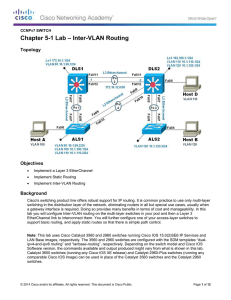
Lab 5-1 Inter-VLAN Routing
... Cisco's switching product line offers robust support for IP routing. It is common practice to use only multi-layer switching in the distribution layer of the network, eliminating routers in all but special use cases, usually when a gateway interface is required. Doing so provides many benefits in te ...
... Cisco's switching product line offers robust support for IP routing. It is common practice to use only multi-layer switching in the distribution layer of the network, eliminating routers in all but special use cases, usually when a gateway interface is required. Doing so provides many benefits in te ...
Chapter 4 - ECE Users Pages
... range of addresses not needed from ISP: just one IP address for all devices can change addresses of devices in local network without notifying outside world can change ISP without changing addresses of devices in local network ...
... range of addresses not needed from ISP: just one IP address for all devices can change addresses of devices in local network without notifying outside world can change ISP without changing addresses of devices in local network ...
18 - UTRGV Faculty Web
... outgoing path. If it is destined for a local computer, the router sends to that computer using its MAC address. Otherwise, it is forwarded to one of the output ports on the router that leads to the destination. – To do this the router examines the destination address and extracts the network portion ...
... outgoing path. If it is destined for a local computer, the router sends to that computer using its MAC address. Otherwise, it is forwarded to one of the output ports on the router that leads to the destination. – To do this the router examines the destination address and extracts the network portion ...
show ip route eigrp - Armstrong State University
... D 192.168.30.0/24 [90/2172] via 192.168.20.2,00:04:36, Serial0/0 C 192.168.10.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 D 192.168.40.0/24 [90/2681] via 192.168.20.2,00:04:36, Serial0/0 C 192.168.20.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/0 D 192.168.50.0/24 [90/2707] via 192.168.20.2,00:04:35, Serial0 ...
... D 192.168.30.0/24 [90/2172] via 192.168.20.2,00:04:36, Serial0/0 C 192.168.10.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 D 192.168.40.0/24 [90/2681] via 192.168.20.2,00:04:36, Serial0/0 C 192.168.20.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/0 D 192.168.50.0/24 [90/2707] via 192.168.20.2,00:04:35, Serial0 ...
Chapter 7: EIGRP
... D 192.168.30.0/24 [90/2172] via 192.168.20.2,00:04:36, Serial0/0 C 192.168.10.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 D 192.168.40.0/24 [90/2681] via 192.168.20.2,00:04:36, Serial0/0 C 192.168.20.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/0 D 192.168.50.0/24 [90/2707] via 192.168.20.2,00:04:35, Serial0 ...
... D 192.168.30.0/24 [90/2172] via 192.168.20.2,00:04:36, Serial0/0 C 192.168.10.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 D 192.168.40.0/24 [90/2681] via 192.168.20.2,00:04:36, Serial0/0 C 192.168.20.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/0 D 192.168.50.0/24 [90/2707] via 192.168.20.2,00:04:35, Serial0 ...
Slide 1
... The routing table, which accepts information from routing process and replies to requests from the forwarding process. The forwarding process, which requests information from the routing table for packet forwarding. ENTS689L: Packet Processing and Switching Networking Technologies ...
... The routing table, which accepts information from routing process and replies to requests from the forwarding process. The forwarding process, which requests information from the routing table for packet forwarding. ENTS689L: Packet Processing and Switching Networking Technologies ...
Chapter 4: Network Layer
... outgoing datagrams: replace (source IP address, port #) of every outgoing datagram to (NAT IP address, new port #) . . . remote clients/servers will respond using (NAT IP address, ...
... outgoing datagrams: replace (source IP address, port #) of every outgoing datagram to (NAT IP address, new port #) . . . remote clients/servers will respond using (NAT IP address, ...
c 2009 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However
... connectivity context in order to make routing decisions. Messages are passed from one node to a node with a higher ‘delivery metric’. The messages for unknown destinations are forwarded to the ‘most mobile’ node available. Spyropoulos et al. [48] use a combination of random walk and utilitybased for ...
... connectivity context in order to make routing decisions. Messages are passed from one node to a node with a higher ‘delivery metric’. The messages for unknown destinations are forwarded to the ‘most mobile’ node available. Spyropoulos et al. [48] use a combination of random walk and utilitybased for ...
Chapter 4 slides
... information? Global: all routers have complete topology, link cost info “link state” algorithms Decentralized: router knows physicallyconnected neighbors, link costs to neighbors iterative process of computation, exchange of info with neighbors “distance vector” algorithms ...
... information? Global: all routers have complete topology, link cost info “link state” algorithms Decentralized: router knows physicallyconnected neighbors, link costs to neighbors iterative process of computation, exchange of info with neighbors “distance vector” algorithms ...
Planning Routing Implementations with OSPF as Scalable Routing
... Adjacencies are built by OSPF routers using the Hello protocol. LSUs are sent over these logical adjacencies, in order to exchange database information between adjacent OSPF routers. Dijkstra’s SPF algorithm is used to calculate best paths for all destinations. SPF is run against the LSDB, and t ...
... Adjacencies are built by OSPF routers using the Hello protocol. LSUs are sent over these logical adjacencies, in order to exchange database information between adjacent OSPF routers. Dijkstra’s SPF algorithm is used to calculate best paths for all destinations. SPF is run against the LSDB, and t ...
Chapter4_revised
... range of addresses not needed from ISP: just one IP address for all devices can change addresses of devices in local network without notifying outside world can change ISP without changing addresses of devices in local network ...
... range of addresses not needed from ISP: just one IP address for all devices can change addresses of devices in local network without notifying outside world can change ISP without changing addresses of devices in local network ...
3rd Edition: Chapter 4
... same subnet part of IP address can physically reach each other without intervening router ...
... same subnet part of IP address can physically reach each other without intervening router ...
$doc.title
... – S-BGP with public key infrastructure, registries, crypto? – Who should be in charge of running PKI and registries? – Worry about data-plane attacks or just control plane? ...
... – S-BGP with public key infrastructure, registries, crypto? – Who should be in charge of running PKI and registries? – Worry about data-plane attacks or just control plane? ...
Tapestry: A Resilient Global-scale Overlay for Service - IC
... live node that has responsibility for the destination key. They can also support higher level interfaces such as a distributed hash table (DHT) or a decentralized object location and routing (DOLR) layer [3]. These systems scale well, and guarantee that queries find existing objects under non-failur ...
... live node that has responsibility for the destination key. They can also support higher level interfaces such as a distributed hash table (DHT) or a decentralized object location and routing (DOLR) layer [3]. These systems scale well, and guarantee that queries find existing objects under non-failur ...
ppt
... Interdomain Routing • AS-level topology –Nodes are Autonomous Systems (ASes) –Edges are links and business relationships ...
... Interdomain Routing • AS-level topology –Nodes are Autonomous Systems (ASes) –Edges are links and business relationships ...
Multicast Routing Algos
... Issues in Multicast Routing • Information stored : We want to store as less state as possible in the hosts. • Messages Exchanged : Because the networks are bandwidth constrained, we would like as less exchange of state as possible between the nodes. • Active Adaptability : We would like the nodes t ...
... Issues in Multicast Routing • Information stored : We want to store as less state as possible in the hosts. • Messages Exchanged : Because the networks are bandwidth constrained, we would like as less exchange of state as possible between the nodes. • Active Adaptability : We would like the nodes t ...
Part I: Introduction
... all routers have complete topology, link cost info “link state” algorithms Decentralized: router knows physicallyconnected neighbors, link costs to neighbors iterative process of computation, exchange of info with neighbors “distance vector” algorithms ...
... all routers have complete topology, link cost info “link state” algorithms Decentralized: router knows physicallyconnected neighbors, link costs to neighbors iterative process of computation, exchange of info with neighbors “distance vector” algorithms ...
The Network Layer - Ohio State Computer Science and Engineering
... run routing algorithms/protocol (RIP, OSPF, BGP) forwarding datagrams from incoming to outgoing link ...
... run routing algorithms/protocol (RIP, OSPF, BGP) forwarding datagrams from incoming to outgoing link ...
Routes - Chabot College
... 2. Specify all directly connected networks on which the router will send and receive route updates (also called advertisements). – Network are specified by major network numbers, not subnets. Example - here the network is 10.0.0.0: ...
... 2. Specify all directly connected networks on which the router will send and receive route updates (also called advertisements). – Network are specified by major network numbers, not subnets. Example - here the network is 10.0.0.0: ...
3rd Edition: Chapter 4
... “smart” end systems “dumb” end systems (computers) (telephones) can adapt, perform control, error recovery reservation, congestion simple inside network, feedback complexity at “edge” complexity in network many network types with restricted network types different characteristics u ...
... “smart” end systems “dumb” end systems (computers) (telephones) can adapt, perform control, error recovery reservation, congestion simple inside network, feedback complexity at “edge” complexity in network many network types with restricted network types different characteristics u ...























