7 Scattering theory and the S matrix
... the appropriate form) on the structure of the interaction Vint . We will investigate this requirement in details and will formulate the sufficient conditions under which the Hamiltonian H = H0 + Vint leads to a Lorentz covariant S matrix. As will turn out, these conditions are not satisfied in all t ...
... the appropriate form) on the structure of the interaction Vint . We will investigate this requirement in details and will formulate the sufficient conditions under which the Hamiltonian H = H0 + Vint leads to a Lorentz covariant S matrix. As will turn out, these conditions are not satisfied in all t ...
QUANTUM MECHANICAL BEACI-IVE SCA
... When reaction probabilities are small, e.g., in the tunneling threshold region of a reaction, then it has been shown [7,8] that the exchange interaction can be treated accurately by first-order perturbation theory (which for scattering theory is the distorted wave Born approximation (DWBA)), provide ...
... When reaction probabilities are small, e.g., in the tunneling threshold region of a reaction, then it has been shown [7,8] that the exchange interaction can be treated accurately by first-order perturbation theory (which for scattering theory is the distorted wave Born approximation (DWBA)), provide ...
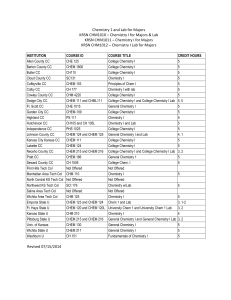
Chemistry 1 and Lab for Majors KRSN CHM1010 – Chemistry I for
... h. Use of other thermodynamic cycles in the determination of thermodynamic quantities, such as the lattice energy of an ionic solid. Conceptually and quantitatively relate spectroscopic observation of atoms to quantum mechanical theories. a. Describe the historical development of and distinction bet ...
... h. Use of other thermodynamic cycles in the determination of thermodynamic quantities, such as the lattice energy of an ionic solid. Conceptually and quantitatively relate spectroscopic observation of atoms to quantum mechanical theories. a. Describe the historical development of and distinction bet ...
Doubly excited nonautoionizing P, D, and F states of helium with
... B. Results with screened Coulomb interaction ...
... B. Results with screened Coulomb interaction ...