1 Highly Accurate Quasi-Static Modeling of Microstrip Lines Over
... 4) only at the very highest frequency and conductivity is there a noticeable difference (which is still less than 20 %). In contrast, Mesa et al. [9], who used a more conventional quasi-static model which did not fully consider the impact of the semiconductor on Z, showed significant disagreement be ...
... 4) only at the very highest frequency and conductivity is there a noticeable difference (which is still less than 20 %). In contrast, Mesa et al. [9], who used a more conventional quasi-static model which did not fully consider the impact of the semiconductor on Z, showed significant disagreement be ...
1 PHYS:1200 LECTURE 21 — VIBRATION, WAVES, AND SOUND
... to 20,000 Hz. Inaudible sound above 20,000 Hz is called ultrasound; sound waves below 30 Hz are referred to as infrasound. As we get older, the upper frequency of audible sound is diminished. This will be dramatically demonstrated in class. Prolonged exposure to very high intensi ...
... to 20,000 Hz. Inaudible sound above 20,000 Hz is called ultrasound; sound waves below 30 Hz are referred to as infrasound. As we get older, the upper frequency of audible sound is diminished. This will be dramatically demonstrated in class. Prolonged exposure to very high intensi ...
THz surface wave collapse on coated metal surfaces
... electromagnetic (EM) surface wave on a metal sheet has proven to be extremely difficult due to the large extent of the wave from the surface and to the very weak guiding by the surface. The theoretical study of this wave started with Sommerfeld’s study of EM propagation on a single metal wire [1], f ...
... electromagnetic (EM) surface wave on a metal sheet has proven to be extremely difficult due to the large extent of the wave from the surface and to the very weak guiding by the surface. The theoretical study of this wave started with Sommerfeld’s study of EM propagation on a single metal wire [1], f ...
This data sheet is a compendium of facts and recommendations on
... voltage ratings than monolithics. Since they only have a single slab, they are found with lower capacitance values (typical range 1.5pF to 2.2uF) than the monolithics (which can have 60-80 layers), but can still get large with a noticeable increase in physical size. At the upper end, too, the tolera ...
... voltage ratings than monolithics. Since they only have a single slab, they are found with lower capacitance values (typical range 1.5pF to 2.2uF) than the monolithics (which can have 60-80 layers), but can still get large with a noticeable increase in physical size. At the upper end, too, the tolera ...
Lecture 7 - Capacitance
... We often refer to electric potential, potential difference, and emf simply and sloppily as “voltage,” because all have units of volts. ...
... We often refer to electric potential, potential difference, and emf simply and sloppily as “voltage,” because all have units of volts. ...
Section H2: Preliminary Material
... If complex, poles (or zeros) must occur in complex conjugate pairs. For example, if a root of the denominator (pole) occurs at 6+j3, there is automatically another pole at 6-j3 (note that the real part of a complex conjugate pair may be equal to zero; i.e., for this example with a zero real part the ...
... If complex, poles (or zeros) must occur in complex conjugate pairs. For example, if a root of the denominator (pole) occurs at 6+j3, there is automatically another pole at 6-j3 (note that the real part of a complex conjugate pair may be equal to zero; i.e., for this example with a zero real part the ...
Lesson 1 - Waves - Hitchcock
... • Waves are disturbances that transfer energy from one place to another. • Waves are caused by vibrations of a medium. A medium is the material through which a wave can travel. • Water waves are just one of many kinds of waves. Sound and light are also waves. ...
... • Waves are disturbances that transfer energy from one place to another. • Waves are caused by vibrations of a medium. A medium is the material through which a wave can travel. • Water waves are just one of many kinds of waves. Sound and light are also waves. ...
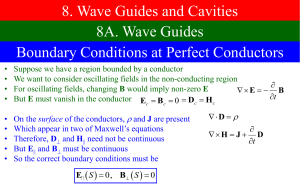
ECE357 introduction slides
... – Radio waves broadcast from an antenna – Light radiation from a laser – X-rays ...
... – Radio waves broadcast from an antenna – Light radiation from a laser – X-rays ...
Chapter 15 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES IN VACUUM
... Maxwell’s equations display a symmetry between electric and magnetic fields. However, this symmetry is broken in that there are no magnetic monopoles and no current of magnetic monopoles corresponding to charges and electric current due to moving charges. Maxwell used vector differential calculus to ...
... Maxwell’s equations display a symmetry between electric and magnetic fields. However, this symmetry is broken in that there are no magnetic monopoles and no current of magnetic monopoles corresponding to charges and electric current due to moving charges. Maxwell used vector differential calculus to ...
C. 8
... A coaxial cable has inner radius a and outer radius b, and is filled with a material with electric permittivity and magnetic susceptibility . Find exact electric and magnetic field solutions for TEM modes. • We will start by finding the electric t Et 0 t Et field, which is transverse and ...
... A coaxial cable has inner radius a and outer radius b, and is filled with a material with electric permittivity and magnetic susceptibility . Find exact electric and magnetic field solutions for TEM modes. • We will start by finding the electric t Et 0 t Et field, which is transverse and ...
Module 2 – Signals & Waves C2
... 2. This changing magnetic field creates an electric field. 3. Then back and forth between magnetic and electric fields from point A to point B. ...
... 2. This changing magnetic field creates an electric field. 3. Then back and forth between magnetic and electric fields from point A to point B. ...
microwaves - Electrical
... produce thermal energy known as dielectic heating and it heats food quickly and efficiently. Food items having high water content are cooked quickly than those having low water content They have a limited role in professional cooking however additional heat sources can be added to M.ovens to pro ...
... produce thermal energy known as dielectic heating and it heats food quickly and efficiently. Food items having high water content are cooked quickly than those having low water content They have a limited role in professional cooking however additional heat sources can be added to M.ovens to pro ...
Optical Nanotransmission Lines: Synthesis of Planar Left
... orientation and polarization of the exciting field. It may be straightforward then to suggest more complex circuits when a system of nano-particles is properly arranged [19]. The circuit model of a “right-handed (RH)” transmission-line is well known in the electrical engineering community, and as de ...
... orientation and polarization of the exciting field. It may be straightforward then to suggest more complex circuits when a system of nano-particles is properly arranged [19]. The circuit model of a “right-handed (RH)” transmission-line is well known in the electrical engineering community, and as de ...
Metal-mesh technology
... well suited for cryogenic, large and compact focal plane systems • drawback: pass-band Fabry-Perot fringe due to the dielectric spacers when matched to free space. Polypropylene has little absorption but n = 1.48 • fringes can be tuned out by applying an anti-reflection coating air-gap hot-pressed • ...
... well suited for cryogenic, large and compact focal plane systems • drawback: pass-band Fabry-Perot fringe due to the dielectric spacers when matched to free space. Polypropylene has little absorption but n = 1.48 • fringes can be tuned out by applying an anti-reflection coating air-gap hot-pressed • ...
Waveguide (electromagnetism)

In electromagnetics and communications engineering, the term waveguide may refer to any linear structure that conveys electromagnetic waves between its endpoints. However, the original and most common meaning is a hollow metal pipe used to carry radio waves. This type of waveguide is used as a transmission line mostly at microwave frequencies, for such purposes as connecting microwave transmitters and receivers to their antennas, in equipment such as microwave ovens, radar sets, satellite communications, and microwave radio links.A dielectric waveguide employs a solid dielectric rod rather than a hollow pipe. An optical fibre is a dielectric guide designed to work at optical frequencies. Transmission lines such as microstrip, coplanar waveguide, stripline or coaxial cable may also be considered to be waveguides.The electromagnetic waves in a (metal-pipe) waveguide may be imagined as travelling down the guide in a zig-zag path, being repeatedly reflected between opposite walls of the guide. For the particular case of rectangular waveguide, it is possible to base an exact analysis on this view. Propagation in a dielectric waveguide may be viewed in the same way, with the waves confined to the dielectric by total internal reflection at its surface. Some structures, such as non-radiative dielectric waveguides and the Goubau line, use both metal walls and dielectric surfaces to confine the wave.