Formation and Stability of High-Spin Alkali Clusters - Max-Born
... Finally, high-spin states of Li-clusters appear to have significantly higher binding energies and cannot be considered as van-der-Waals clusters [9]. Hence, even high-spin states might not be carried by the droplets. If already on that account Li-clusters are not agglomerated on helium droplets or, ...
... Finally, high-spin states of Li-clusters appear to have significantly higher binding energies and cannot be considered as van-der-Waals clusters [9]. Hence, even high-spin states might not be carried by the droplets. If already on that account Li-clusters are not agglomerated on helium droplets or, ...
Band Theories
... In order to do this revisit basic ideas of molecular orbitals Molecular Orbitals for Diatomic Molecules These orbitals are formed from linear combinations of the atomic orbitals. They differ from the atomic orbitals in that they are new orbitals that spread out over the molecule Can we solve Schrodi ...
... In order to do this revisit basic ideas of molecular orbitals Molecular Orbitals for Diatomic Molecules These orbitals are formed from linear combinations of the atomic orbitals. They differ from the atomic orbitals in that they are new orbitals that spread out over the molecule Can we solve Schrodi ...
Complex symmetric operators
... 1. Complex symmetric operators This section is a brief introduction to complex symmetric operators, a certain class of Hilbert space operators which arise in complex analysis, matrix theory, functional analysis, and even quantum mechanics. The basic definitions and examples are discussed in [8, 10, ...
... 1. Complex symmetric operators This section is a brief introduction to complex symmetric operators, a certain class of Hilbert space operators which arise in complex analysis, matrix theory, functional analysis, and even quantum mechanics. The basic definitions and examples are discussed in [8, 10, ...
A short description how to calculate absorption and energy transfer
... the method, it is applied to study optical absorption and the coherent-incoherent transition of energy transfer in ringshaped molecular aggregates [6], as they appear, e.g., in the light-harvesting units of some bacteria. We consider QAs where the wave functions of different monomers do not overlap ...
... the method, it is applied to study optical absorption and the coherent-incoherent transition of energy transfer in ringshaped molecular aggregates [6], as they appear, e.g., in the light-harvesting units of some bacteria. We consider QAs where the wave functions of different monomers do not overlap ...
The Hydrogen atom.
... problem shows up in many guises in physical chemistry and is not restricted at all to finding atomic orbitals. We will use a very powerful way of finding solutions to this problem that can be used in precisely the same way for such diverse problems as finding the eigenfunctions of the rigid rotor, t ...
... problem shows up in many guises in physical chemistry and is not restricted at all to finding atomic orbitals. We will use a very powerful way of finding solutions to this problem that can be used in precisely the same way for such diverse problems as finding the eigenfunctions of the rigid rotor, t ...
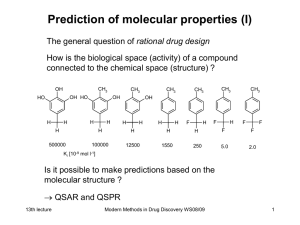
Modern Methods in Drug Discovery
... Removal of one electron ionization potential In general a disturbance by an electric field can be expressed in the form of a Taylor expansion. In the case of an external electrical field F the induced dipole moment ind is obtained as: ...
... Removal of one electron ionization potential In general a disturbance by an electric field can be expressed in the form of a Taylor expansion. In the case of an external electrical field F the induced dipole moment ind is obtained as: ...
Analytical method for determining quantum well exciton properties in
... Therefore finding the approximate ground state of the Hamiltonian is equivalent to solving Eq. (5). Up to now we have followed the standard variational procedure. Solving Eq. (5) requires fixing the perpendicular wave functions Ue , Uh , determining the effective Coulomb potential V (ρ), and solving ...
... Therefore finding the approximate ground state of the Hamiltonian is equivalent to solving Eq. (5). Up to now we have followed the standard variational procedure. Solving Eq. (5) requires fixing the perpendicular wave functions Ue , Uh , determining the effective Coulomb potential V (ρ), and solving ...
Newton-Equivalent Hamiltonians for the Harmonic Oscillator
... admits an infinite-dimensional solution space: Assuming F(x) solves (3.5) and f (x) is a meromorphic function with period i hβ, then also f (x)F(x) solves (3.5). This state of affairs is the main reason that analytic difference operators cannot be readily studied within the well-established Hilbert ...
... admits an infinite-dimensional solution space: Assuming F(x) solves (3.5) and f (x) is a meromorphic function with period i hβ, then also f (x)F(x) solves (3.5). This state of affairs is the main reason that analytic difference operators cannot be readily studied within the well-established Hilbert ...
Glossary - The Open University
... determine the eigenvalues and eigenfunctions of an eigenvalue equation. bound state (91) A stationary state in which one part of a system is always found in close proximity to another part of the same system. Bound states have discrete energy eigenvalues, which lie below the energies of states of th ...
... determine the eigenvalues and eigenfunctions of an eigenvalue equation. bound state (91) A stationary state in which one part of a system is always found in close proximity to another part of the same system. Bound states have discrete energy eigenvalues, which lie below the energies of states of th ...