PHI 110 Lecture 1 1 Welcome to Philosophy 110, Introduction to
... couldn’t define philosophy in terms of a specific subject matter. Philosophy covers everything from ethics to politics, to linguistics, to science, to religion. You might be able to define philosophy as a certain kind of way of asking questions and I think that that might get us closer to the truth. ...
... couldn’t define philosophy in terms of a specific subject matter. Philosophy covers everything from ethics to politics, to linguistics, to science, to religion. You might be able to define philosophy as a certain kind of way of asking questions and I think that that might get us closer to the truth. ...
Ancient Greek Philosophers Socrates • Socrates
... described the ideal state. Three groups in society. Top was an upperclass of Philosopher-Kings (political power and wise). Second, warriors to protect society. Third, everyone else not driven by wisdom or courage ...
... described the ideal state. Three groups in society. Top was an upperclass of Philosopher-Kings (political power and wise). Second, warriors to protect society. Third, everyone else not driven by wisdom or courage ...
NC-Contractualism
... Next, we must adopt moral principles that stem from individual perspectives. First, the general will is not an aggregation of individual wills, but a reflection of the individual interests of every citizen. Although citizens rally around a sovereign this does not deny that only individuals are capab ...
... Next, we must adopt moral principles that stem from individual perspectives. First, the general will is not an aggregation of individual wills, but a reflection of the individual interests of every citizen. Although citizens rally around a sovereign this does not deny that only individuals are capab ...
gst113 ethics and human conduct in the society
... What s ethics? Ethics is a part of philosophy where the analytical and critical tools of philosophy are focused on human actions. As a review, it touches every side of life where one can point to one human conduct to another. This is the reason for the existence of an ethics of nearly everything: bu ...
... What s ethics? Ethics is a part of philosophy where the analytical and critical tools of philosophy are focused on human actions. As a review, it touches every side of life where one can point to one human conduct to another. This is the reason for the existence of an ethics of nearly everything: bu ...
SEMANTICS – AN INTERVIEW WITH JERRY FODOR
... evidence is that there are, at most, not very many. (Quite possibly there are none that are untendentious including ‘unmarried men are bachelors’. Is the Pope a bachelor?) - The view of meaning that I’m supposing Chomsky endorses avoids skepticism about whether bachelors are unmarried; we really can ...
... evidence is that there are, at most, not very many. (Quite possibly there are none that are untendentious including ‘unmarried men are bachelors’. Is the Pope a bachelor?) - The view of meaning that I’m supposing Chomsky endorses avoids skepticism about whether bachelors are unmarried; we really can ...
manuel delanda in conversation with christoph cox – pdf
... ontology, a materialist cannot use the phrase “mind-independent” to characterize the ontological status of communities, institutional organizations, cities, and other social entities. These are clearly not independent of our minds because without minds there would be no community life, no organizati ...
... ontology, a materialist cannot use the phrase “mind-independent” to characterize the ontological status of communities, institutional organizations, cities, and other social entities. These are clearly not independent of our minds because without minds there would be no community life, no organizati ...
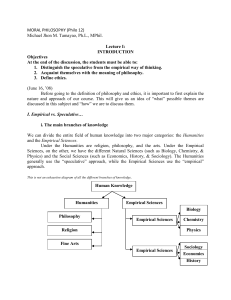
MORAL PHILOSOPHY (Philo 12) - Law, Politics, and Philosophy
... Although the above given definitions will tell us some basic characteristics of philosophy, these definitions are still vague and misleading. The words truth and knowledge, for example, are very vague, and they usually go beyond the grips of common everyday thinking. In a way we already know them, ...
... Although the above given definitions will tell us some basic characteristics of philosophy, these definitions are still vague and misleading. The words truth and knowledge, for example, are very vague, and they usually go beyond the grips of common everyday thinking. In a way we already know them, ...
Philosophy of Science
... facts on earth that we prove in various ways to be certain in our own sight. And facts that are not true in places where we are, we know through other wise men that have experience them…. And this experience is human and philosophical just as far as a man is able to make use of the beneficent grace ...
... facts on earth that we prove in various ways to be certain in our own sight. And facts that are not true in places where we are, we know through other wise men that have experience them…. And this experience is human and philosophical just as far as a man is able to make use of the beneficent grace ...
12 Purva Mimamsa and Vedanta
... sequence of logical implications beginning with axioms that have been assumed without question. Explanation only means this. We relate it to what has been known before or what has been deduced before. We associate it with past impressions. When it comes to existential questions raised by philosophy ...
... sequence of logical implications beginning with axioms that have been assumed without question. Explanation only means this. We relate it to what has been known before or what has been deduced before. We associate it with past impressions. When it comes to existential questions raised by philosophy ...
This project draws on the work of two thinkers, C.... Brave New World
... 279). When this belief falls, and no new system can take its place, European morality and identity will collapse with it. This is what Nietzsche calls nihilism: A nihilist believes in nothing, and feels his life to have no purpose. Although Lewis does not use the same term, he discusses essentially ...
... 279). When this belief falls, and no new system can take its place, European morality and identity will collapse with it. This is what Nietzsche calls nihilism: A nihilist believes in nothing, and feels his life to have no purpose. Although Lewis does not use the same term, he discusses essentially ...
Plato and Vedanta
... contemporary of the Buddha, Mahavira and Confucius. Human culture was being developed and the basic ideas that have shaped human destiny ever since were being formulated. It is my view th at Plato's thinking hos influenced religious and social thinking in every part of the globe. " He hos always bee ...
... contemporary of the Buddha, Mahavira and Confucius. Human culture was being developed and the basic ideas that have shaped human destiny ever since were being formulated. It is my view th at Plato's thinking hos influenced religious and social thinking in every part of the globe. " He hos always bee ...
Study Guide: René Descartes
... clearness and distinctness criterion of truth: A belief will be accepted as true if one has a clear and distinct idea of it. An idea is clear and distinct if there is nothing hidden or unclear in it, it can be entirely present to one’s mind at the same time, and all parts of the idea are vivid. T ...
... clearness and distinctness criterion of truth: A belief will be accepted as true if one has a clear and distinct idea of it. An idea is clear and distinct if there is nothing hidden or unclear in it, it can be entirely present to one’s mind at the same time, and all parts of the idea are vivid. T ...
Two Key Texts in Practical Ethics - Society for Philosophy in Practice
... Thomson is well aware that distinguishing moral arguments from non-arguments and non-moral arguments is more an art than a science (in the sense that it requires judgement, not simply the working through of an algorithm). An illustration of this can be drawn from one of the examples that she offers ...
... Thomson is well aware that distinguishing moral arguments from non-arguments and non-moral arguments is more an art than a science (in the sense that it requires judgement, not simply the working through of an algorithm). An illustration of this can be drawn from one of the examples that she offers ...
November 2007 Seminar in Academic Integrity
... action, is not really a theory of ethics. It is, instead, a descriptive or anthropological account of human behavior that has no moral import. That is, the psychological egoist does not say that people ought to be self-interested. The psychological egoist says that people are self-interested. Anothe ...
... action, is not really a theory of ethics. It is, instead, a descriptive or anthropological account of human behavior that has no moral import. That is, the psychological egoist does not say that people ought to be self-interested. The psychological egoist says that people are self-interested. Anothe ...
PDF
... definition implies the existence of a decision procedure for all arithmetic problems and Turing proved that there is no such a procedure. There is however another definition of the term ’analytic’ which could be more appealing to logicist foundations. In this new definition a proposition ...
... definition implies the existence of a decision procedure for all arithmetic problems and Turing proved that there is no such a procedure. There is however another definition of the term ’analytic’ which could be more appealing to logicist foundations. In this new definition a proposition ...
EMPIRICISM John Locke`s Radical Empiricism Contents Ideas
... “the perception of the relation between any two ideas, of what kind soever, whether substances, modes, or any other. For, since all distinct ideas must eternally be known not to be the same, and so be universally and constantly denied one of another, there could be no room for any positive knowledge ...
... “the perception of the relation between any two ideas, of what kind soever, whether substances, modes, or any other. For, since all distinct ideas must eternally be known not to be the same, and so be universally and constantly denied one of another, there could be no room for any positive knowledge ...
An Emerson Mood
... yourself an authority for yourself you have been compelled to invest elsewhere. So the matter of authority is as much one of hearing as it is one of uttering…” (159 – ...
... yourself an authority for yourself you have been compelled to invest elsewhere. So the matter of authority is as much one of hearing as it is one of uttering…” (159 – ...
ethics and human conduct in the society
... disciplines and facets of life that require effective response that is able to ensure that moral principles are ‘sustained in the various areas of human operations.’ Ethics is a rational inquiry into the grounds of moral conduct which stands in contrast to revelations, special intuition, mystical in ...
... disciplines and facets of life that require effective response that is able to ensure that moral principles are ‘sustained in the various areas of human operations.’ Ethics is a rational inquiry into the grounds of moral conduct which stands in contrast to revelations, special intuition, mystical in ...
Asian Philosophy CH. 10 of AP
... In order for one perception to be judged as being false, there must be a body of claims that one accepts as being true. One cannot judge that a prior perception was false unless one has sufficient warrant from another set of beliefs to judge that the prior perception was false. Those alternative bel ...
... In order for one perception to be judged as being false, there must be a body of claims that one accepts as being true. One cannot judge that a prior perception was false unless one has sufficient warrant from another set of beliefs to judge that the prior perception was false. Those alternative bel ...
VKS Synoptic Prese
... just that people haven't learned some fact that they need to know, but rather that their habitual ways of perceiving the world are fundamentally mistaken, and thus they are "blinded" (by greed, desire, lust, etc.). ...
... just that people haven't learned some fact that they need to know, but rather that their habitual ways of perceiving the world are fundamentally mistaken, and thus they are "blinded" (by greed, desire, lust, etc.). ...
Philosophy 324A Philosophy of Logic 2016 Note Eighteen
... Over time there have been different namings of the various habitations at that site. It turns out that, like everything else in human life, names have life-spans. If Sally wants to know whether there is jet-service to Istanbul on Thursday afternoon at 5:00, she’ll be doing herself no good by asking ...
... Over time there have been different namings of the various habitations at that site. It turns out that, like everything else in human life, names have life-spans. If Sally wants to know whether there is jet-service to Istanbul on Thursday afternoon at 5:00, she’ll be doing herself no good by asking ...
Can a Buddhist become a Mason?
... restricting his food intake to around a leaf or nut per day, he collapsed in a river and almost drowned. As he laid there, a boat passed him and he overheard the conversation that the two musicians aboard it were saying: "If you tighten the string too tight it will snap, but if it is too loose it w ...
... restricting his food intake to around a leaf or nut per day, he collapsed in a river and almost drowned. As he laid there, a boat passed him and he overheard the conversation that the two musicians aboard it were saying: "If you tighten the string too tight it will snap, but if it is too loose it w ...
Divine Command Theory and Moral Obligations
... Notice that, against the possibility of God creating a world with moral agencies to whom he issues no commands, there may be good reason to think that God’s freely choosing to create a world with moral agencies may just involve issuing commandments to them. I have not the space to work out such an a ...
... Notice that, against the possibility of God creating a world with moral agencies to whom he issues no commands, there may be good reason to think that God’s freely choosing to create a world with moral agencies may just involve issuing commandments to them. I have not the space to work out such an a ...
Pragmatism Lite - NYU Philosophy
... claim about what beliefs are; it is rather to make a historical claim about how they come into existence. The thought is that what we believe is not to be explained by the way the world is or by the available evidence, but rather by the fact that some of our beliefs turn out to be more useful than o ...
... claim about what beliefs are; it is rather to make a historical claim about how they come into existence. The thought is that what we believe is not to be explained by the way the world is or by the available evidence, but rather by the fact that some of our beliefs turn out to be more useful than o ...