Name ………………………………………………… Unit 7: States of
... fractionating tower allows the separation of this mixture based on the boiling points of the hydrocarbons. To begin the separation process, the crude oil is heated to about 400°C in a furnace, causing many of the hydrocarbons of the crude oil to vaporize. The vaporized mixture is pumped into a fract ...
... fractionating tower allows the separation of this mixture based on the boiling points of the hydrocarbons. To begin the separation process, the crude oil is heated to about 400°C in a furnace, causing many of the hydrocarbons of the crude oil to vaporize. The vaporized mixture is pumped into a fract ...
Ch.1 Section 1.9 Notes - Effingham County Schools
... visibly distinguishable parts consists of two or more regions called phases that differ in properties Examples: pizza, chicken noodle soup, ice cubes in water ...
... visibly distinguishable parts consists of two or more regions called phases that differ in properties Examples: pizza, chicken noodle soup, ice cubes in water ...
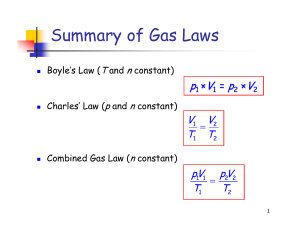
Summary of Gas Laws
... temperature, its vapor pressure can become equal to the applied (atmospheric) pressure Gas phase in the form of bubbles is formed within the volume of the liquid and the bubbles rise to the surface and burst releasing the vapor into the air This process is called boiling The boiling point of a liqui ...
... temperature, its vapor pressure can become equal to the applied (atmospheric) pressure Gas phase in the form of bubbles is formed within the volume of the liquid and the bubbles rise to the surface and burst releasing the vapor into the air This process is called boiling The boiling point of a liqui ...
Separation and Purification Methods
... are required for analyzing any number of complex mixtures—from contaminants in well water to forensic DNA samples to pharmaceutical formulations. Second, it is often necessary to purify compounds for further use—for example, the isolation of morphine from poppy seeds or the purification of intermedi ...
... are required for analyzing any number of complex mixtures—from contaminants in well water to forensic DNA samples to pharmaceutical formulations. Second, it is often necessary to purify compounds for further use—for example, the isolation of morphine from poppy seeds or the purification of intermedi ...
Unit 2: Mixture and Matter Study Guide Ch 2 Vocab to know: Matter
... Use appropriate vocabulary to describe state changes Identify physical and chemical properties of a substance Identify examples of chemical and physical changes Describe and identify intensive and extensive physical properties Identify the difference between pure substances and mixtures Identify exa ...
... Use appropriate vocabulary to describe state changes Identify physical and chemical properties of a substance Identify examples of chemical and physical changes Describe and identify intensive and extensive physical properties Identify the difference between pure substances and mixtures Identify exa ...
9/21 properties of matter ppt
... been collected from the world’s oceans for thousands of years using this technique. ...
... been collected from the world’s oceans for thousands of years using this technique. ...
Physical properties
... • Distillation is used to purify a compound by separating it from a non-volatile or less-volatile material. When different compounds in a mixture have different boiling points, they separate into individual components when the mixture is carefully distilled. • Distillation is the process of heating ...
... • Distillation is used to purify a compound by separating it from a non-volatile or less-volatile material. When different compounds in a mixture have different boiling points, they separate into individual components when the mixture is carefully distilled. • Distillation is the process of heating ...
Continuous distillation

Continuous distillation, a form of distillation, is an ongoing separation in which a mixture is continuously (without interruption) fed into the process and separated fractions are removed continuously as output streams. A distillation is the separation or partial separation of a liquid feed mixture into components or fractions by selective boiling (or evaporation) and condensation. A distillation produces at least two output fractions. These fractions include at least one volatile distillate fraction, which has boiled and been separately captured as a vapor condensed to a liquid, and practically always a bottoms (or residuum) fraction, which is the least volatile residue that has not been separately captured as a condensed vapor.An alternative to continuous distillation is batch distillation, where the mixture is added to the unit at the start of the distillation, distillate fractions are taken out sequentially in time (one after another) during the distillation, and the remaining bottoms fraction is removed at the end. Because each of the distillate fractions are taken out at different times, only one distillate exit point (location) is needed for a batch distillation and the distillate can just be switched to a different receiver, a fraction-collecting container. Batch distillation is often used when smaller quantities are distilled. In a continuous distillation, each of the fraction streams is taken simultaneously throughout operation; therefore, a separate exit point is needed for each fraction. In practice when there are multiple distillate fractions, each of the distillate exit points are located at different heights on a fractionating column. The bottoms fraction can be taken from the bottom of the distillation column or unit, but is often taken from a reboiler connected to the bottom of the column.Each fraction may contain one or more components (types of chemical compounds). When distilling crude oil or a similar feedstock, each fraction contains many components of similar volatility and other properties. Although it is possible to run a small-scale or laboratory continuous distillation, most often continuous distillation is used in a large-scale industrial process.