Computing intersections in a set of line segments: the Bentley
... consider the line segment intersection problem, which is defined as follows. We are given a set S = {L1 , L2 , . . . , Ln } of n line segments in the plane. Our task is to compute all pairs (Li , Lj ), i 6= j, of segments that intersect. ¡n¢ A trivial solution to this problem considers all 2 pairs ( ...
... consider the line segment intersection problem, which is defined as follows. We are given a set S = {L1 , L2 , . . . , Ln } of n line segments in the plane. Our task is to compute all pairs (Li , Lj ), i 6= j, of segments that intersect. ¡n¢ A trivial solution to this problem considers all 2 pairs ( ...
Document
... – Split L into two lists prefix and suffix, each of size n/2 – Sort, by merging, the prefix and the suffix separately: MergeSort(prefix) and MergeSort(suffix) – Merge sorted prefix with sorted suffix as follows: • Initialize final list as empty • Repeat until either prefix or suffix is empty: – Comp ...
... – Split L into two lists prefix and suffix, each of size n/2 – Sort, by merging, the prefix and the suffix separately: MergeSort(prefix) and MergeSort(suffix) – Merge sorted prefix with sorted suffix as follows: • Initialize final list as empty • Repeat until either prefix or suffix is empty: – Comp ...
- Wiley Online Library
... uniformly sample the unknown function in the random domain. Thus, in an effort to achieve high accuracy for the moments, such a construction would attempt to accurately approximate the stochastic solution throughout the random domain, which may unnecessarily increase the computational cost. For exam ...
... uniformly sample the unknown function in the random domain. Thus, in an effort to achieve high accuracy for the moments, such a construction would attempt to accurately approximate the stochastic solution throughout the random domain, which may unnecessarily increase the computational cost. For exam ...
Cambridge Public Schools Page 1 2013-2014
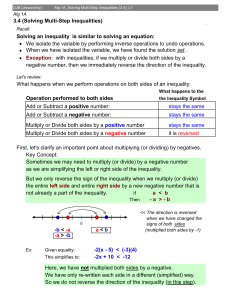
... forms of linear equations and inequalities, and use them to solve problems. They master the solution of linear equations and apply related solution techniques and the laws of exponents to the creation and solution of simple exponential equations. (2) In earlier grades, students define, evaluate, and ...
... forms of linear equations and inequalities, and use them to solve problems. They master the solution of linear equations and apply related solution techniques and the laws of exponents to the creation and solution of simple exponential equations. (2) In earlier grades, students define, evaluate, and ...
Simplex algorithm
In mathematical optimization, Dantzig's simplex algorithm (or simplex method) is a popular algorithm for linear programming. The journal Computing in Science and Engineering listed it as one of the top 10 algorithms of the twentieth century.The name of the algorithm is derived from the concept of a simplex and was suggested by T. S. Motzkin. Simplices are not actually used in the method, but one interpretation of it is that it operates on simplicial cones, and these become proper simplices with an additional constraint. The simplicial cones in question are the corners (i.e., the neighborhoods of the vertices) of a geometric object called a polytope. The shape of this polytope is defined by the constraints applied to the objective function.