General and Organic Chemistry Review Primer
... the number of protons and neutrons. Calculating an element’s mass number is complicated by the existence of isotopes, atoms of an element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Many naturally occurring elements exist as a mixture of isotopes. For example, carbon has three ...
... the number of protons and neutrons. Calculating an element’s mass number is complicated by the existence of isotopes, atoms of an element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Many naturally occurring elements exist as a mixture of isotopes. For example, carbon has three ...
to Dowload Part 1: PowerPoint Presentation.
... Contain the functional group -SH Named by adding thiol to the name of the longest carbon chain Number the -SH group in longer chains CH3-SH ...
... Contain the functional group -SH Named by adding thiol to the name of the longest carbon chain Number the -SH group in longer chains CH3-SH ...
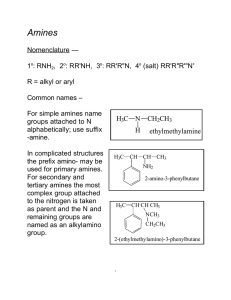
Chapter 24. Amines
... Most amines that have 3 different substituents on N are not resolved because the molecules interconvert by pyramidal inversion ...
... Most amines that have 3 different substituents on N are not resolved because the molecules interconvert by pyramidal inversion ...
Heterocyclic Chemistry
... who proposed similar methods for the systematic naming of heterocyclic compounds in 1887 and 1888 respectively. According to this system three to ten-membered rings are named by combining the appropriate prefix (or prefixes) that denotes the type and position of the heteroatom present in the ring ...
... who proposed similar methods for the systematic naming of heterocyclic compounds in 1887 and 1888 respectively. According to this system three to ten-membered rings are named by combining the appropriate prefix (or prefixes) that denotes the type and position of the heteroatom present in the ring ...
CH 18 blackboard
... Simple aldehydes are systematically named according to the number of carbon atoms in the longest continuous carbon chain that contains the carbonyl group. The base name is formed by dropping the -e and adding the ending -al. Simple ketones are systematically named according to the longest continuous ...
... Simple aldehydes are systematically named according to the number of carbon atoms in the longest continuous carbon chain that contains the carbonyl group. The base name is formed by dropping the -e and adding the ending -al. Simple ketones are systematically named according to the longest continuous ...
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
... Activating, O-, PDirecting Substituents • Alkyl groups stabilize the sigma complex by induction, donating electron density through the sigma bond. • Substituents with a lone pair of electrons stabilize the sigma complex by resonance. ...
... Activating, O-, PDirecting Substituents • Alkyl groups stabilize the sigma complex by induction, donating electron density through the sigma bond. • Substituents with a lone pair of electrons stabilize the sigma complex by resonance. ...
amine
... • Name the longest chain attached to the nitrogen. • Replace the final –e with –amine. • Number the chain so the carbon bonded to the nitrogen has the lowest possible number. • Number the other substituents on the carbon chain. • An italic “N” is used as a prefix for a substituent on nitrogen. Examp ...
... • Name the longest chain attached to the nitrogen. • Replace the final –e with –amine. • Number the chain so the carbon bonded to the nitrogen has the lowest possible number. • Number the other substituents on the carbon chain. • An italic “N” is used as a prefix for a substituent on nitrogen. Examp ...
Summary of AS-level Paper 2 content - A
... I can distinguish between thermal cracking (takes place at high pressure and high temperature and produces a high percentage of alkenes) and catalytic cracking (takes place at a slight pressure, high temperature and in the presence of a zeolite catalyst and is used mainly to produce motor fuels and ...
... I can distinguish between thermal cracking (takes place at high pressure and high temperature and produces a high percentage of alkenes) and catalytic cracking (takes place at a slight pressure, high temperature and in the presence of a zeolite catalyst and is used mainly to produce motor fuels and ...
rev2
... 3. Understand why aldehydes and ketones have lower bps than alcohols, but about the same solubility in water as alcohols. 4. Know the chemical properties of aldehydes and ketones a. Oxidation with chromic acid, Benedict’s/Fehling’s, or Tollens- aldehydes oxidize to carboxylic acids, ketones cannot b ...
... 3. Understand why aldehydes and ketones have lower bps than alcohols, but about the same solubility in water as alcohols. 4. Know the chemical properties of aldehydes and ketones a. Oxidation with chromic acid, Benedict’s/Fehling’s, or Tollens- aldehydes oxidize to carboxylic acids, ketones cannot b ...