Optics - Tensors for Tots
... separating white light into components of different wavelength (different colors). The different colors refract at different angles, splitting white light into a rainbow. When light passes through a prism, it is refracted twice, when it enters the prism and when it leaves. Refraction is the change i ...
... separating white light into components of different wavelength (different colors). The different colors refract at different angles, splitting white light into a rainbow. When light passes through a prism, it is refracted twice, when it enters the prism and when it leaves. Refraction is the change i ...
Sine Wave Notes: Amplitude, Period, Frequency, Wavelength
... per second (about 770 MPH or 1130 feet per second). Sound waves through other media such as steel or helium are considerably different (in the case of helium, almost three times faster). The velocity of sound waves will also change with temperature (it gets faster as the air warms up). Given a veloc ...
... per second (about 770 MPH or 1130 feet per second). Sound waves through other media such as steel or helium are considerably different (in the case of helium, almost three times faster). The velocity of sound waves will also change with temperature (it gets faster as the air warms up). Given a veloc ...
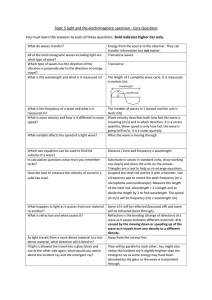
Topic 5 Core Questions
... caused by the slowing down or speeding up of the wave as it travels from one density to a different density. Away from the normal line. They will be parallel to each other. You might also notice the incident ray is slightly brighter than the emergent ray as some energy may have been absorbed by the ...
... caused by the slowing down or speeding up of the wave as it travels from one density to a different density. Away from the normal line. They will be parallel to each other. You might also notice the incident ray is slightly brighter than the emergent ray as some energy may have been absorbed by the ...
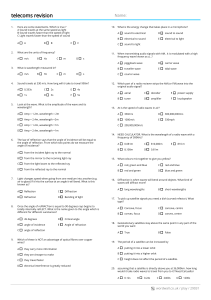
EM Waves Summary Sheet File
... Be able to describe the properties of all EM Waves: EM waves can travel through a vacuum; they do not need a material in which to travel. All EM waves travel at the same speed in vacuum i.e. 300,000,000 metres per second. EM waves change speed when they travel through a material i.e. light a ...
... Be able to describe the properties of all EM Waves: EM waves can travel through a vacuum; they do not need a material in which to travel. All EM waves travel at the same speed in vacuum i.e. 300,000,000 metres per second. EM waves change speed when they travel through a material i.e. light a ...