Chapter 10
... • Simplest algorithm for packet transmission. – transmission occurs in the same order as messages are received – Until recently, FIFO queuing was the default for all router interfaces ...
... • Simplest algorithm for packet transmission. – transmission occurs in the same order as messages are received – Until recently, FIFO queuing was the default for all router interfaces ...
Video Over Wireless
... strategy independently for each of the objects. • For instance, if we consider a video-conference system with “speaker” and “background” as different objects. •The only interest for end-users is to obtain the best possible quality for the most relevant object (i.e. “the speaker”). We can then, alloc ...
... strategy independently for each of the objects. • For instance, if we consider a video-conference system with “speaker” and “background” as different objects. •The only interest for end-users is to obtain the best possible quality for the most relevant object (i.e. “the speaker”). We can then, alloc ...
IP Packet Switching COS 461: Computer Networks Spring 2008 (MW 1:30‐2:50 in COS 105) Mike Freedman
... – StaTsTcal mulTplexing through packet switching – … though packet headers and retransmissions wasteful ...
... – StaTsTcal mulTplexing through packet switching – … though packet headers and retransmissions wasteful ...
ADVANCED COMPUTER NETWORKS - Sample Paper 1
... The connection-hijacking attack is shown in Figure. A, B and C are IPv6 addresses. The Internet nodes A and B are honest and communicating with each other. An attacker at the address C sends a false binding update to B, claiming to be a mobile with the home address A. If B, acting in the role of a c ...
... The connection-hijacking attack is shown in Figure. A, B and C are IPv6 addresses. The Internet nodes A and B are honest and communicating with each other. An attacker at the address C sends a false binding update to B, claiming to be a mobile with the home address A. If B, acting in the role of a c ...
Dia 1
... Modeling process Structural aspect Behavioral aspect Non-functional aspect Conclusion Discussion ...
... Modeling process Structural aspect Behavioral aspect Non-functional aspect Conclusion Discussion ...
ppt
... • Packet switching – Divide messages into a sequence of packets – Headers with source and destination address ...
... • Packet switching – Divide messages into a sequence of packets – Headers with source and destination address ...
BRHEALTH0511
... Our position among the top-ranked semiconductor manufacturers, combined with strong cooperation with global healthcare leaders, enables us to develop optimized process technology and to design semiconductor devices with best-fit characteristics. We are addressing the healthcare market with a broad p ...
... Our position among the top-ranked semiconductor manufacturers, combined with strong cooperation with global healthcare leaders, enables us to develop optimized process technology and to design semiconductor devices with best-fit characteristics. We are addressing the healthcare market with a broad p ...
Base-Band Digital Data Transmission
... minimum attenuation and distortion as it is transmitted through a medium. ...
... minimum attenuation and distortion as it is transmitted through a medium. ...
A method for IP multicast performance monitoring
... • … count the number of packets of each “block” to measure packet loss • … or take the timestamp of a particular packet within a block (f.i. the first packet of each block) to measure delay / jitter MBONED WG ...
... • … count the number of packets of each “block” to measure packet loss • … or take the timestamp of a particular packet within a block (f.i. the first packet of each block) to measure delay / jitter MBONED WG ...
System Integration Overview in PDF Format
... There will always be some time-lag between when data is updated in the first system by a user or transaction processing, and when that same data is updated into the second system. This time-lag, called degree of synchronization, can be substantial but acceptable, or with greater development focus ca ...
... There will always be some time-lag between when data is updated in the first system by a user or transaction processing, and when that same data is updated into the second system. This time-lag, called degree of synchronization, can be substantial but acceptable, or with greater development focus ca ...
ppt - School of Computer Science
... » Standards are defined first by a standards committee » Risk of defining standards that are untested or unnecessary » Standard may be available before there is serious use of the technology ...
... » Standards are defined first by a standards committee » Risk of defining standards that are untested or unnecessary » Standard may be available before there is serious use of the technology ...
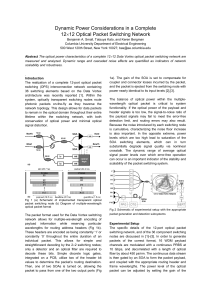
Dynamic Power Considerations in a Complete 12×12 Optical Packet
... A series of experiments to investigate the optical power levels within the 12-port switching network are performed. First, the injected packets’ optical power spectrum was compared to that of the ejected packets, in order to confirm the almost perfect transparency of the implemented OPS architecture ...
... A series of experiments to investigate the optical power levels within the 12-port switching network are performed. First, the injected packets’ optical power spectrum was compared to that of the ejected packets, in order to confirm the almost perfect transparency of the implemented OPS architecture ...
A(t)
... Link length, L, is the length of a link in meters. Data rate, R, is the rate at which bits can be sent, in bits/second, or b/s.1 Propagation delay, PROP, is the time for one bit to travel along a link of length, L. PROP = L/c. Transmission time, TRANSP, is the time to transmit a packet of length P. ...
... Link length, L, is the length of a link in meters. Data rate, R, is the rate at which bits can be sent, in bits/second, or b/s.1 Propagation delay, PROP, is the time for one bit to travel along a link of length, L. PROP = L/c. Transmission time, TRANSP, is the time to transmit a packet of length P. ...
MST200 OuTdOOR WIReleSS MeSH AcceSS
... or fiber. Running the Aruba MeshOS operating system, the MST200 features a single 5-GHz 2x2 MIMO radio with dual spatial streams and patented Adaptive Wireless Routing™ (AWR™) technology. Together, these features offer unparalleled speed, reliability, and low latency for voice, video and other real- ...
... or fiber. Running the Aruba MeshOS operating system, the MST200 features a single 5-GHz 2x2 MIMO radio with dual spatial streams and patented Adaptive Wireless Routing™ (AWR™) technology. Together, these features offer unparalleled speed, reliability, and low latency for voice, video and other real- ...
week8-1
... 7. P-S checks this packet and find destination is “C” 8. NIC-3 modulates the packet send out 9. After a while, NIC-C will receive the m-carrier 10. NIC-C demodulates the packet and put it into its cache 11. NIC-C does two checkings; If failed, the packet will be discarded a) Length checking: the p ...
... 7. P-S checks this packet and find destination is “C” 8. NIC-3 modulates the packet send out 9. After a while, NIC-C will receive the m-carrier 10. NIC-C demodulates the packet and put it into its cache 11. NIC-C does two checkings; If failed, the packet will be discarded a) Length checking: the p ...
Serial digital interface
.jpg?width=300)
Serial digital interface (SDI) is a family of digital video interfaces first standardized by SMPTE (The Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers) in 1989. For example, ITU-R BT.656 and SMPTE 259M define digital video interfaces used for broadcast-grade video. A related standard, known as high-definition serial digital interface (HD-SDI), is standardized in SMPTE 292M; this provides a nominal data rate of 1.485 Gbit/s.Additional SDI standards have been introduced to support increasing video resolutions (HD, UHD and beyond), frame rates, stereoscopic (3D) video, and color depth. Dual link HD-SDI consists of a pair of SMPTE 292M links, standardized by SMPTE 372M in 1998; this provides a nominal 2.970 Gbit/s interface used in applications (such as digital cinema or HDTV 1080P) that require greater fidelity and resolution than standard HDTV can provide. 3G-SDI (standardized in SMPTE 424M) consists of a single 2.970 Gbit/s serial link that allows replacing dual link HD-SDI. As of August 2014, 6G-SDI and 12G-SDI products are already in the market, although their corresponding standards are still in proposal phase.These standards are used for transmission of uncompressed, unencrypted digital video signals (optionally including embedded audio and time code) within television facilities; they can also be used for packetized data. Coaxial variants of the specification range in length but are typically less than 300 meters. Fiber optic variants of the specification such as 297M allow for long-distance transmission limited only by maximum fiber length or repeaters. SDI and HD-SDI are usually available only in professional video equipment because various licensing agreements restrict the use of unencrypted digital interfaces, such as SDI, prohibiting their use in consumer equipment. Several professional video and HD-video capable DSLR cameras and all uncompressed video capable consumer cameras use the HDMI interface, often called Clean HDMI. There are various mod kits for existing DVD players and other devices, which allow a user to add a serial digital interface to these devices.