Section 22.2 Minerals
... 2. Is the following sentence true or false? A mineral is a naturally occurring, inorganic solid with a crystal structure and a characteristic chemical composition. 3. A material is called if it is not produced from a living thing. 4. Circle the letters of sentences that are true about minerals. a. W ...
... 2. Is the following sentence true or false? A mineral is a naturally occurring, inorganic solid with a crystal structure and a characteristic chemical composition. 3. A material is called if it is not produced from a living thing. 4. Circle the letters of sentences that are true about minerals. a. W ...
Document
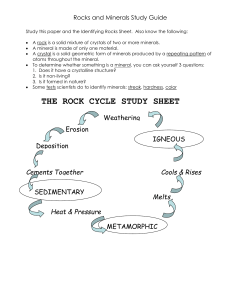
... Rocks and Minerals Study Guide Study this paper and the Identifying Rocks Sheet. Also know the following: ...
... Rocks and Minerals Study Guide Study this paper and the Identifying Rocks Sheet. Also know the following: ...
Minerals - WordPress.com
... in a wet area, they pile up into peat. It takes between 4,000 and 100,000 years for one meter of peat to accumulate. This process happens best in river deltas or coastal plains. • Over time, these peat seams are compressed by further deposits and the carbon content of the coal is concentrated. The o ...
... in a wet area, they pile up into peat. It takes between 4,000 and 100,000 years for one meter of peat to accumulate. This process happens best in river deltas or coastal plains. • Over time, these peat seams are compressed by further deposits and the carbon content of the coal is concentrated. The o ...
MINERALS AND THEIR PROPERTIES
... ○ Can the LifeGem diamonds be considered true minerals? Explain your answer. ○ How are these diamonds different than diamonds mined out of the ground? ○ Would you want to use this company for yourself or for a relative? ...
... ○ Can the LifeGem diamonds be considered true minerals? Explain your answer. ○ How are these diamonds different than diamonds mined out of the ground? ○ Would you want to use this company for yourself or for a relative? ...
B. Structure of Minerals
... 2. How Minerals Form a. Form from molten rock or __________ -As magma cools _______ and ____________ move closer together forming _____________ bonds that create compounds B. Structure of Minerals 1. Crystal = regular _____________ solid with smooth surfaces a. All minerals have _____________ struct ...
... 2. How Minerals Form a. Form from molten rock or __________ -As magma cools _______ and ____________ move closer together forming _____________ bonds that create compounds B. Structure of Minerals 1. Crystal = regular _____________ solid with smooth surfaces a. All minerals have _____________ struct ...
Chapter 2 Section 2.1
... A crystal is a solid in which the atoms are arranged in an orderly, repeating threedimensional pattern. ...
... A crystal is a solid in which the atoms are arranged in an orderly, repeating threedimensional pattern. ...
Name: ANSWERS
... The Mohs scale of mineral hardness is based on the ability of one natural sample of matter to scratch another. It was created by Friedrich Mohs in 1812 to help scientists determine the hardness of minerals from the softest (talc-1) to the hardest (diamond-10). ...
... The Mohs scale of mineral hardness is based on the ability of one natural sample of matter to scratch another. It was created by Friedrich Mohs in 1812 to help scientists determine the hardness of minerals from the softest (talc-1) to the hardest (diamond-10). ...
Flash Card requirements
... ____ 7) A mineral that splits into even sheets shows which of the following properties? ...
... ____ 7) A mineral that splits into even sheets shows which of the following properties? ...
Recognising Minerals
... Streak can be determined by scratching the mineral across a white plate or the unglazed side of a white tile. The streak is the colour of the powder of the mineral so it can also be crushed or filed. Often the streak can be a different colour than the mineral appears. Iron pyrites which appears gold ...
... Streak can be determined by scratching the mineral across a white plate or the unglazed side of a white tile. The streak is the colour of the powder of the mineral so it can also be crushed or filed. Often the streak can be a different colour than the mineral appears. Iron pyrites which appears gold ...
Identifying Minerals
... Mineralogy is the study of minerals and their properties. Many minerals ...
... Mineralogy is the study of minerals and their properties. Many minerals ...
Slide 1
... A vocabulary worksheet will be passed out for you to complete by the end of class. We will grade this together. ...
... A vocabulary worksheet will be passed out for you to complete by the end of class. We will grade this together. ...
Minerals
... The slower magma cools, the larger the crystal formation The faster magma cools, the smaller the crystal ...
... The slower magma cools, the larger the crystal formation The faster magma cools, the smaller the crystal ...
Section-2 Mineral Identification pg.68
... Minerals are often found in ores. Ores are minerals or rock that contains a useful substance AND can be mined at a profit. Bauxite Yields aluminum through smelting. Smelting is a process where a rock is crushed and the metals are melted out of the rock. ...
... Minerals are often found in ores. Ores are minerals or rock that contains a useful substance AND can be mined at a profit. Bauxite Yields aluminum through smelting. Smelting is a process where a rock is crushed and the metals are melted out of the rock. ...
Chapter 1
... Weight of a mineral/weight of an equal volume of water Average value = 2.5 – 3.0 ...
... Weight of a mineral/weight of an equal volume of water Average value = 2.5 – 3.0 ...
Minerals are all around us.
... • How minerals are classified into groups • Which mineral group is most common ...
... • How minerals are classified into groups • Which mineral group is most common ...
MIneral Resources PowerPoint
... When they’re gone, they’re gone. Mineral resources are non-renewable – we are using rocks and minerals faster than the Earth can make them. Eventually we will run out of resources such as coal (fuel) and hematite (iron ore) How many Earth’s would we need? ...
... When they’re gone, they’re gone. Mineral resources are non-renewable – we are using rocks and minerals faster than the Earth can make them. Eventually we will run out of resources such as coal (fuel) and hematite (iron ore) How many Earth’s would we need? ...
Chapter 2
... of protons = # of electrons (but ONLY protons are in nucleus, electrons orbit around the nucleus) Atoms of the same element ALWAYS have the same # of ...
... of protons = # of electrons (but ONLY protons are in nucleus, electrons orbit around the nucleus) Atoms of the same element ALWAYS have the same # of ...
Minerals - WordPress.com
... in a wet area, they pile up into peat. It takes between 4,000 and 100,000 years for one meter of peat to accumulate. This process happens best in river deltas or coastal plains. • Over time, these peat seams are compressed by further deposits and the carbon content of the coal is concentrated. The o ...
... in a wet area, they pile up into peat. It takes between 4,000 and 100,000 years for one meter of peat to accumulate. This process happens best in river deltas or coastal plains. • Over time, these peat seams are compressed by further deposits and the carbon content of the coal is concentrated. The o ...
Name Date
... 6.Which mineral has a different color in its powdered form than in its original form? 1. pyrite 3. kaolinite 2. graphite 4. magnetite ...
... 6.Which mineral has a different color in its powdered form than in its original form? 1. pyrite 3. kaolinite 2. graphite 4. magnetite ...
Name_________________________ Date_______ Period
... Rocks and Minerals Test Circle the best answer. 1. A naturally formed, inorganic solid with a crystalline structure is called a a. atom b. compound c. mineral d. element 2. If the atoms of a substance are arranged in a specific, geometric, repetitive pattern, the substance is a. amorphous b. colorfu ...
... Rocks and Minerals Test Circle the best answer. 1. A naturally formed, inorganic solid with a crystalline structure is called a a. atom b. compound c. mineral d. element 2. If the atoms of a substance are arranged in a specific, geometric, repetitive pattern, the substance is a. amorphous b. colorfu ...
Mineral Nutrition In Plants
... Mineral Nutrition In Plants In addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, which are obtained from carbon dioxide and water, green plants also need at least thirteen essential elements in order to produce new tissues and maintain their correct functioning. The three main minerals required are MINERAL ...
... Mineral Nutrition In Plants In addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, which are obtained from carbon dioxide and water, green plants also need at least thirteen essential elements in order to produce new tissues and maintain their correct functioning. The three main minerals required are MINERAL ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE and MINERALS
... 5. What are the two most common elements by weight in the crust and what is the percentage of each? For each, give the chemical symbol and charge. ...
... 5. What are the two most common elements by weight in the crust and what is the percentage of each? For each, give the chemical symbol and charge. ...
3.2anr
... Match the terms in Column I with the phrases in Column II. Write the letter of the correct phrase in the blank on the left. ...
... Match the terms in Column I with the phrases in Column II. Write the letter of the correct phrase in the blank on the left. ...
Ch 2 3 Properties of Minerals
... Density (d) = mass (m) / Volume (V) Density is usually expressed in g/cm3 in Geology Many common minerals have densities between 2 and 5 g/cm3 The density of a pure mineral is a constant value, and can be used to determine the purity or identity of some minerals ...
... Density (d) = mass (m) / Volume (V) Density is usually expressed in g/cm3 in Geology Many common minerals have densities between 2 and 5 g/cm3 The density of a pure mineral is a constant value, and can be used to determine the purity or identity of some minerals ...
Mineral

A mineral is a naturally occurring substance that is solid and inorganic, representable by a chemical formula, usually abiogenic, and has an ordered atomic structure. It is different from a rock, which can be an aggregate of minerals or non-minerals and does not have a specific chemical composition. The exact definition of a mineral is under debate, especially with respect to the requirement a valid species be abiogenic, and to a lesser extent with regard to it having an ordered atomic structure. The study of minerals is called mineralogy.There are over 4,900 known mineral species; over 4,660 of these have been approved by the International Mineralogical Association (IMA). The silicate minerals compose over 90% of the Earth's crust. The diversity and abundance of mineral species is controlled by the Earth's chemistry. Silicon and oxygen constitute approximately 75% of the Earth's crust, which translates directly into the predominance of silicate minerals. Minerals are distinguished by various chemical and physical properties. Differences in chemical composition and crystal structure distinguish various species, and these properties in turn are influenced by the mineral's geological environment of formation. Changes in the temperature, pressure, or bulk composition of a rock mass cause changes in its minerals. Minerals can be described by various physical properties which relate to their chemical structure and composition. Common distinguishing characteristics include crystal structure and habit, hardness, lustre, diaphaneity, colour, streak, tenacity, cleavage, fracture, parting, and specific gravity. More specific tests for minerals include magnetism, taste or smell, radioactivity and reaction to acid.Minerals are classified by key chemical constituents; the two dominant systems are the Dana classification and the Strunz classification. The silicate class of minerals is subdivided into six subclasses by the degree of polymerization in the chemical structure. All silicate minerals have a base unit of a [SiO4]4− silica tetrahedra—that is, a silicon cation coordinated by four oxygen anions, which gives the shape of a tetrahedron. These tetrahedra can be polymerized to give the subclasses: orthosilicates (no polymerization, thus single tetrahedra), disilicates (two tetrahedra bonded together), cyclosilicates (rings of tetrahedra), inosilicates (chains of tetrahedra), phyllosilicates (sheets of tetrahedra), and tectosilicates (three-dimensional network of tetrahedra). Other important mineral groups include the native elements, sulfides, oxides, halides, carbonates, sulfates, and phosphates.