Click here ------> Lesson Plans
... – Warships covered with iron – Were a big improvement over wooden ships of the past ...
... – Warships covered with iron – Were a big improvement over wooden ships of the past ...
The Battle of Antietam: A Turning Point in the Civil War
... victory. The Northern press puffed it into a great triumph, all the more heartening because of the pessimism that had preceded it. The New York Times proclaimed that the effects of this “GREAT VICTORY” would be “felt in the destinies of the Nation for centuries to come.”[9] The Times was right about ...
... victory. The Northern press puffed it into a great triumph, all the more heartening because of the pessimism that had preceded it. The New York Times proclaimed that the effects of this “GREAT VICTORY” would be “felt in the destinies of the Nation for centuries to come.”[9] The Times was right about ...
Section 1 The Civil War Begins
... reelection, but is assassinated as the war ends. Abraham Lincoln, 16th president of the US ...
... reelection, but is assassinated as the war ends. Abraham Lincoln, 16th president of the US ...
JB APUSH Unit IVB
... states seceded as warned ► Lincoln promised not to interfere with slavery in the South, but explained secession was unconstitutional and prohibited Warned about the use of force to preserve the union and placed the blame toward the secessionists “a more perfect union” ...
... states seceded as warned ► Lincoln promised not to interfere with slavery in the South, but explained secession was unconstitutional and prohibited Warned about the use of force to preserve the union and placed the blame toward the secessionists “a more perfect union” ...
Chapter 20- Girding for War- North and the South
... democracy. But when republicans put empire above liberty, and resorted to political oppression and war rather than suffer any abatement of national power, it was clear that nature at Washington was precisely the same as nature at St. Petersburg. There was not, in fact, a single argument advanced in ...
... democracy. But when republicans put empire above liberty, and resorted to political oppression and war rather than suffer any abatement of national power, it was clear that nature at Washington was precisely the same as nature at St. Petersburg. There was not, in fact, a single argument advanced in ...
The Civil War 1861-1865
... Bull Run • First major battle of Civil War • About 25 miles from Washington, D.C. • “Stonewall” Jackson became famous • Confederate victory ...
... Bull Run • First major battle of Civil War • About 25 miles from Washington, D.C. • “Stonewall” Jackson became famous • Confederate victory ...
Patriotic Essentialism, the Civil War and Postbellum
... Confederate cause. Both cite the memory and philosophy of the founding fathers, both use rhetoric from the Revolution, and both refer to the doctrines of the government they created. Two politicians, fundamentally opposed and at war, evoked the same brand of American patriotism to justify their beli ...
... Confederate cause. Both cite the memory and philosophy of the founding fathers, both use rhetoric from the Revolution, and both refer to the doctrines of the government they created. Two politicians, fundamentally opposed and at war, evoked the same brand of American patriotism to justify their beli ...
Civil War Powerpoint
... Confederate strategy during the war was an Offensive Defense: –Protect Southern territory from “Northern aggression” but attack into Union territory when the opportunity presents itself –Get Britain & France to join their cause because of European dependency on “King Cotton” –Drag out the war as lon ...
... Confederate strategy during the war was an Offensive Defense: –Protect Southern territory from “Northern aggression” but attack into Union territory when the opportunity presents itself –Get Britain & France to join their cause because of European dependency on “King Cotton” –Drag out the war as lon ...
The Civil War - middletonhsapush
... northern interference ranging from the Underground Railroad to John Brown’s raid. They believed that the north wouldn’t care if they seceded. An independent Dixieland could develop its own banking, shipping, and trade with Europe. They reasoned that the 13 original colonies had voluntarily joine ...
... northern interference ranging from the Underground Railroad to John Brown’s raid. They believed that the north wouldn’t care if they seceded. An independent Dixieland could develop its own banking, shipping, and trade with Europe. They reasoned that the 13 original colonies had voluntarily joine ...
LIFEPAC?? - Amazon Web Services
... Lincoln acted calmly after he finally became president in March. He did not believe the southern states could leave the Union simply because they did not like the election results. However, he did not want to start a war. Matters were taken out of his hands on April 12, 1861 when Confederate troops ...
... Lincoln acted calmly after he finally became president in March. He did not believe the southern states could leave the Union simply because they did not like the election results. However, he did not want to start a war. Matters were taken out of his hands on April 12, 1861 when Confederate troops ...
Slide 1
... B. States can secede from the Union, but only with Congressional approval. C. The rights of states are based on the Constitution. D. Under the Constitution, states may not secede from the Union under any circumstances. ...
... B. States can secede from the Union, but only with Congressional approval. C. The rights of states are based on the Constitution. D. Under the Constitution, states may not secede from the Union under any circumstances. ...
Chapter 10/11
... • Robert E. Lee and Jefferson Davis believed that an invasion of the North was the only way to convince the Union to accept the South’s independence, gain help from Great Britain, and help the Peace Democrats win control of Congress in upcoming elections. • Lee and his troops invaded Maryland. • The ...
... • Robert E. Lee and Jefferson Davis believed that an invasion of the North was the only way to convince the Union to accept the South’s independence, gain help from Great Britain, and help the Peace Democrats win control of Congress in upcoming elections. • Lee and his troops invaded Maryland. • The ...
THE CIVIL WAR Hello, I am Professor Doug Cantrell at
... States. The eleven Confederate states were not going to free their slaves because Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, told residents of the Confederacy, another country, to free their slaves. If the Emancipation Proclamation did not free a single slave, why then did Lincoln issue it? Ac ...
... States. The eleven Confederate states were not going to free their slaves because Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, told residents of the Confederacy, another country, to free their slaves. If the Emancipation Proclamation did not free a single slave, why then did Lincoln issue it? Ac ...
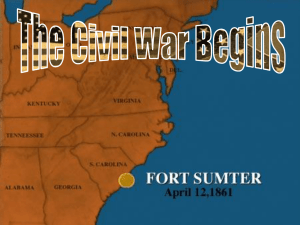
THE CIVIL WAR 1861-1865 The Civil War began over
... Charleston Harbor in South Carolina, was in a dangerous situation: federal property on Confederate soil. Lincoln notified Jefferson Davis that he was sending food and supplies to the Fort. With no arms included, this was not a hostile act. ...
... Charleston Harbor in South Carolina, was in a dangerous situation: federal property on Confederate soil. Lincoln notified Jefferson Davis that he was sending food and supplies to the Fort. With no arms included, this was not a hostile act. ...
Civil War 2013 powerpoint
... –Protect Southern territory from “Northern aggression” but attack into Union territory when the opportunity presents itself –Get Britain & France to join their cause because of European dependency on “King Cotton” –Drag out the war as long as possible to make the North quit ...
... –Protect Southern territory from “Northern aggression” but attack into Union territory when the opportunity presents itself –Get Britain & France to join their cause because of European dependency on “King Cotton” –Drag out the war as long as possible to make the North quit ...
Lesson: The Civil War - NC-Net
... many years did it take to settle the first 13 colonies? How many years did it take to add 13 more colonies? Add the three new colonies that joined the Union prior to the start of the Civil War. These are Minnesota (May 11, 1858), Oregon (February 14, 1859), and Kansas (January 29, 1861). Now ask le ...
... many years did it take to settle the first 13 colonies? How many years did it take to add 13 more colonies? Add the three new colonies that joined the Union prior to the start of the Civil War. These are Minnesota (May 11, 1858), Oregon (February 14, 1859), and Kansas (January 29, 1861). Now ask le ...
Presidential Reconstruction
... Two congressional factions formed over the subject of Reconstruction. A majority group of moderate Republicans in Congress supported Lincoln’s position that the Confederate states should be reintegrated as quickly as possible. A minority group of Radical Republicans--led by Thaddeus Stevens in the ...
... Two congressional factions formed over the subject of Reconstruction. A majority group of moderate Republicans in Congress supported Lincoln’s position that the Confederate states should be reintegrated as quickly as possible. A minority group of Radical Republicans--led by Thaddeus Stevens in the ...
Slide 1
... • Lincoln received his first endorsement to run for president at the Illinois Republican State Convention. • On November 6,1860 Lincoln became the 16th president of the United States • Lincoln was not even on the ballot in 9 southern states ...
... • Lincoln received his first endorsement to run for president at the Illinois Republican State Convention. • On November 6,1860 Lincoln became the 16th president of the United States • Lincoln was not even on the ballot in 9 southern states ...
APUSH – Chapter 20 Vocabulary and Guided Reading Questions
... The British upper classes sympathized with the South and abetted Confederate naval efforts. But effective diplomacy and Union military success thwarted those efforts and kept Britain, as well as France, neutral in the war. Lincoln’s political leadership proved effective in mobilizing the North fo ...
... The British upper classes sympathized with the South and abetted Confederate naval efforts. But effective diplomacy and Union military success thwarted those efforts and kept Britain, as well as France, neutral in the war. Lincoln’s political leadership proved effective in mobilizing the North fo ...
Coming of Age in the Midst of War - H-Net
... debate. An 1863 cartoon of a young white boy beating a black doll while his approving sister looks on captures the fears of antislavery activists who “argue[d] that slavery effectively destroyed the cherished institution of family life and corrupted childhood’s innocence” (p. 29). Two photographic i ...
... debate. An 1863 cartoon of a young white boy beating a black doll while his approving sister looks on captures the fears of antislavery activists who “argue[d] that slavery effectively destroyed the cherished institution of family life and corrupted childhood’s innocence” (p. 29). Two photographic i ...
Battle of Port Royal
... Battle of Port Royal Originally published by America's Civil War magazine. Published Online: June 12, 2006 http://www.historynet.com/battle-of-port-royal.htm#sthash.ZkuQW7Tp.dpuf ...
... Battle of Port Royal Originally published by America's Civil War magazine. Published Online: June 12, 2006 http://www.historynet.com/battle-of-port-royal.htm#sthash.ZkuQW7Tp.dpuf ...
Confederate privateer

The Confederate privateers were privately owned ships that were authorized by the government of the Confederate States of America to attack the shipping of the United States. Although the appeal was to profit by capturing merchant vessels and seizing their cargoes, the government was most interested in diverting the efforts of the Union Navy away from the blockade of Southern ports, and perhaps to encourage European intervention in the conflict.At the beginning of the American Civil War, the Confederate government sought to counter the United States Navy in part by appealing to private enterprise world-wide to engage in privateering against United States Shipping. [[