Find the Demand Function Find the Revenue Function
... Find the Revenue Function The revenue function is found by observing that ...
... Find the Revenue Function The revenue function is found by observing that ...
ppt
... “Turing-Computable” means the same thing as Algorithmically computable. In other words, if you can prove a function computable on a turing machine, it must also be computable by a definite algorithm The converse also holds ...
... “Turing-Computable” means the same thing as Algorithmically computable. In other words, if you can prove a function computable on a turing machine, it must also be computable by a definite algorithm The converse also holds ...
1 - Slovak University of Technology in Bratislava
... of complicated optimization problems. (2) Different coevolutionary models of the above competitive and cooperative approaches are possible. (3) Their applicability is strongly restricted to problems with “almost ...
... of complicated optimization problems. (2) Different coevolutionary models of the above competitive and cooperative approaches are possible. (3) Their applicability is strongly restricted to problems with “almost ...
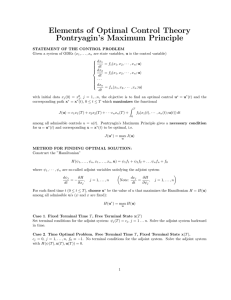
Elements of Optimal Control Theory Pontryagin’s Maximum Principle
... Many insects, such as wasps (including hornets and yellowjackets) live in colonies and have an annual life cycle. Their population consists of two castes: workers and reproductives (the latter comprised of queens and males). At the end of each summer all members of the colony die out except for the ...
... Many insects, such as wasps (including hornets and yellowjackets) live in colonies and have an annual life cycle. Their population consists of two castes: workers and reproductives (the latter comprised of queens and males). At the end of each summer all members of the colony die out except for the ...
Mathematical optimization

In mathematics, computer science and operations research, mathematical optimization (alternatively, optimization or mathematical programming) is the selection of a best element (with regard to some criteria) from some set of available alternatives.In the simplest case, an optimization problem consists of maximizing or minimizing a real function by systematically choosing input values from within an allowed set and computing the value of the function. The generalization of optimization theory and techniques to other formulations comprises a large area of applied mathematics. More generally, optimization includes finding ""best available"" values of some objective function given a defined domain (or a set of constraints), including a variety of different types of objective functions and different types of domains.