COMPLIANCE RESIDENTIAL M A N U A L
... 2.2 Compliance and Enforcement Phases..................................................................................2-1 ...
... 2.2 Compliance and Enforcement Phases..................................................................................2-1 ...
An energy efficient building for the Arctic climate
... investigations of building parameters including the building envelope and systems, and investigations of boundary situations in the Arctic regions. The passive house uses the basic idea of a super energy efficient house in which the normal hydronic heating system can be omitted. The savings in inves ...
... investigations of building parameters including the building envelope and systems, and investigations of boundary situations in the Arctic regions. The passive house uses the basic idea of a super energy efficient house in which the normal hydronic heating system can be omitted. The savings in inves ...
radiant cooling systems
... counter radiant loads using more cooler air - This requires more air movement, inefficiently countering a high MRT With an air-based system in combination with a radiant cooling system, surface temperatures are naturally lower - This increases the heat emitted from the occupant to cooled surfaces vi ...
... counter radiant loads using more cooler air - This requires more air movement, inefficiently countering a high MRT With an air-based system in combination with a radiant cooling system, surface temperatures are naturally lower - This increases the heat emitted from the occupant to cooled surfaces vi ...
A Retrofit of a Victorian House in New Bolsover
... constructions, these interventions could potentially be detrimental to the health of the building and its occupants. 1.4 PERFORMANCE OF TRADITIONAL BUILDINGS Available data suggest that actual energy use in traditional buildings is often less than predicted, and that there can be wide discrepancies ...
... constructions, these interventions could potentially be detrimental to the health of the building and its occupants. 1.4 PERFORMANCE OF TRADITIONAL BUILDINGS Available data suggest that actual energy use in traditional buildings is often less than predicted, and that there can be wide discrepancies ...
chapter 11 - Description
... secondarily, a surface can modify air temperature (as when cool air moves across a warm surface). As important as these two determinants of comfort are, they are often not sufficient by themselves. In cooling situations, air motion and relative humidity are significant comfort determinants. For most ...
... secondarily, a surface can modify air temperature (as when cool air moves across a warm surface). As important as these two determinants of comfort are, they are often not sufficient by themselves. In cooling situations, air motion and relative humidity are significant comfort determinants. For most ...
User Guide for Hospitals
... guides accompanying them. This guide is specifically for the design and construction of new hospitals. EDGE is an innovation of IFC, a member of the World Bank Group. ...
... guides accompanying them. This guide is specifically for the design and construction of new hospitals. EDGE is an innovation of IFC, a member of the World Bank Group. ...
11Chapter11_MEEB12-W..
... secondarily, a surface can modify air temperature (as when cool air moves across a warm surface). As important as these two determinants of comfort are, they are often not sufficient by themselves. In cooling situations, air motion and relative humidity are significant comfort determinants. For most ...
... secondarily, a surface can modify air temperature (as when cool air moves across a warm surface). As important as these two determinants of comfort are, they are often not sufficient by themselves. In cooling situations, air motion and relative humidity are significant comfort determinants. For most ...
Possibilities of using thermal mass in buildings to save energy, cut
... Another aspect to consider is the user behaviour, which may cause substantial differences in energy use; therefore, savings can also be achieved through information. New systems for indoor air conditioning have been developed and introduced. This has contributed to greater comfort, but at the same t ...
... Another aspect to consider is the user behaviour, which may cause substantial differences in energy use; therefore, savings can also be achieved through information. New systems for indoor air conditioning have been developed and introduced. This has contributed to greater comfort, but at the same t ...
User Guide for Offices
... guides accompanying them. This guide is specifically for new office building design and construction. EDGE is an innovation of IFC, a member of the World Bank Group. ...
... guides accompanying them. This guide is specifically for new office building design and construction. EDGE is an innovation of IFC, a member of the World Bank Group. ...
chapter 11 - Description
... secondarily, a surface can modify air temperature (as when cool air moves across a warm surface). As important as these two determinants of comfort are, they are often not sufficient by themselves. In cooling situations, air motion and relative humidity are significant comfort determinants. For most ...
... secondarily, a surface can modify air temperature (as when cool air moves across a warm surface). As important as these two determinants of comfort are, they are often not sufficient by themselves. In cooling situations, air motion and relative humidity are significant comfort determinants. For most ...
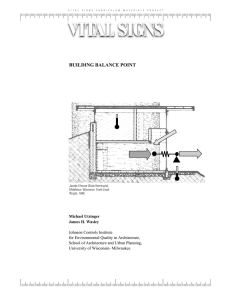
building balance point
... the sunken garden is bermed against the convex north wall, providing an airfoil directing winter winds over the house and leaving dead air near the glazed south wall. The house is one room deep, admitting winter solar radiation into all occupied spaces. The design, referred to as the 'solar hemicycl ...
... the sunken garden is bermed against the convex north wall, providing an airfoil directing winter winds over the house and leaving dead air near the glazed south wall. The house is one room deep, admitting winter solar radiation into all occupied spaces. The design, referred to as the 'solar hemicycl ...
THERMOCHEMISTRY or Thermodynamics
... ENERGY is the capacity to do work or transfer heat. work is the energy used to cause an object with mass to move (w= F x d). When chemical reactions involve gases, the work done may involve compression or expansion of gases. (w = -P∆V where P = pressure and ∆V = Vfinal-Vinitial) ...
... ENERGY is the capacity to do work or transfer heat. work is the energy used to cause an object with mass to move (w= F x d). When chemical reactions involve gases, the work done may involve compression or expansion of gases. (w = -P∆V where P = pressure and ∆V = Vfinal-Vinitial) ...
H 2 (g) - SFP Online!
... ENERGY is the capacity to do work or transfer heat. work is the energy used to cause an object with mass to move (w= F x d). When chemical reactions involve gases, the work done may involve compression or expansion of gases. (w = -P∆V where P = pressure and ∆V = Vfinal-Vinitial) ...
... ENERGY is the capacity to do work or transfer heat. work is the energy used to cause an object with mass to move (w= F x d). When chemical reactions involve gases, the work done may involve compression or expansion of gases. (w = -P∆V where P = pressure and ∆V = Vfinal-Vinitial) ...
Supporting the Eindhoven University of Technology to
... production, the available data of all buildings will be analyzed, mainly focusing on the total ATES balance. The amount of heat or cold extracted for use and the heat extracted for the cooling towers will be analyzed to see what the actual imbalance is. 2.1. Classification of buildings To create som ...
... production, the available data of all buildings will be analyzed, mainly focusing on the total ATES balance. The amount of heat or cold extracted for use and the heat extracted for the cooling towers will be analyzed to see what the actual imbalance is. 2.1. Classification of buildings To create som ...
Unit 10 Exam - Sharp Honors Chemistry Multiple Choice Identify the
... heat capacity of steel is lower than the specific heat capacity of wood. c. steel has the ability to resist a temperature change better than wood. d. the mass of steel is less than wood, so it loses heat faster. e. Two of the above statements are true. ...
... heat capacity of steel is lower than the specific heat capacity of wood. c. steel has the ability to resist a temperature change better than wood. d. the mass of steel is less than wood, so it loses heat faster. e. Two of the above statements are true. ...
Case Study
... systems may compare to similar systems used under the same work conditions. However not all HVAC systems may benefit from high performance conditions using water cooled condensers. There are multiple technical advantages using HHHP, but this HVAC system appears, from those cases, to be well adapted ...
... systems may compare to similar systems used under the same work conditions. However not all HVAC systems may benefit from high performance conditions using water cooled condensers. There are multiple technical advantages using HHHP, but this HVAC system appears, from those cases, to be well adapted ...
Analysis of Historic Buildings in Terms of their Microclimatic and
... of the Building Regulations the greatest emphasis must lie on the environmental aspect, and specifically the use of fossil energy. This is closely allied to the generation of carbon dioxide both from the creation of buildings and from their daily use. When they were first built and inhabited, all pr ...
... of the Building Regulations the greatest emphasis must lie on the environmental aspect, and specifically the use of fossil energy. This is closely allied to the generation of carbon dioxide both from the creation of buildings and from their daily use. When they were first built and inhabited, all pr ...
Aalborg Universitet Zero Energy Buildings Bejder, Anne Kirkegaard; Knudstrup, Mary-Ann
... be produced individually on the basis of other additional resources. Furthermore, district heating enables the use of renewable energy sources such as geothermal heat and solar thermal collectors, often in combination with large heat storages. Figure 2 shows the development of resource use in Dani ...
... be produced individually on the basis of other additional resources. Furthermore, district heating enables the use of renewable energy sources such as geothermal heat and solar thermal collectors, often in combination with large heat storages. Figure 2 shows the development of resource use in Dani ...
Development and evaluation of a building energy model integrated
... minimum indoor air temperature threshold is used to calculate the heating loads of the building associated with transmission through building surfaces (Pigeon et al., 2008). In order to improve the representation of buildings in TEB, we have considered two different approaches. The first approach is ...
... minimum indoor air temperature threshold is used to calculate the heating loads of the building associated with transmission through building surfaces (Pigeon et al., 2008). In order to improve the representation of buildings in TEB, we have considered two different approaches. The first approach is ...
Building envelope design as a passive cooling technique
... A highly reflective envelope may result in a smaller cooling load, but glare from the surface can significantly increase loads on and complaints from adjacent building occupants. Reflective roofing products help reduce cooling loads because the roof is exposed to the sun for the entire operating day ...
... A highly reflective envelope may result in a smaller cooling load, but glare from the surface can significantly increase loads on and complaints from adjacent building occupants. Reflective roofing products help reduce cooling loads because the roof is exposed to the sun for the entire operating day ...
Building Energy Code of Pakistan
... measured at the boiler outlet, at the design inlet and outlet conditions and rated fuel/energy input. British thermal unit (Btu). Approximately the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one Fahrenheit degree, at 60 F. International Steam Table Btu x 1.055 = W. ...
... measured at the boiler outlet, at the design inlet and outlet conditions and rated fuel/energy input. British thermal unit (Btu). Approximately the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one Fahrenheit degree, at 60 F. International Steam Table Btu x 1.055 = W. ...
الشريحة 1
... The heat equivalent of an air-conditioning fan horsepower is added as the sensible heat to the system. If the fan motor is outside the air stream, the energy lost due to the inefficiency of the motor is not added to the air. There are two types of air supply systems. 1-Draw-through system In the dra ...
... The heat equivalent of an air-conditioning fan horsepower is added as the sensible heat to the system. If the fan motor is outside the air stream, the energy lost due to the inefficiency of the motor is not added to the air. There are two types of air supply systems. 1-Draw-through system In the dra ...
Solar passive design – combining orientation, thermal mass and
... double glazing work, and even the way clothing works to keep you warm. Reflective insulation (aka sarking, sisilation, anti-con) comes in rolls or boards and looks like aluminium foil. It acts as a mirror to radiant heat – that is, heat in the form of electromagnetic waves, such as the heat in sunli ...
... double glazing work, and even the way clothing works to keep you warm. Reflective insulation (aka sarking, sisilation, anti-con) comes in rolls or boards and looks like aluminium foil. It acts as a mirror to radiant heat – that is, heat in the form of electromagnetic waves, such as the heat in sunli ...
notable example of a thermal mass
... fifties in degrees Fahrenheit) year-round. year Earth-bound bound walls are not exposed to extreme air temperatures in cold weather [1]. The large thermal inertia of the soil cover causes the temperature in the surrounding soil to be higher/lower than the outdoor air temperature during winter/summer ...
... fifties in degrees Fahrenheit) year-round. year Earth-bound bound walls are not exposed to extreme air temperatures in cold weather [1]. The large thermal inertia of the soil cover causes the temperature in the surrounding soil to be higher/lower than the outdoor air temperature during winter/summer ...
Aalborg Universitet Measuring Device
... equipment on the test piece leaving some cracks or drill holes on the object. For all of the existing apparatus there is direct contact between the heat absorption sensor (sensor plate) and the surface of the test piece, thereby seriously affecting the result due to the transition insulation factor ...
... equipment on the test piece leaving some cracks or drill holes on the object. For all of the existing apparatus there is direct contact between the heat absorption sensor (sensor plate) and the surface of the test piece, thereby seriously affecting the result due to the transition insulation factor ...
Geothermal heat pump

A geothermal heat pump or ground source heat pump (GSHP) is a central heating and/or cooling system that transfers heat to or from the ground.It uses the earth as a heat source (in the winter) or a heat sink (in the summer). This design takes advantage of the moderate temperatures in the ground to boost efficiency and reduce the operational costs of heating and cooling systems, and may be combined with solar heating to form a geosolar system with even greater efficiency. Ground source heat pumps are also known as ""geothermal heat pumps"" although, strictly, the heat does not come primarily from the centre of the Earth, but from the Sun. They are also known by other names, including geoexchange, earth-coupled, earth energy systems. The engineering and scientific communities prefer the terms ""geoexchange"" or ""ground source heat pumps"" to avoid confusion with traditional geothermal power, which uses a high temperature heat source to generate electricity. Ground source heat pumps harvest heat absorbed at the Earth's surface from solar energy. The temperature in the ground below 6 metres (20 ft) is roughly equal to the mean annual air temperature at that latitude at the surface.Depending on latitude, the temperature beneath the upper 6 metres (20 ft) of Earth's surface maintains a nearly constant temperature between 10 and 16 °C (50 and 60 °F), if the temperature is undisturbed by the presence of a heat pump. Like a refrigerator or air conditioner, these systems use a heat pump to force the transfer of heat from the ground. Heat pumps can transfer heat from a cool space to a warm space, against the natural direction of flow, or they can enhance the natural flow of heat from a warm area to a cool one. The core of the heat pump is a loop of refrigerant pumped through a vapor-compression refrigeration cycle that moves heat. Air-source heat pumps are typically more efficient at heating than pure electric heaters, even when extracting heat from cold winter air, although efficiencies begin dropping significantly as outside air temperatures drop below 5 °C (41 °F). A ground source heat pump exchanges heat with the ground. This is much more energy-efficient because underground temperatures are more stable than air temperatures through the year. Seasonal variations drop off with depth and disappear below 7 metres (23 ft) to 12 metres (39 ft) due to thermal inertia. Like a cave, the shallow ground temperature is warmer than the air above during the winter and cooler than the air in the summer. A ground source heat pump extracts ground heat in the winter (for heating) and transfers heat back into the ground in the summer (for cooling). Some systems are designed to operate in one mode only, heating or cooling, depending on climate.Geothermal pump systems reach fairly high coefficient of performance (CoP), 3 to 6, on the coldest of winter nights, compared to 1.75-2.5 for air-source heat pumps on cool days. Ground source heat pumps (GSHPs) are among the most energy efficient technologies for providing HVAC and water heating.Setup costs are higher than for conventional systems, but the difference is usually returned in energy savings in 3 to 10 years, and even shorter lengths of time with federal, state and utility tax credits and incentives. Geothermal heat pump systems are reasonably warranted by manufacturers, and their working life is estimated at 25 years for inside components and 50+ years for the ground loop. As of 2004, there are over a million units installed worldwide providing 12 GW of thermal capacity, with an annual growth rate of 10%.