Solutions to Homework 4
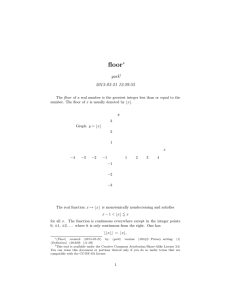
... 2. By considering different paths of approach show that the function f (x, y) = x4 /(x4 + y 2 ) has no limit as (x, y) approaches (0, 0). Solution: The limit as y = 0 and x → 0+ is equal to 1. The limit as x = 0 and y → 0+ is 0. Therefore, the limit of f (x, y) as (x, y) → (0, 0) does not exist. 3. ...
... 2. By considering different paths of approach show that the function f (x, y) = x4 /(x4 + y 2 ) has no limit as (x, y) approaches (0, 0). Solution: The limit as y = 0 and x → 0+ is equal to 1. The limit as x = 0 and y → 0+ is 0. Therefore, the limit of f (x, y) as (x, y) → (0, 0) does not exist. 3. ...
Chapter 46 – Basics of functional programming
... What are the main reasons for using functional languages compared to procedural languages? As a function always returns the same value given the same inputs, there are no ‘side effects’ where the value of the variable changes and can become difficult to trace. Functional programs lend themselves to ...
... What are the main reasons for using functional languages compared to procedural languages? As a function always returns the same value given the same inputs, there are no ‘side effects’ where the value of the variable changes and can become difficult to trace. Functional programs lend themselves to ...
Math 1210-1 HW 8
... , 0 ≤ x ≤ 4. (c) h(x) = 1+x (d) s(t) = t2/3 , −4 ≤ t ≤ 4. 2. Find two positive numbers whose sum is 23 and whose product is a maximum. 3. Find the volume of the largest open box that can be made from a piece of cardboard with width 10 and length 12 by cutting squares from the corners and turning up ...
... , 0 ≤ x ≤ 4. (c) h(x) = 1+x (d) s(t) = t2/3 , −4 ≤ t ≤ 4. 2. Find two positive numbers whose sum is 23 and whose product is a maximum. 3. Find the volume of the largest open box that can be made from a piece of cardboard with width 10 and length 12 by cutting squares from the corners and turning up ...
introduction to mathematical modeling and ibm ilog cplex
... • But the analysis and defining/constructing modeling components of a system are the art. • For example, questions such as how much detail to include in the model or how to represent a certain phenomena (i.e., interaction between system components) are all a part of the art. ...
... • But the analysis and defining/constructing modeling components of a system are the art. • For example, questions such as how much detail to include in the model or how to represent a certain phenomena (i.e., interaction between system components) are all a part of the art. ...
Mathematical optimization

In mathematics, computer science and operations research, mathematical optimization (alternatively, optimization or mathematical programming) is the selection of a best element (with regard to some criteria) from some set of available alternatives.In the simplest case, an optimization problem consists of maximizing or minimizing a real function by systematically choosing input values from within an allowed set and computing the value of the function. The generalization of optimization theory and techniques to other formulations comprises a large area of applied mathematics. More generally, optimization includes finding ""best available"" values of some objective function given a defined domain (or a set of constraints), including a variety of different types of objective functions and different types of domains.