Endangered Species Day
... health of the planet. Each species plays a unique role in the ecosystem and affects all other species around it. Often, one species could not live with out the other. Plants and wildlife also have many economic and medicinal values to humans, and these may be lost with the decline of biodiversity. o ...
... health of the planet. Each species plays a unique role in the ecosystem and affects all other species around it. Often, one species could not live with out the other. Plants and wildlife also have many economic and medicinal values to humans, and these may be lost with the decline of biodiversity. o ...
Biodiversity – Threats
... destruction of habitat. Natural habitats always have some degree of heterogeneity, but increased disturbance due to human causes has created a new problem. Isolation of habitats to fragments of their original size leads to ‘edge effects’, habitat islands, decreased organismal dispersal capability, an ...
... destruction of habitat. Natural habitats always have some degree of heterogeneity, but increased disturbance due to human causes has created a new problem. Isolation of habitats to fragments of their original size leads to ‘edge effects’, habitat islands, decreased organismal dispersal capability, an ...
ICES CM 0:37, Deepwater Fish and Fisheries Can ecological knowledge catch
... fished commercially since 1965, with catches climbing quickly to a peak of over 80,OOO;tiyr in 1971, but then falling off almost as quickly to reach the current modest level of about 6000 t/yr by 1980. Initially, only the Soviet Union took any interest in this fish, but the number of nations fishing ...
... fished commercially since 1965, with catches climbing quickly to a peak of over 80,OOO;tiyr in 1971, but then falling off almost as quickly to reach the current modest level of about 6000 t/yr by 1980. Initially, only the Soviet Union took any interest in this fish, but the number of nations fishing ...
Adaptations, Biodiversity, Population CQs
... Which of these pairs of terms is included as causes of biodiversity loss? a. Pollution and Indicator species b. Harvesting and Population decline c. Habitat alteration and Invasive species d. Overexploitation and Pollination e. Indicator species and Population growth ...
... Which of these pairs of terms is included as causes of biodiversity loss? a. Pollution and Indicator species b. Harvesting and Population decline c. Habitat alteration and Invasive species d. Overexploitation and Pollination e. Indicator species and Population growth ...
Chapter 11 power point
... check if populations are within appropriate levels. With suitable habitat and protection, most wild animals can maintain a sizeable population. High reproductive capacities and heavy protection have caused very large populations to arise from once-rare animals. ...
... check if populations are within appropriate levels. With suitable habitat and protection, most wild animals can maintain a sizeable population. High reproductive capacities and heavy protection have caused very large populations to arise from once-rare animals. ...
Lake Victoria - University of Liverpool
... Barbus sp.), Bagrus sp. , Schilbe sp. , Clarias sp. all catfish and some Haplochromis spp. Since 1985 food fish catches have fallen and remained low Combined pressure exerted by these species on stocks in lakes not considered significant as they are only part time predators and no problems in ...
... Barbus sp.), Bagrus sp. , Schilbe sp. , Clarias sp. all catfish and some Haplochromis spp. Since 1985 food fish catches have fallen and remained low Combined pressure exerted by these species on stocks in lakes not considered significant as they are only part time predators and no problems in ...
Ecosystems and Biodiversity
... • Many commercially important fish shoal and this behavior makes them more vulnerable to fishing pressure and capture in large numbers • In many commercial species the largest shoaling occurs during migrations, when smaller shoals join together. • Some North Atlantic herring shoals have been measure ...
... • Many commercially important fish shoal and this behavior makes them more vulnerable to fishing pressure and capture in large numbers • In many commercial species the largest shoaling occurs during migrations, when smaller shoals join together. • Some North Atlantic herring shoals have been measure ...
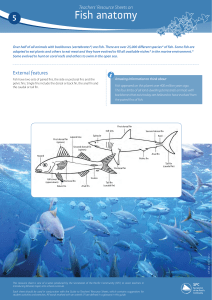
05-Teachers` Resource sheets on fish anatomy
... Many fish produce sounds and this is often reflected in their common English names — drums, croakers and grunts. And, fish have one sense that we don’t have. They have a lateral line which runs down each of its sides. The lateral line is believed to be capable of detecting low-frequency vibrations i ...
... Many fish produce sounds and this is often reflected in their common English names — drums, croakers and grunts. And, fish have one sense that we don’t have. They have a lateral line which runs down each of its sides. The lateral line is believed to be capable of detecting low-frequency vibrations i ...
Carrying Capacity and Limiting Factors
... ecosystem. – Ex: Bobcats will hunt and eat rabbits. The size of a rabbit population is limited by the number of bobcats that are hunting and eating the rabbits. ...
... ecosystem. – Ex: Bobcats will hunt and eat rabbits. The size of a rabbit population is limited by the number of bobcats that are hunting and eating the rabbits. ...
VIMS to Begin New Ecosystem Management Study
... and prey species. “The delineation and understanding of such interactions are critical to the sustainable management of the lower Bay ecosystem,” said Dr. John Graves, Chair Department of Fisheries Science, VIMS. “The award from the Virginia Environmental Endowment provides us with a unique opportun ...
... and prey species. “The delineation and understanding of such interactions are critical to the sustainable management of the lower Bay ecosystem,” said Dr. John Graves, Chair Department of Fisheries Science, VIMS. “The award from the Virginia Environmental Endowment provides us with a unique opportun ...
Ecology Review
... B) In some mutualistic relationships, two species are unable to survive without each other. C) In one type of mutualism, one species defends another species against attacks in return for food and shelter. D) One species protects another species from predators by camouflage. The host species is not h ...
... B) In some mutualistic relationships, two species are unable to survive without each other. C) In one type of mutualism, one species defends another species against attacks in return for food and shelter. D) One species protects another species from predators by camouflage. The host species is not h ...
File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... -they have been ______________ for long times and the result is lots of endemic species ...
... -they have been ______________ for long times and the result is lots of endemic species ...
Biodiversity of World Biomes
... • For at least 3.8 billion years, a complex web of life has been evolving here on Earth. • Biodiversity ( short for biological diversity) - is the variety of all living organisms and their interactions in an ecosystem. Scientists often speak of three levels of diversity – ...
... • For at least 3.8 billion years, a complex web of life has been evolving here on Earth. • Biodiversity ( short for biological diversity) - is the variety of all living organisms and their interactions in an ecosystem. Scientists often speak of three levels of diversity – ...
Mechanisms of Growth Regulation
... in isolation. They engage in interspeci c competition: that is, they share the environment with other species, competing with them for the same resources. These factors are also important to understanding how a speci c population will grow. Nature regulates population growth in a variety of ways. Th ...
... in isolation. They engage in interspeci c competition: that is, they share the environment with other species, competing with them for the same resources. These factors are also important to understanding how a speci c population will grow. Nature regulates population growth in a variety of ways. Th ...
A Closer Look at Whooping Cranes
... the point that it is nearly eliminated from the Earth. Some reasons that species become threatened or endangered are: 1. Loss of habitat – When an organism loses its home, it can be difficult to find food, shelter, and protection. Many populations decline because their habitats are modified or destr ...
... the point that it is nearly eliminated from the Earth. Some reasons that species become threatened or endangered are: 1. Loss of habitat – When an organism loses its home, it can be difficult to find food, shelter, and protection. Many populations decline because their habitats are modified or destr ...
The Needs of Living Things
... consumers are in the food web/chain? Can you tell if the ecosystem is healthy? Food chains and webs lack number data to go between the different levels ...
... consumers are in the food web/chain? Can you tell if the ecosystem is healthy? Food chains and webs lack number data to go between the different levels ...
Bornean Orangutans are now officially Critically
... Two major strategies exist to save the orangutans from extinction: protecting the individuals or protecting their forest habitat. These strategies are both complex, but everyone can contribute to make a difference. Hunting is the major reason for orangutan decline in Borneo. This threat must be stop ...
... Two major strategies exist to save the orangutans from extinction: protecting the individuals or protecting their forest habitat. These strategies are both complex, but everyone can contribute to make a difference. Hunting is the major reason for orangutan decline in Borneo. This threat must be stop ...
Natural Resources
... energy can neither be created nor destroyed, only transformed. The second law of thermodynamics: energy transformations – in every energy conversion some useful energy is converted to useless (heat) energy (entropy) ...
... energy can neither be created nor destroyed, only transformed. The second law of thermodynamics: energy transformations – in every energy conversion some useful energy is converted to useless (heat) energy (entropy) ...
Full PDF Report... - The Rewilding Institute
... world into one exponentially expanding agro-techno-economy. In the First Wave, extinctions were caused mostly by hunting, and perhaps by firesetting and introductions of dogs and diseases into areas that had not previously experienced them. The victims were primarily large mammals, birds, and reptil ...
... world into one exponentially expanding agro-techno-economy. In the First Wave, extinctions were caused mostly by hunting, and perhaps by firesetting and introductions of dogs and diseases into areas that had not previously experienced them. The victims were primarily large mammals, birds, and reptil ...
Ecology notes
... The types of disturbances and their frequency and severity vary from community to community. Small-scale disturbance often have positive effects. For example, when a large tree falls in a windstorm, it disturbs the immediate surroundings, but it also creates new habitats. For instance, more light ma ...
... The types of disturbances and their frequency and severity vary from community to community. Small-scale disturbance often have positive effects. For example, when a large tree falls in a windstorm, it disturbs the immediate surroundings, but it also creates new habitats. For instance, more light ma ...
Small River Communities - North Carolina Wildlife Resources
... Predicted Effects to Wildlife Species Tables 2 through 7 at the end of this report identify the species of conservation concern and priority species that use habitats in this ecosystem. Piedmont riverine aquatic communities provide a number of important habitats, life cycle, or prey components to a ...
... Predicted Effects to Wildlife Species Tables 2 through 7 at the end of this report identify the species of conservation concern and priority species that use habitats in this ecosystem. Piedmont riverine aquatic communities provide a number of important habitats, life cycle, or prey components to a ...
Does invasion history matter to the establishment success
... research would not be possible without a CARSCA, as funds are required to purchase chemicals, water filters for a reverse osmosis system in the greenhouse, and other critical supplies. This work will provide research opportunities for one graduate and several undergraduate students. The results will ...
... research would not be possible without a CARSCA, as funds are required to purchase chemicals, water filters for a reverse osmosis system in the greenhouse, and other critical supplies. This work will provide research opportunities for one graduate and several undergraduate students. The results will ...
Document
... Drive Each Other’s Evolution • Intense natural selection pressures between predator and prey populations • Coevolution • Interact over a long period of time • Bats and moths: echolocation of bats and sensitive hearing of moths ...
... Drive Each Other’s Evolution • Intense natural selection pressures between predator and prey populations • Coevolution • Interact over a long period of time • Bats and moths: echolocation of bats and sensitive hearing of moths ...
Overexploitation

Overexploitation, also called overharvesting, refers to harvesting a renewable resource to the point of diminishing returns. Sustained overexploitation can lead to the destruction of the resource. The term applies to natural resources such as: wild medicinal plants, grazing pastures, game animals, fish stocks, forests, and water aquifers.In ecology, overexploitation describes one of the five main activities threatening global biodiversity. Ecologists use the term to describe populations that are harvested at a rate that is unsustainable, given their natural rates of mortality and capacities for reproduction. This can result in extinction at the population level and even extinction of whole species. In conservation biology the term is usually used in the context of human economic activity that involves the taking of biological resources, or organisms, in larger numbers than their populations can withstand. The term is also used and defined somewhat differently in fisheries, hydrology and natural resource management.Overexploitation can lead to resource destruction, including extinctions. However it is also possible for overexploitation to be sustainable, as discussed below in the section on fisheries. In the context of fishing, the term overfishing can be used instead of overexploitation, as can overgrazing in stock management, overlogging in forest management, overdrafting in aquifer management, and endangered species in species monitoring. Overexploitation is not an activity limited to humans. Introduced predators and herbivores, for example, can overexploit native flora and fauna.