here
... 5. Enumerate, explain, and differentiate between different mechanisms of interprocess communication and synchronisation 6. Analyse the architecture of a computer system and understand the significance of different architectural features and their affect on system administration. 7. Perform basic and ...
... 5. Enumerate, explain, and differentiate between different mechanisms of interprocess communication and synchronisation 6. Analyse the architecture of a computer system and understand the significance of different architectural features and their affect on system administration. 7. Perform basic and ...
Module 3: Operating-System Structures
... secondary storage to back up main memory. Most modern computer systems use disks as the principle on-line storage medium, for both programs and data. The operating system is responsible for the following activities in connection with disk management: ...
... secondary storage to back up main memory. Most modern computer systems use disks as the principle on-line storage medium, for both programs and data. The operating system is responsible for the following activities in connection with disk management: ...
Module 3: Operating
... provide secondary storage to back up main memory. Most modern computer systems use disks as the principle on-line storage medium, for both programs and data. The operating system is responsible for the following activities in connection with disk management: Free space management Storage all ...
... provide secondary storage to back up main memory. Most modern computer systems use disks as the principle on-line storage medium, for both programs and data. The operating system is responsible for the following activities in connection with disk management: Free space management Storage all ...
virtual machine
... logical conclusion. It treats hardware and the operating system kernel as though they were all hardware • A virtual machine provides an interface identical to the underlying bare hardware • The operating system creates the illusion of multiple processes, each executing on its own processor with its ...
... logical conclusion. It treats hardware and the operating system kernel as though they were all hardware • A virtual machine provides an interface identical to the underlying bare hardware • The operating system creates the illusion of multiple processes, each executing on its own processor with its ...
Module 3: Operating-System Structures
... – specify the controls to be imposed. – provide a means of enforcement. ...
... – specify the controls to be imposed. – provide a means of enforcement. ...
Lecture 3 - The College of New Jersey
... kernel as though they were all hardware. A virtual machine provides an interface identical to the underlying bare hardware. The operating system creates the illusion of multiple processes, each executing on its own processor with its own (virtual) memory. ...
... kernel as though they were all hardware. A virtual machine provides an interface identical to the underlying bare hardware. The operating system creates the illusion of multiple processes, each executing on its own processor with its own (virtual) memory. ...
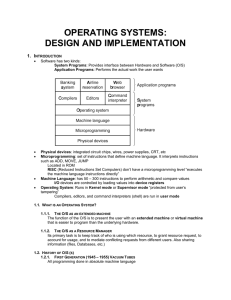
OPERATING SYSTEMS:
... create a process for it. When it is finished, it executes a system call to terminate itself Child Processes: when a process creates one or more other processes, and these processes in turn create child processes Interprocess Communication: related processes that are cooperating must communicate sync ...
... create a process for it. When it is finished, it executes a system call to terminate itself Child Processes: when a process creates one or more other processes, and these processes in turn create child processes Interprocess Communication: related processes that are cooperating must communicate sync ...
2.4 The service and functions provided by an operating system can
... One class of services provided by an operating system is to enforce protection between different processes running concurrently in the system. Processes are allowed to access only those memory locations that are associated with their address spaces. Also, processes are not allowed to corrupt files a ...
... One class of services provided by an operating system is to enforce protection between different processes running concurrently in the system. Processes are allowed to access only those memory locations that are associated with their address spaces. Also, processes are not allowed to corrupt files a ...