Chapter 2 Outline
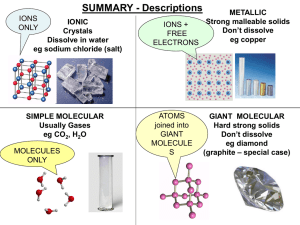
... Chemical bonds A. Electron energy is shared or donated B. Only valence electrons involved in chemical bonds (Octet rule) C. Ionic bonds – electrons are transferred from one atom to another, forming ions. Ions of opposite charge attract forming an ionic bond D. Most ionic compounds are salts E. Coval ...
... Chemical bonds A. Electron energy is shared or donated B. Only valence electrons involved in chemical bonds (Octet rule) C. Ionic bonds – electrons are transferred from one atom to another, forming ions. Ions of opposite charge attract forming an ionic bond D. Most ionic compounds are salts E. Coval ...
dmi cleaning and maintenance
... gallon of water. A long-handled soft bristle brush will make cleaning easier. Follow cleaning operation with a clear water rinse. In areas subject to high humidity levels, mildew can occur. Most fluorocarbon finishes like DynaClad® are inherently mildew-resistant, but dirt and spore deposits can per ...
... gallon of water. A long-handled soft bristle brush will make cleaning easier. Follow cleaning operation with a clear water rinse. In areas subject to high humidity levels, mildew can occur. Most fluorocarbon finishes like DynaClad® are inherently mildew-resistant, but dirt and spore deposits can per ...
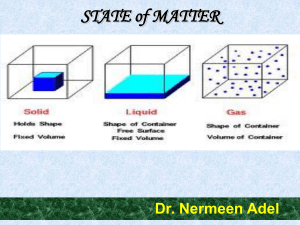
Chemical reaction
... Cohesion • Cohesion: attractive force between particles of the same kind Example: surface tension of water • Polar nature of water causes water molecules to be attracted to each other. • This attraction: hydrogen bond. ...
... Cohesion • Cohesion: attractive force between particles of the same kind Example: surface tension of water • Polar nature of water causes water molecules to be attracted to each other. • This attraction: hydrogen bond. ...
Bonding and Nomenclature
... • VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of atoms about a central atom in a covalent compound, or charged ion, is determined solely by the repulsions between electron pairs present in the valence shell of the central atom. • The number of electron pairs aro ...
... • VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of atoms about a central atom in a covalent compound, or charged ion, is determined solely by the repulsions between electron pairs present in the valence shell of the central atom. • The number of electron pairs aro ...
Basic Chemistry notes
... Atoms are considered stable when their outermost orbital has __________electrons The exception to this rule of eights is Shell 1, which can only hold _________ electrons ...
... Atoms are considered stable when their outermost orbital has __________electrons The exception to this rule of eights is Shell 1, which can only hold _________ electrons ...
Period #2 Notes: Electronic Structure of Atoms
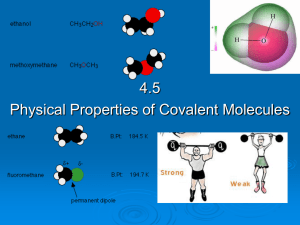
... The three prior types of bonding (ionic, covalent, metallic) are the primary ones in that they form “stable” compounds in which the net charge balances are satisfied. Often, the molecules of the stable compounds formed by primary bonding mechanisms, while having no net charge, will have some polarit ...
... The three prior types of bonding (ionic, covalent, metallic) are the primary ones in that they form “stable” compounds in which the net charge balances are satisfied. Often, the molecules of the stable compounds formed by primary bonding mechanisms, while having no net charge, will have some polarit ...
Adhesion

Adhesion is the tendency of dissimilar particles or surfaces to cling to one another (cohesion refers to the tendency of similar or identical particles/surfaces to cling to one another). The forces that cause adhesion and cohesion can be divided into several types. The intermolecular forces responsible for the function of various kinds of stickers and sticky tape fall into the categories of chemical adhesion, dispersive adhesion, and diffusive adhesion. In addition to the cumulative magnitudes of these intermolecular forces, there are certain emergent mechanical effects that will also be discussed at the end of the article.