • The feed-forward sweep is the initial response of each visual area “in turn” as information is passed to it from a “lower” area • Consider the latencies of the first responses in various areas ...
Sensory uncertainty decoded from visual cortex
... analysis, we found that probability distributions reflecting sensory uncertainty could reliably be estimated from human visual cortex and, moreover, that observers appeared to use knowledge of this uncertainty in their perceptual decisions. The information that the brain receives from the senses is ...
... analysis, we found that probability distributions reflecting sensory uncertainty could reliably be estimated from human visual cortex and, moreover, that observers appeared to use knowledge of this uncertainty in their perceptual decisions. The information that the brain receives from the senses is ...
Lecture : Spinal Reflexes
... afferent, whose magnitude and timing are determined respectively by the intensity and onset of the stimulus” 4. This definition is correct but does not convey the fact that the spinal circuits responsible for reflexes can be used for voluntary behaviors. The idea that there is one stereotypical resp ...
... afferent, whose magnitude and timing are determined respectively by the intensity and onset of the stimulus” 4. This definition is correct but does not convey the fact that the spinal circuits responsible for reflexes can be used for voluntary behaviors. The idea that there is one stereotypical resp ...
The Skin Senses
... – Half see video inducing high empathy for actor – Half see video inducing low empathy for actor – All given painful heat s;mulus, while watching actor receiving the same s;mulus – Those in high empa ...
... – Half see video inducing high empathy for actor – Half see video inducing low empathy for actor – All given painful heat s;mulus, while watching actor receiving the same s;mulus – Those in high empa ...
lec#37 by Dalin Mohammad corrected by Bayan
... difference in the information of both is differentiated by the frequency. The action potential does not differ in the amplitude. The quantity and size of the potential depends on the kinetics of its ion gates. It’s height depends on the same thing, when will they open and close, the ion composition ...
... difference in the information of both is differentiated by the frequency. The action potential does not differ in the amplitude. The quantity and size of the potential depends on the kinetics of its ion gates. It’s height depends on the same thing, when will they open and close, the ion composition ...
Biology 231
... position to the upper brain, where the inputs are consciously perceived sends motor impulses to skeletal muscles to cause body movements autonomic nervous system (ANS) – involuntary (self-regulated) sends sensory information about the internal environment to the lower brain (not consciously perceive ...
... position to the upper brain, where the inputs are consciously perceived sends motor impulses to skeletal muscles to cause body movements autonomic nervous system (ANS) – involuntary (self-regulated) sends sensory information about the internal environment to the lower brain (not consciously perceive ...
Motor Cortex, Basal Ganglia, Cerebellum
... Note: most (80-90%) of corticospinal tract fibers decussate (cross) at the junction of the medulla and spinal cord; most of the rest decussate in the spinal cord; thus, contralateral control Note: some cortical axons in the pyramidal tract synapse directly on alpha motoneurons, rather then interneur ...
... Note: most (80-90%) of corticospinal tract fibers decussate (cross) at the junction of the medulla and spinal cord; most of the rest decussate in the spinal cord; thus, contralateral control Note: some cortical axons in the pyramidal tract synapse directly on alpha motoneurons, rather then interneur ...
Spinal Cord Worksheet - District 196 e
... !3.! What is a dermatome and why are they clinically important? ! .! On figure 2, circle and label the location where the VZV may lay dormant in ...
... !3.! What is a dermatome and why are they clinically important? ! .! On figure 2, circle and label the location where the VZV may lay dormant in ...
Clinical Evaluation of Cranial Nerve V Function
... • Occasionally, oculosympathetic paresis (without anhidrosis) may occur because of the involvement of the sympathetic fibers. • Exophthalmos, due to blockade of the ophthalmic veins, and • blindness, due to extension of the pathologic process to involve the optic canal, may also occur. • Except for ...
... • Occasionally, oculosympathetic paresis (without anhidrosis) may occur because of the involvement of the sympathetic fibers. • Exophthalmos, due to blockade of the ophthalmic veins, and • blindness, due to extension of the pathologic process to involve the optic canal, may also occur. • Except for ...
22 reflexes 1 - The reflex arc
... The frequency of the action potentials is what determines the intensity of the stimulus At the synapse, the action potentials from the afferent neuron produce excitatory post synaptic potentials in the efferent neuron If these excitatory potentials summate enough to bring the efferent membrane to th ...
... The frequency of the action potentials is what determines the intensity of the stimulus At the synapse, the action potentials from the afferent neuron produce excitatory post synaptic potentials in the efferent neuron If these excitatory potentials summate enough to bring the efferent membrane to th ...
Using Sound Therapy for Development and Wellness
... The diagnosis of the person seeking to make change does not matter, for it is the sound energy patterns of the body that determine the possibilities for change for each individual. In other words, sound-based therapies force the evaluator and the client to focus on the energy patterns of the bod ...
... The diagnosis of the person seeking to make change does not matter, for it is the sound energy patterns of the body that determine the possibilities for change for each individual. In other words, sound-based therapies force the evaluator and the client to focus on the energy patterns of the bod ...
Document
... exteroceptors, proprioceptors, and interoceptors • The three main levels of neural integration in the somatosensory system are: • Receptor level – the sensor receptors • Circuit level – ascending pathways ...
... exteroceptors, proprioceptors, and interoceptors • The three main levels of neural integration in the somatosensory system are: • Receptor level – the sensor receptors • Circuit level – ascending pathways ...
From Nerve Cells to Cognition: The Internal
... the behavioral analysis of patients with brain lesions that interfere with mental functioning. This area, neuropsychology, had remained a strong subspecialty of neurology in Europe but was neglected for a time in the United States. Lesions of different regions of the brain can result in quite specif ...
... the behavioral analysis of patients with brain lesions that interfere with mental functioning. This area, neuropsychology, had remained a strong subspecialty of neurology in Europe but was neglected for a time in the United States. Lesions of different regions of the brain can result in quite specif ...
Cranial Nerve II - Maryville University
... infection?). Affected side: paralysis of facial muscles, loss of taste (ageusia) in the anterior two thirds of the tongue, impaired secretion of sublingual and submandibular glands, and hyperacusis (paralysis of stapedius muscle). • Most Bell's Palsy can be recovered fully without any complications. ...
... infection?). Affected side: paralysis of facial muscles, loss of taste (ageusia) in the anterior two thirds of the tongue, impaired secretion of sublingual and submandibular glands, and hyperacusis (paralysis of stapedius muscle). • Most Bell's Palsy can be recovered fully without any complications. ...
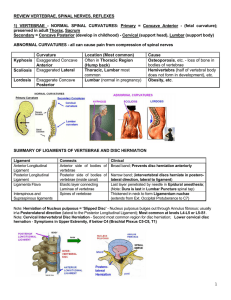
REVIEW VERTEBRAE, SPINAL NERVES, REFLEXES 1
... not pathological but due to increased activation of Gamma motor neurons associated with nervousness and anxiety. Which of the following is an action of Gamma motor neurons that could produce the mild hyperreflexia? A. Increase sensitivity of Golgi tendon organs B. Increase sensitivity of Ia fibers i ...
... not pathological but due to increased activation of Gamma motor neurons associated with nervousness and anxiety. Which of the following is an action of Gamma motor neurons that could produce the mild hyperreflexia? A. Increase sensitivity of Golgi tendon organs B. Increase sensitivity of Ia fibers i ...
Allochiria

Allochiria (from the Greek meaning ""other hand"") is a neurological disorder in which the patient responds to stimuli presented to one side of their body as if the stimuli had been presented at the opposite side. It is associated with spatial transpositions, usually symmetrical, of stimuli from one side of the body (or of the space) to the opposite one. Thus a touch to the left arm will be reported as a touch to the right arm, which is also known as somatosensory allochiria. If the auditory or visual senses are affected, sounds (a person's voice for instance) will be reported as being heard on the opposite side to that on which they occur and objects presented visually will be reported as having been presented on the opposite side. Often patients may express allochiria in their drawing while copying an image. Allochiria often co-occurs with unilateral neglect and, like hemispatial neglect, the disorder arises commonly from damage to the right parietal lobe.Allochiria is often confused with alloesthesia, also known as false allochiria. True allochiria is a symptom of dyschiria and unilateral neglect. Dyschiria is a disorder in the localization of sensation due to various degrees of dissociation and cause impairment in one side causing the inability to tell which side of the body was touched.