Zoology Exercise #10: Phylum Nematoda Lab Guide All animals
... The females reproductive system fills most of the pseudocoel. The system is a Y-shaped set of tubes. The short base of the Y is the vagina. It opens to the outside at the vulva. The long tubes of the inverted Y are the uteri. They extend to the posterior end and then double back as more slender, muc ...
... The females reproductive system fills most of the pseudocoel. The system is a Y-shaped set of tubes. The short base of the Y is the vagina. It opens to the outside at the vulva. The long tubes of the inverted Y are the uteri. They extend to the posterior end and then double back as more slender, muc ...
vert strand 3 - csi-parent-student
... Illustrate and explain the path water and nutrients take as they move through the transport system of a plant Explain the interactions between the circulatory and digestive systems as nutrients are processed by the digestive system, passed into the blood stream, and transported in and out of the cel ...
... Illustrate and explain the path water and nutrients take as they move through the transport system of a plant Explain the interactions between the circulatory and digestive systems as nutrients are processed by the digestive system, passed into the blood stream, and transported in and out of the cel ...
Arthropods - Green Local Schools
... Sensory hairs on exoskeleton 2,000 light sensitive units on each eye Statocyte at base of antennae for balance ...
... Sensory hairs on exoskeleton 2,000 light sensitive units on each eye Statocyte at base of antennae for balance ...
Section 29–2 Form and Function in Invertebrates
... 20. Is the following sentence true or false? The more complex an animal’s nervous system, the more developed its sense organs are. ...
... 20. Is the following sentence true or false? The more complex an animal’s nervous system, the more developed its sense organs are. ...
Biology 1 End-of-Course Assessment Practice Test For Multiple
... A. During prophase I, DNA replication takes place, and homologous chromosomes trade places with each other before lining up in preparation for metaphase. *B. During prophase I, DNA segments are exchanged b ...
... A. During prophase I, DNA replication takes place, and homologous chromosomes trade places with each other before lining up in preparation for metaphase. *B. During prophase I, DNA segments are exchanged b ...
Unit 5, Module 14 Animals
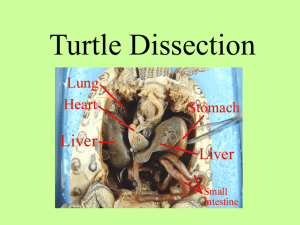
... surface area and allow for more efficient absorption. Accessory organs such as the liver and pancreas produce and secrete digestive chemicals. ...
... surface area and allow for more efficient absorption. Accessory organs such as the liver and pancreas produce and secrete digestive chemicals. ...
SURFIN` THROUGH STAAR Session 2: Cellular Processes
... a. This type of cell division is humans produces sex cells as well as body cells. b. This type of cell division in humans occurs while bones are forming during development. c. This type of cell division in humans can be affected by viruses. d. This type of cell division in humans is necessary to hea ...
... a. This type of cell division is humans produces sex cells as well as body cells. b. This type of cell division in humans occurs while bones are forming during development. c. This type of cell division in humans can be affected by viruses. d. This type of cell division in humans is necessary to hea ...
What is an Animal? Animals: General Characteristics 1. by far, the
... their sex based on environmental cues. 6. Sexual Dimorphism: in many dioecious animals the males and females are not identical, but differ in appearance. in most invertebrates, the male is usually smaller than the female in vertebrates the female is usually the smaller one. In birds the male is usua ...
... their sex based on environmental cues. 6. Sexual Dimorphism: in many dioecious animals the males and females are not identical, but differ in appearance. in most invertebrates, the male is usually smaller than the female in vertebrates the female is usually the smaller one. In birds the male is usua ...
Introduction to Helminthology
... Two main groups (phyla) • Platyhelminths (Flatworms) • Nematoda (Roundworms) Life Cycle • Extremely complex (egg → larva → adult) • Intermediate hosts harbor larval (developmental) stage. • Definitive host harbors adult stage. ...
... Two main groups (phyla) • Platyhelminths (Flatworms) • Nematoda (Roundworms) Life Cycle • Extremely complex (egg → larva → adult) • Intermediate hosts harbor larval (developmental) stage. • Definitive host harbors adult stage. ...
Biology ORGANISMS Practice Test with Answer Key
... B. Males do not need to use as much energy. C. Sperm cells will reach most of the eggs. D. Males can fertilize eggs at their convenience. 22. Which describes pollination? A. pollen landing on the stigma B. pollen forming a pollen tube C. pollen fertilizing an egg cell D. pollen forming the seed 23. ...
... B. Males do not need to use as much energy. C. Sperm cells will reach most of the eggs. D. Males can fertilize eggs at their convenience. 22. Which describes pollination? A. pollen landing on the stigma B. pollen forming a pollen tube C. pollen fertilizing an egg cell D. pollen forming the seed 23. ...
Biology 1 (Year 10)
... Green plants absorb only a small percentage of this energy (about 1%), using the chlorophyll in their chloroplasts. The rest of the light is either reflected or is at the wrong wavelength. The absorbed energy is used for photosynthesis to produce substances that become part of the cells. These incre ...
... Green plants absorb only a small percentage of this energy (about 1%), using the chlorophyll in their chloroplasts. The rest of the light is either reflected or is at the wrong wavelength. The absorbed energy is used for photosynthesis to produce substances that become part of the cells. These incre ...
File - Once Upon A Cell
... a. This type of cell division is humans produces sex cells as well as body cells. b. This type of cell division in humans occurs while bones are forming during development. c. This type of cell division in humans can be affected by viruses. d. This type of cell division in humans is necessary to hea ...
... a. This type of cell division is humans produces sex cells as well as body cells. b. This type of cell division in humans occurs while bones are forming during development. c. This type of cell division in humans can be affected by viruses. d. This type of cell division in humans is necessary to hea ...
Bellringer: 3/31/2017 (Friday) PROJECT TIME!! Level of
... Two parents come together with gametes (sperm and egg) to form an offspring genetically different from both parents. Meiosis: process of forming gametes, all gametes are genetically different from each other. ...
... Two parents come together with gametes (sperm and egg) to form an offspring genetically different from both parents. Meiosis: process of forming gametes, all gametes are genetically different from each other. ...
unit_5 - Homework Market
... 3. What is common between the circulatory system of organisms from samples 5, 6, and 7, but different in organisms from sample 4? The commonalities between 5, 6, and 7 are that they all are closed with 4-chambered heart while sample 4 is closed with a 3-chambered heart. 4. What is common in the re ...
... 3. What is common between the circulatory system of organisms from samples 5, 6, and 7, but different in organisms from sample 4? The commonalities between 5, 6, and 7 are that they all are closed with 4-chambered heart while sample 4 is closed with a 3-chambered heart. 4. What is common in the re ...
ď - Google Sites
... • Exist as trophozoite - motile feeding stage • Many can enter into a dormant resting stage when conditions are unfavorable for growth and feeding – cyst. • All reproduce asexually, mitosis or multiple fission; many also reproduce sexually – conjugation. ...
... • Exist as trophozoite - motile feeding stage • Many can enter into a dormant resting stage when conditions are unfavorable for growth and feeding – cyst. • All reproduce asexually, mitosis or multiple fission; many also reproduce sexually – conjugation. ...
Chapter 1 The Framework of Biology
... Eggs and sperm are produced by animals and the way each parent provides these gametes for sexual reproduction is diverse. Hermaphrodites have both male and female sexual organs and so produce both eggs and sperm. Some organisms such as in the Cnidaria have a complex life cycle which involves two lif ...
... Eggs and sperm are produced by animals and the way each parent provides these gametes for sexual reproduction is diverse. Hermaphrodites have both male and female sexual organs and so produce both eggs and sperm. Some organisms such as in the Cnidaria have a complex life cycle which involves two lif ...
Living Things are Highly Organized
... 3.Based on a Genetic Code 4.Growth and Development 5.Need for Materials and Energy 6.Response to the Environment 7.Maintaining Internal Balance 8.Evolution ...
... 3.Based on a Genetic Code 4.Growth and Development 5.Need for Materials and Energy 6.Response to the Environment 7.Maintaining Internal Balance 8.Evolution ...
Cellular Reproduction notes
... Chromosomes begin to disappear into tangle of dense material (Chromatin fibers uncoil and ...
... Chromosomes begin to disappear into tangle of dense material (Chromatin fibers uncoil and ...
Spherical Symmetry 1. center point Radial Symmetry
... 1. Free-living: Planarians, freshwater worms, live on bottom a. Mouth – pharynx – gastrovascular cavity: incomplete digestive system w/ many branches that increase surface area of digestive tract b. Nervous system w/ dorsal ganglia “brain” and lateral nerve cords c. Eyespots: sensitive to light but ...
... 1. Free-living: Planarians, freshwater worms, live on bottom a. Mouth – pharynx – gastrovascular cavity: incomplete digestive system w/ many branches that increase surface area of digestive tract b. Nervous system w/ dorsal ganglia “brain” and lateral nerve cords c. Eyespots: sensitive to light but ...
Sex

Organisms of many species are specialized into male and female varieties, each known as a sex. Sexual reproduction involves the combining and mixing of genetic traits: specialized cells known as gametes combine to form offspring that inherit traits from each parent. Gametes can be identical in form and function (known as isogamy), but in many cases an asymmetry has evolved such that two sex-specific types of gametes (heterogametes) exist (known as anisogamy). By definition, male gametes are small, motile, and optimized to transport their genetic information over a distance, while female gametes are large, non-motile and contain the nutrients necessary for the early development of the young organism. Among humans and other mammals, males typically carry XY chromosomes, whereas females typically carry XX chromosomes, which are a part of the XY sex-determination system. Other animals have a sex-determination system as well, such as the ZW sex-determination system in birds, and the X0 sex-determination system in insects. The gametes produced by an organism are determined by its sex: males produce male gametes (spermatozoa, or sperm, in animals; pollen in plants) while females produce female gametes (ova, or egg cells); individual organisms which produce both male and female gametes are termed hermaphroditic. Frequently, physical differences are associated with the different sexes of an organism; these sexual dimorphisms can reflect the different reproductive pressures the sexes experience.