Simulation of Heat Gain through Building Envelope for Buildings in
... Heat gain through glass areas facing different directions would be unequal such that the one facing north would have minimum heat gain and the one facing northwest would gain most. The important factors influenced the heat gain of the building models are window to wall ratio, WWR , and the building ...
... Heat gain through glass areas facing different directions would be unequal such that the one facing north would have minimum heat gain and the one facing northwest would gain most. The important factors influenced the heat gain of the building models are window to wall ratio, WWR , and the building ...
Heat Pipe Background
... Permeability, K, is a measure of the ability of a material to transmit fluids and depends on factors such as the wick diameter, wick thickness, pore size. Porosity, φ, and the effective pore radius, R, contribute to an increase in permeability. ...
... Permeability, K, is a measure of the ability of a material to transmit fluids and depends on factors such as the wick diameter, wick thickness, pore size. Porosity, φ, and the effective pore radius, R, contribute to an increase in permeability. ...
Document
... currents flow when hot gas rises and cool gas sink. — Convection in liquids also occurs because of differences in density. ...
... currents flow when hot gas rises and cool gas sink. — Convection in liquids also occurs because of differences in density. ...
Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
... R-11 is used in large-capacity water chillers serving A-C systems in buildings. R-134a (replaced R-12, which damages ozone layer) is used in domestic refrigerators and freezers, as well as automotive air conditioners. R-22 is used in window air conditioners, heat pumps, air conditioners of commercia ...
... R-11 is used in large-capacity water chillers serving A-C systems in buildings. R-134a (replaced R-12, which damages ozone layer) is used in domestic refrigerators and freezers, as well as automotive air conditioners. R-22 is used in window air conditioners, heat pumps, air conditioners of commercia ...
Defining the “Ideal Construction Methods and Conditions”
... This in turn provides an opportunity to create sheltered, comfortable spaces around the building which can have a significant amenity value at certain times of the year, and these external spaces can have a beneficial effect on the internal environment of the building by minimizing the need for ar ...
... This in turn provides an opportunity to create sheltered, comfortable spaces around the building which can have a significant amenity value at certain times of the year, and these external spaces can have a beneficial effect on the internal environment of the building by minimizing the need for ar ...
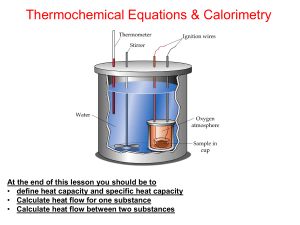
Thermochemistry Lesson 2
... Use data of standard enthalpy of formation (ΔHf) Use data of standard enthalpy of combustion (ΔHc) Use data of standard enthalpy of atomization (ΔHa) or Energy bonding (D). At the end of this lesson you should be to • define calorimeter and calorimetry • Know five (5) ways to determine enthalpy chan ...
... Use data of standard enthalpy of formation (ΔHf) Use data of standard enthalpy of combustion (ΔHc) Use data of standard enthalpy of atomization (ΔHa) or Energy bonding (D). At the end of this lesson you should be to • define calorimeter and calorimetry • Know five (5) ways to determine enthalpy chan ...
Overview
... raised. Due to the small fossil energy proportion of industrial waste heat this source is proper for achieving the given aims. The utilisation of industrial waste heat can complement the generation-portfolio of district heating very well. Waste heat is a by-product of many industrial processes. Thus ...
... raised. Due to the small fossil energy proportion of industrial waste heat this source is proper for achieving the given aims. The utilisation of industrial waste heat can complement the generation-portfolio of district heating very well. Waste heat is a by-product of many industrial processes. Thus ...
THErmAl mAss AND INsulATIoN for TEmPErATE ClImATEs
... Value): how much resistance it presents to heat transfer (the more resistance, the higher the R Value, the better the insulator). Good insulators include foam, wool and air; poor insulators include glass, metal, earth and concrete. Thermal mass stores heat. As heat moves from the hot side to the col ...
... Value): how much resistance it presents to heat transfer (the more resistance, the higher the R Value, the better the insulator). Good insulators include foam, wool and air; poor insulators include glass, metal, earth and concrete. Thermal mass stores heat. As heat moves from the hot side to the col ...
Analysis
... stationary, while the other plate is moving at a speed of 200m/s. both plates are maintained at 27°C. Consider two cases, one for which the plates are separated by water and the other for which the plates are separated by air. For each of the two fluids, which is the force per unit surface area requ ...
... stationary, while the other plate is moving at a speed of 200m/s. both plates are maintained at 27°C. Consider two cases, one for which the plates are separated by water and the other for which the plates are separated by air. For each of the two fluids, which is the force per unit surface area requ ...
vii. bringing air to saturation
... It is particularly slippery when newly formed. That means the temperature is close to freezing. If a thin surface layer of liquid water develops on that ice, it is especially slick, and you can melt a thin layer of thin black ice by friction, by walking on it, or by driving on it. b. If air were abl ...
... It is particularly slippery when newly formed. That means the temperature is close to freezing. If a thin surface layer of liquid water develops on that ice, it is especially slick, and you can melt a thin layer of thin black ice by friction, by walking on it, or by driving on it. b. If air were abl ...
Binnie Thermochemistry Practice
... (w>0 work done on system, w<0 work done by system on surroundings) Energy is conserved (1st Law of thermodynamics) Energy is a state function (does not depend on history of sample, only present conditions) Kinetic Energy = ½ m v2 energy of motion, measured in Joules Potential Energy = stored energy ...
... (w>0 work done on system, w<0 work done by system on surroundings) Energy is conserved (1st Law of thermodynamics) Energy is a state function (does not depend on history of sample, only present conditions) Kinetic Energy = ½ m v2 energy of motion, measured in Joules Potential Energy = stored energy ...
Here - Australian Passive House Association
... a building envelope with enough insulation to remain warm with only solar gains and other internal heat gains from people and appliances. However, the additional money and resources required to do so would not make economic sense. Instead, a modest amount of energy (up to 15 kWh/m2/yr) is deemed acc ...
... a building envelope with enough insulation to remain warm with only solar gains and other internal heat gains from people and appliances. However, the additional money and resources required to do so would not make economic sense. Instead, a modest amount of energy (up to 15 kWh/m2/yr) is deemed acc ...
Project 1.3.4 Renewable Insulation R
... between two metal plates held at different constant temperatures. The amount of energy flowing through the material or the amount of energy required to keep the plates at their constant temperature difference provides the data to determine R values. We are not at a steady state ΔT, so the P=Q/t=kAΔT ...
... between two metal plates held at different constant temperatures. The amount of energy flowing through the material or the amount of energy required to keep the plates at their constant temperature difference provides the data to determine R values. We are not at a steady state ΔT, so the P=Q/t=kAΔT ...
Window Condensation - RLC Engineering, LLC
... temperature of the outside air. In the southeast US, summer dew point temperatures range from about 65F to 75F. When temperatures inside the building are within this range, summer condensation problems can occur. The outside glass surface in energy efficient windows will be closer to the outside air ...
... temperature of the outside air. In the southeast US, summer dew point temperatures range from about 65F to 75F. When temperatures inside the building are within this range, summer condensation problems can occur. The outside glass surface in energy efficient windows will be closer to the outside air ...
MICROFLOWS: AN INTRODUCTION Michael Shusser
... 1 d dT du r 0 r dr dr k dr ...
... 1 d dT du r 0 r dr dr k dr ...
Introduction
... (Something to think about: Read the sentence just below Equation (22.16). Is it obvious that this integral represents the change in vapor concentration divided by the average driving force?) Refer back to Figures [23.8(a) and 23.8(b)]. There is resistance to heat transfer in both the liquid and gas ...
... (Something to think about: Read the sentence just below Equation (22.16). Is it obvious that this integral represents the change in vapor concentration divided by the average driving force?) Refer back to Figures [23.8(a) and 23.8(b)]. There is resistance to heat transfer in both the liquid and gas ...
TAREA 1. Resuelva las siguientes preguntas y problemas. Además
... were not mutually exclusive and that they were accepted together as complementary. Note that the success and wide acceptance of the newer theory (the caloric theory) was the result of the great service that this theory rendered to the quantitative fields of thermochemistry and ‘‘heat engineering.’’ N ...
... were not mutually exclusive and that they were accepted together as complementary. Note that the success and wide acceptance of the newer theory (the caloric theory) was the result of the great service that this theory rendered to the quantitative fields of thermochemistry and ‘‘heat engineering.’’ N ...
Measuring the Specific Heat of Sand
... object must gain or lose to change its temperature by a given amount. In the MKS system, heat capacity would be expressed in units of Joules per degree Centigrade (°C)—that is, the heat capacity of the object would be the amount of heat (in Joules) that the object would have to gain or lose for its ...
... object must gain or lose to change its temperature by a given amount. In the MKS system, heat capacity would be expressed in units of Joules per degree Centigrade (°C)—that is, the heat capacity of the object would be the amount of heat (in Joules) that the object would have to gain or lose for its ...
Literature review summary
... The main objective was to determine the effects of wind on the performance of the UTSC. Experiments have been conducted on a SolarWall® Building where wind speed, temperature, irradiance, and air velocity ,measurements have been taken to measure the relation between wind speed and direction, and the ...
... The main objective was to determine the effects of wind on the performance of the UTSC. Experiments have been conducted on a SolarWall® Building where wind speed, temperature, irradiance, and air velocity ,measurements have been taken to measure the relation between wind speed and direction, and the ...
The physiological equivalent temperature – a universal - FAU
... (air temperature, radiant temperature, air velocity, air humidity) in a thermophysiologically relevant way, evaluating their real effect on the regulatory processes and on the thermal state of the body. This means, however, that PET cannot be an absolute measure of thermal comfort or thermal strain, ...
... (air temperature, radiant temperature, air velocity, air humidity) in a thermophysiologically relevant way, evaluating their real effect on the regulatory processes and on the thermal state of the body. This means, however, that PET cannot be an absolute measure of thermal comfort or thermal strain, ...
calorimetry
... Discussion: In nearly all chemical and physical changes occurring in nature, energy is either evolved or absorbed. In the laboratory a calorimeter is used to measure the heat flow for a chemical reaction. Reactions which evolve heat are exothermic; their H values are negative. Reactions that absorb ...
... Discussion: In nearly all chemical and physical changes occurring in nature, energy is either evolved or absorbed. In the laboratory a calorimeter is used to measure the heat flow for a chemical reaction. Reactions which evolve heat are exothermic; their H values are negative. Reactions that absorb ...
Refrigeration And Air Conditioning
... While most small- and medium-capacity refrigeration systems use hermetically sealed, electricmotor-driven compressor units or open (externally powered) reciprocating compressors, centrifugal compressors are frequently found ...
... While most small- and medium-capacity refrigeration systems use hermetically sealed, electricmotor-driven compressor units or open (externally powered) reciprocating compressors, centrifugal compressors are frequently found ...
Solar passive design – combining orientation, thermal mass and
... more comfortable you are, and the lower your bills and environmental impact. Heating and cooling makes up 60% or more of the energy consumption of most households in the Capital Region, so major savings can be made by reducing the need for heating and cooling. Insulation helps reduce use of heating ...
... more comfortable you are, and the lower your bills and environmental impact. Heating and cooling makes up 60% or more of the energy consumption of most households in the Capital Region, so major savings can be made by reducing the need for heating and cooling. Insulation helps reduce use of heating ...
Brewing Week 4
... b) How much heat must be added to the tank to bring its temperature to 65C? c) If a 30 kW electric heater is used, how long will the heating process take? ...
... b) How much heat must be added to the tank to bring its temperature to 65C? c) If a 30 kW electric heater is used, how long will the heating process take? ...
HVAC
HVAC (heating, ventilating, and air conditioning; also heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) is the technology of indoor and vehicular environmental comfort. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer. Refrigeration is sometimes added to the field's abbreviation as HVAC&R or HVACR, or ventilating is dropped as in HACR (such as the designation of HACR-rated circuit breakers).HVAC is important in the design of medium to large industrial and office buildings such as skyscrapers and in marine environments such as aquariums, where safe and healthy building conditions are regulated with respect to temperature and humidity, using fresh air from outdoors.Ventilating or ventilation (the V in HVAC) is the process of ""exchanging"" or replacing air in any space to provide high indoor air quality which involves temperature control, oxygen replenishment, and removal of moisture, odors, smoke, heat, dust, airborne bacteria, and carbon dioxide. Ventilation removes unpleasant smells and excessive moisture, introduces outside air, keeps interior building air circulating, and prevents stagnation of the interior air.Ventilation includes both the exchange of air to the outside as well as circulation of air within the building. It is one of the most important factors for maintaining acceptable indoor air quality in buildings. Methods for ventilating a building may be divided into mechanical/forced and natural types.