An Information-Centric Architecture for Data Center Networks
... achieve. This is because all data requests for one file converge to the same path, even when there are multiple information publishers that can provide the requested data simultaneously. For example, if a producer announces “/movies/diehard" and another one announces “/movies," all data requests for ...
... achieve. This is because all data requests for one file converge to the same path, even when there are multiple information publishers that can provide the requested data simultaneously. For example, if a producer announces “/movies/diehard" and another one announces “/movies," all data requests for ...
3rd Edition: Chapter 2
... D(b) = min( D(b), D(c) + c(c,b) ) 13 /* new cost to b is either old cost to b or known 14 shortest path cost to c plus cost from c to b */ 15 until all nodes in N' Chapter 4, slide: 47 ...
... D(b) = min( D(b), D(c) + c(c,b) ) 13 /* new cost to b is either old cost to b or known 14 shortest path cost to c plus cost from c to b */ 15 until all nodes in N' Chapter 4, slide: 47 ...
Lecture 3 Slides
... • In order to ensure that the three conditions do really prevent looping, a node has to maintain the latest source tree transmitted to its neighbors. • If one of the conditions is satisfied, the complete source tree is to be transmitted. (sudden thought – what is meant by broadcast in this environme ...
... • In order to ensure that the three conditions do really prevent looping, a node has to maintain the latest source tree transmitted to its neighbors. • If one of the conditions is satisfied, the complete source tree is to be transmitted. (sudden thought – what is meant by broadcast in this environme ...
tom
... Scalable & efficient: small amount of probing traffic Accurate: capture congestion/failures Incrementally deployable Easy to use ...
... Scalable & efficient: small amount of probing traffic Accurate: capture congestion/failures Incrementally deployable Easy to use ...
Document
... Border Router) Topology size is changed by changing Number of areas and Number of routers per area ...
... Border Router) Topology size is changed by changing Number of areas and Number of routers per area ...
M051055
... associated with link-state protocols. OSPF's best traits, such as partial updates and neighbor discovery, are similarly put to use by EIGRP. As we mentioned before, IGRP is a distance vector Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP). Distance vector routing protocols mathematically compare routes using some m ...
... associated with link-state protocols. OSPF's best traits, such as partial updates and neighbor discovery, are similarly put to use by EIGRP. As we mentioned before, IGRP is a distance vector Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP). Distance vector routing protocols mathematically compare routes using some m ...
StrobeLight: Lightweight Availability Mapping and Anomaly Detection Brian Noble
... – Fast enough for near real-time analysis – Archive results for use by other services ...
... – Fast enough for near real-time analysis – Archive results for use by other services ...
Desired Claim Coverage Assessment Authoring
... Compare and contrast the basic characteristics of the different distance- metrics used, types of updates, vector routing protocols in use today. algorithms used. IGRP is only used as a historical reference and classification only. Operation of IGRP is not tested. Describe the network discovery proce ...
... Compare and contrast the basic characteristics of the different distance- metrics used, types of updates, vector routing protocols in use today. algorithms used. IGRP is only used as a historical reference and classification only. Operation of IGRP is not tested. Describe the network discovery proce ...
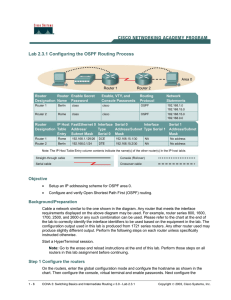
Lab 2.3.1 Configuring the OSPF Routing Process Objective
... In order to find out exactly how the router is configured, look at the interfaces. This will identify what type and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all of the combinations of configurations for each router class. What is provided are the identifiers for the po ...
... In order to find out exactly how the router is configured, look at the interfaces. This will identify what type and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all of the combinations of configurations for each router class. What is provided are the identifiers for the po ...
performance analysis of wdm optical shuffle – exchange
... implementation [3].We show in the later part of the section that our algorithm is better than BFS algorithm in terms of cost function. Given such a directed graph G = (V, E) and a vertex v in V (G), for the netwoks considered, we wish to visit all vertices in G that are reachable from v (ie all vert ...
... implementation [3].We show in the later part of the section that our algorithm is better than BFS algorithm in terms of cost function. Given such a directed graph G = (V, E) and a vertex v in V (G), for the netwoks considered, we wish to visit all vertices in G that are reachable from v (ie all vert ...
Managing Ad Hoc Networks of Smartphones
... advantage is that routes are available at any time and the disadvantage is the high routing overhead. On-demand routing protocols, such as AODV and DSR [11], discover routes on an “on demand” basis. Route discovery messages are only flooded in the network when there is a need to reach an unknown des ...
... advantage is that routes are available at any time and the disadvantage is the high routing overhead. On-demand routing protocols, such as AODV and DSR [11], discover routes on an “on demand” basis. Route discovery messages are only flooded in the network when there is a need to reach an unknown des ...
LD3618981905
... the path will know the route to the destination in the event that the source selects this route for data packet transmission. The node then unicast the RREP to its next hop towards the source node. This hop-by-hop forwarding continues until the RREP reaches the source. Once the source receives a RRE ...
... the path will know the route to the destination in the event that the source selects this route for data packet transmission. The node then unicast the RREP to its next hop towards the source node. This hop-by-hop forwarding continues until the RREP reaches the source. Once the source receives a RRE ...
IP Multicast Tutorial
... • Each LSR makes independent decision on when to generate labels and communicate them to upstream peers • Communicate label-FEC binding to peers once next-hop has been recognized • LSP is formed as incoming and outgoing labels are spliced together ...
... • Each LSR makes independent decision on when to generate labels and communicate them to upstream peers • Communicate label-FEC binding to peers once next-hop has been recognized • LSP is formed as incoming and outgoing labels are spliced together ...
Information Networks
... “P2P is a class of applications that take advantage of resources – storage, cycles, content, human presence – available at the edges of the Internet. Because accessing these decentralized resources means operating in an environment of unstable and unpredictable IP addresses P2P nodes must operate ...
... “P2P is a class of applications that take advantage of resources – storage, cycles, content, human presence – available at the edges of the Internet. Because accessing these decentralized resources means operating in an environment of unstable and unpredictable IP addresses P2P nodes must operate ...
Path Probing Relay Routing for Achieving High End-to
... reliability or efficiency of routing by relaying packets for each other. An overlay network can provide end hosts with a means to have some control of packet routing over the Internet. The overlay routes can be specific to an application, or even to a TCP/UDP flow. This implies that a node participa ...
... reliability or efficiency of routing by relaying packets for each other. An overlay network can provide end hosts with a means to have some control of packet routing over the Internet. The overlay routes can be specific to an application, or even to a TCP/UDP flow. This implies that a node participa ...
2017_Gopi_Deepthi_Thesis
... rigid and intricate system thus narrowing the adaptability of networks to the ever changing Internet, the emergence of Software Defined Networking (SDN) provides a solution for this problem. Due to the handiness of a centralized controller, SDN has provided an effective method in terms of routing co ...
... rigid and intricate system thus narrowing the adaptability of networks to the ever changing Internet, the emergence of Software Defined Networking (SDN) provides a solution for this problem. Due to the handiness of a centralized controller, SDN has provided an effective method in terms of routing co ...
CloudWatcher: Network Security Monitoring Using OpenFlow in
... 3) How to Control Network Flows: If C LOUD WATCHER finds network packets meeting a flow condition specified by a policy, then it will route these packets to satisfy security requirements. When C LOUD WATCHER routes network packets, it should consider the following two conditions: (i) network packets ...
... 3) How to Control Network Flows: If C LOUD WATCHER finds network packets meeting a flow condition specified by a policy, then it will route these packets to satisfy security requirements. When C LOUD WATCHER routes network packets, it should consider the following two conditions: (i) network packets ...
njit-etd2005-146 - New Jersey Institute of Technology
... The scalability problem of routing algorithms in Mobile Ad-hoc networks (MANET) has conventionally been addressed by introducing hierarchical architectures, clusters, and neighborhood zones. In all of these approaches, some nodes are assigned different routing related roles than others. Examples inc ...
... The scalability problem of routing algorithms in Mobile Ad-hoc networks (MANET) has conventionally been addressed by introducing hierarchical architectures, clusters, and neighborhood zones. In all of these approaches, some nodes are assigned different routing related roles than others. Examples inc ...
MPLS
... • Routers must be label-switched routers (LSRs) and each LSR must maintain a valid mapping from the label of an incoming packet. • The router uses the label to identify the LSP. • This label looks up the LSP in its own forwarding table to determine the best path over which to forward the packet and ...
... • Routers must be label-switched routers (LSRs) and each LSR must maintain a valid mapping from the label of an incoming packet. • The router uses the label to identify the LSP. • This label looks up the LSP in its own forwarding table to determine the best path over which to forward the packet and ...
Opportunistic Routing in Multi
... hardware [2] with minor MAC firmware modifications. Figure 3 shows the two modified MAC frame formats required by ExOR, in the context of the Physical Layer Convergence Protocol (PLCP) frame. The frame control field, which follows the 802.11 MAC specification, is set to either an otherwise reserved ...
... hardware [2] with minor MAC firmware modifications. Figure 3 shows the two modified MAC frame formats required by ExOR, in the context of the Physical Layer Convergence Protocol (PLCP) frame. The frame control field, which follows the 802.11 MAC specification, is set to either an otherwise reserved ...
Decentralized Location Services
... how does node A send message to B? IP addresses are too static, need app-level location independent names ...
... how does node A send message to B? IP addresses are too static, need app-level location independent names ...