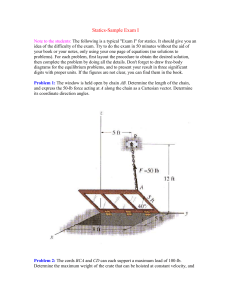
Probability distribution modelling process: Look at the data
... ● Look at the data (hopefully in a graph) and describe the features ● Read the information about the context and identify any parameters ● Select a distribution and justify your selection (use visual features and contextual reasons) ● Check fit of model VISUALLY by calculating a few probabilities ...
... ● Look at the data (hopefully in a graph) and describe the features ● Read the information about the context and identify any parameters ● Select a distribution and justify your selection (use visual features and contextual reasons) ● Check fit of model VISUALLY by calculating a few probabilities ...
objective
... BBA 120- BUSINESS MATHEMATICS First year –First semester Course Outline OBJECTIVE The course aims to provide an introduction to mathematical concepts and lay down a foundation for applications of basic tools and techniques for various areas of business such as economics, accountancy and the life and ...
... BBA 120- BUSINESS MATHEMATICS First year –First semester Course Outline OBJECTIVE The course aims to provide an introduction to mathematical concepts and lay down a foundation for applications of basic tools and techniques for various areas of business such as economics, accountancy and the life and ...
solutions
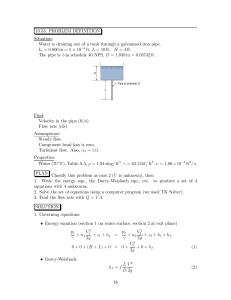
... We want to minimize the distance function h(x, y) = x2 + y 2 . Nobody likes square roots, so notice that we can just as well minimize the distance squared, which is f (x, y) = x2 + y 2 . This is subject to the constraint y = x2 −1. This is better written as g(x, y) = y −x2 +1 = 0. We have ∇f (x, y) ...
... We want to minimize the distance function h(x, y) = x2 + y 2 . Nobody likes square roots, so notice that we can just as well minimize the distance squared, which is f (x, y) = x2 + y 2 . This is subject to the constraint y = x2 −1. This is better written as g(x, y) = y −x2 +1 = 0. We have ∇f (x, y) ...
“Additive Inverse” Classroom Activities
... involve adding groups of negative and positive integers that sum to zero. To get the most out of this activity, students should be familiar with plotting positive and negative integers on a number line. Activity Text Learning Outcomes Students will be able to ● define additive inverse and demonstrat ...
... involve adding groups of negative and positive integers that sum to zero. To get the most out of this activity, students should be familiar with plotting positive and negative integers on a number line. Activity Text Learning Outcomes Students will be able to ● define additive inverse and demonstrat ...