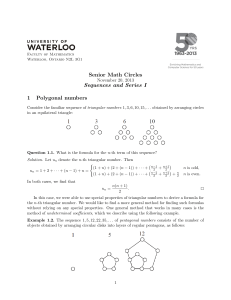
Int Math 1 Formula, Definition, and Symbols Handout
... 19.Not equal to Symbol: _____________________________________________________ 20.Approximately equal to Symbol: __________________________________________ 21.Congruent Symbol: ______________________________________________________ 22.Transformation rules: A. Translation: ____________________________ ...
... 19.Not equal to Symbol: _____________________________________________________ 20.Approximately equal to Symbol: __________________________________________ 21.Congruent Symbol: ______________________________________________________ 22.Transformation rules: A. Translation: ____________________________ ...
2.3. Random variables. Let (Ω, F, P) be a probability space and let (E
... This is called Borel’s normal number theorem: almost every point in (0, 1] is normal, that is, has ‘equal’ proportions of 0’s and 1’s in its binary expansion. We now use a trick involving the Rademacher functions to construct on Ω = (0, 1], not just one random variable, but an infinite sequence of i ...
... This is called Borel’s normal number theorem: almost every point in (0, 1] is normal, that is, has ‘equal’ proportions of 0’s and 1’s in its binary expansion. We now use a trick involving the Rademacher functions to construct on Ω = (0, 1], not just one random variable, but an infinite sequence of i ...
MATH 162: SUMS OF POISSON RANDOM VARIABLES 1. Review
... Abstract. We show that, appropriately scaled, the mean of n independent Poisson variables converges to the standard normal distribution N (0, 1). ...
... Abstract. We show that, appropriately scaled, the mean of n independent Poisson variables converges to the standard normal distribution N (0, 1). ...
PDF
... g(x) = b0 + b1 (x − a) + b2 (x − a)2 + . . . on an interval I (or a circle in C) centered at x = a. If b0 6= 0, then also the f (x) quotient apparently has the derivatives of all orders on I. It is not hard g(x) to justify that if one divides the series of f by the series of g, the obtained series f ...
... g(x) = b0 + b1 (x − a) + b2 (x − a)2 + . . . on an interval I (or a circle in C) centered at x = a. If b0 6= 0, then also the f (x) quotient apparently has the derivatives of all orders on I. It is not hard g(x) to justify that if one divides the series of f by the series of g, the obtained series f ...
Homework 5 – March 1, 2006 Solution prepared by Tobin Fricke
... (Though the normalization is not correct here. Renormalizing we find p(x) = π2 e−x /2 .) This is the result we should have expected from the central limit theorem. 14. Write a computer program that generates n uniform random variables, and calculates ξn as defined above. Then repeat this a large num ...
... (Though the normalization is not correct here. Renormalizing we find p(x) = π2 e−x /2 .) This is the result we should have expected from the central limit theorem. 14. Write a computer program that generates n uniform random variables, and calculates ξn as defined above. Then repeat this a large num ...
6
... 4. For the polynomial p(x) = x3 + 6x2 + 14x + 12 it is known that p(−2) = 0 (a) find all the zeroes using long or synthetic division ...
... 4. For the polynomial p(x) = x3 + 6x2 + 14x + 12 it is known that p(−2) = 0 (a) find all the zeroes using long or synthetic division ...
Explanation-of-a-recursive-formula-1
... preceding terms (e.g., xn = xn - 1 + 2, or Next = Now + 2); and 2.An initial condition that gives the starting point (e.g., x1 = 1 or Start = ...
... preceding terms (e.g., xn = xn - 1 + 2, or Next = Now + 2); and 2.An initial condition that gives the starting point (e.g., x1 = 1 or Start = ...
Stats Review Lecture 5 - Limit Theorems 07.25.12
... Convergence in probability • A sequence of random variables, X1, X2, …, converges in probability to a random variable X if, for every e > 0, ...
... Convergence in probability • A sequence of random variables, X1, X2, …, converges in probability to a random variable X if, for every e > 0, ...
Chapter 3
... how far a set of random numbers are spread out from their mean). Variance is the average of the squared differences from the Mean. Variance is used to produce standard deviation. The variance of a constant is: Var (a) = 0 ...
... how far a set of random numbers are spread out from their mean). Variance is the average of the squared differences from the Mean. Variance is used to produce standard deviation. The variance of a constant is: Var (a) = 0 ...