A Historical Perspective on Quantum Physics and its Impact on Society
... Broglie’s ideas through the theory of quantum mechanics. This theory brought about a complete resolution to the problems by showing the wave aspect of quantum mechanics. Since its birth, quantum mechanics has proved to be a very successful theory of physics. It is believed to be the most fundamenta ...
... Broglie’s ideas through the theory of quantum mechanics. This theory brought about a complete resolution to the problems by showing the wave aspect of quantum mechanics. Since its birth, quantum mechanics has proved to be a very successful theory of physics. It is believed to be the most fundamenta ...
QOLECTURE4
... for transitions in the visible-frequency range – observation of Rabi flopping requires powerful laser beams - pulsed, so that the electric field amplitude varies with time therefore, the Rabi frequency ΩR/2π also varies with time, and so it is useful to define the pulse area Θ A pulse with an area e ...
... for transitions in the visible-frequency range – observation of Rabi flopping requires powerful laser beams - pulsed, so that the electric field amplitude varies with time therefore, the Rabi frequency ΩR/2π also varies with time, and so it is useful to define the pulse area Θ A pulse with an area e ...
The Calculus Reveals Special Properties of Light
... would be the arc length of the sine function from 0 to 2 divided by the time required for a wave to travel its own wavelength. The line integral of the sine function computes the actual distance through space traveled by the field edge where for a full wavelength of lateral travel is: arc length = ...
... would be the arc length of the sine function from 0 to 2 divided by the time required for a wave to travel its own wavelength. The line integral of the sine function computes the actual distance through space traveled by the field edge where for a full wavelength of lateral travel is: arc length = ...
Nature and Properties of Light
... expressed as c = 2.99 × 108 m/s. Light travels in a vacuum at a constant speed, and this speed is considered a universal constant. It is important to note that speed changes for light traveling through nonvacuum media such as air (0.03% slower) or glass (30.0% slower). For most purposes, we may repr ...
... expressed as c = 2.99 × 108 m/s. Light travels in a vacuum at a constant speed, and this speed is considered a universal constant. It is important to note that speed changes for light traveling through nonvacuum media such as air (0.03% slower) or glass (30.0% slower). For most purposes, we may repr ...
Chapter 24 Notes
... • Be sure to include two effects when analyzing the interference pattern from a thin film. – Path length – Phase change ...
... • Be sure to include two effects when analyzing the interference pattern from a thin film. – Path length – Phase change ...
Chapter 22: Problems
... Exercises 13 – 17 deal with the electromagnetic spectrum and EM waves. 13. Do a web search for the “United States Frequency Allocation Chart.” The chart shows how different parts of the spectrum are used for various purposes in the United States. Compare the parts of the spectrum reserved for broad ...
... Exercises 13 – 17 deal with the electromagnetic spectrum and EM waves. 13. Do a web search for the “United States Frequency Allocation Chart.” The chart shows how different parts of the spectrum are used for various purposes in the United States. Compare the parts of the spectrum reserved for broad ...
Resource Doc File - Dayton Regional Stem Center
... one medium into another, and changes its speed. Light waves are refracted when crossing the boundary from one transparent medium into another because the speed of light is different in different media. he bending occurs because the wave fronts do not travel as far in one cycle in the glass as they d ...
... one medium into another, and changes its speed. Light waves are refracted when crossing the boundary from one transparent medium into another because the speed of light is different in different media. he bending occurs because the wave fronts do not travel as far in one cycle in the glass as they d ...
Pearson Physics Level 30 Unit VII Electromagnetic Radiation: Unit
... diffraction grating: a sheet of glass or plastic etched with a large number of parallel lines; when light is incident on the grating, each line or slit acts as one individual light source dispersion: separation of white light into its components diverging: the process whereby refracted or reflected ...
... diffraction grating: a sheet of glass or plastic etched with a large number of parallel lines; when light is incident on the grating, each line or slit acts as one individual light source dispersion: separation of white light into its components diverging: the process whereby refracted or reflected ...
polarized light - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... equation of the best-fit line to answer this question. 3. At what angle θ is most light transmitted? Does this angle make sense? WHY? ...
... equation of the best-fit line to answer this question. 3. At what angle θ is most light transmitted? Does this angle make sense? WHY? ...
Opt301
... Your demonstrator will show you the effect of placing certain transparent objects between crossed polaroids. It is interesting to think about applications of this phenomenon. An understanding of option D is a necessary basis for understanding the phenomenon. Record your observations and ...
... Your demonstrator will show you the effect of placing certain transparent objects between crossed polaroids. It is interesting to think about applications of this phenomenon. An understanding of option D is a necessary basis for understanding the phenomenon. Record your observations and ...
Chapter 2 (Particle Properties of Waves)
... If is constant with time (i.e., d/dt=0), then we are moving with the wave, and ...
... If is constant with time (i.e., d/dt=0), then we are moving with the wave, and ...
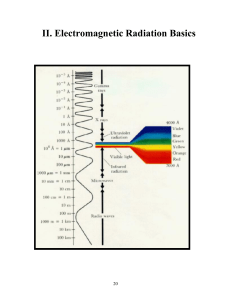
II. Electromagnetic Radiation Basics
... light. These waves reflect off of hills, are absorbed into the atmosphere, bounce off airplanes, reflect off of an ionized trail left behind from a meteor and then finally make it to your radio receiver where they are converted back into sound waves. At first, it seems like visible light and radio w ...
... light. These waves reflect off of hills, are absorbed into the atmosphere, bounce off airplanes, reflect off of an ionized trail left behind from a meteor and then finally make it to your radio receiver where they are converted back into sound waves. At first, it seems like visible light and radio w ...
Modern Physics - University of Colorado Boulder
... The message is profound - you can't always impose a simple model of the world on nature. Light is complicated. It was a revolution in physics, and the model that emerged is still unsatisfying to many people. It's a model with "wave-particle duality". We describe it accurately, mathematically, but it ...
... The message is profound - you can't always impose a simple model of the world on nature. Light is complicated. It was a revolution in physics, and the model that emerged is still unsatisfying to many people. It's a model with "wave-particle duality". We describe it accurately, mathematically, but it ...
Program of the workshop
... pioneering technique is frequency-resolved optical gating (FROG), which can also be seen as the prototypical tomographic pulse measurement technique. A few years later, spectral-phase interferometry for direct electric-field reconstruction (SPIDER) appeared as an alternative technique with similar c ...
... pioneering technique is frequency-resolved optical gating (FROG), which can also be seen as the prototypical tomographic pulse measurement technique. A few years later, spectral-phase interferometry for direct electric-field reconstruction (SPIDER) appeared as an alternative technique with similar c ...
English Medium - sakshieducation.com
... 3. The distance between pole and focus is ____. 4. Mirror formula is ____. 5. Light chooser the path which takes the least time to travel. This is called____ principle. 6. The geometric centre of the mirror is ____. 7. A concave mirror can form a ____. 8. Convex and concave mirrors are known collect ...
... 3. The distance between pole and focus is ____. 4. Mirror formula is ____. 5. Light chooser the path which takes the least time to travel. This is called____ principle. 6. The geometric centre of the mirror is ____. 7. A concave mirror can form a ____. 8. Convex and concave mirrors are known collect ...
The calculation of the bending of star light grazing the sun.
... In this paper, I refocus on the second one of the findings that I described in my paper: Did Einstein cheat? The precise and detailed bending of star light grazing the sun can be found for light rays, just by applying the Maxwell Analogy (which has firstly been suggested by Heavyside at the end of t ...
... In this paper, I refocus on the second one of the findings that I described in my paper: Did Einstein cheat? The precise and detailed bending of star light grazing the sun can be found for light rays, just by applying the Maxwell Analogy (which has firstly been suggested by Heavyside at the end of t ...
Physics - Practice Final Exam
... A. the force is perpendicular to the object’s velocity. B. the force is in the same direction as the object’s velocity. C. the force is in the opposite direction of the object’s velocity. D. there is an equal and opposite force acting on the object and the object is at rest. A 1.00 103 kg sports c ...
... A. the force is perpendicular to the object’s velocity. B. the force is in the same direction as the object’s velocity. C. the force is in the opposite direction of the object’s velocity. D. there is an equal and opposite force acting on the object and the object is at rest. A 1.00 103 kg sports c ...
The Michelson Interferometer
... on the screen. Adjust the angle of the fixed mirror until these two spots overlap. You can use lenses to expand the beam if necessary. Note, take care when moving M2 as the interference is very sensitive to its alignment. As you translate mirror M1 , you will see fringes appearing and disappearing o ...
... on the screen. Adjust the angle of the fixed mirror until these two spots overlap. You can use lenses to expand the beam if necessary. Note, take care when moving M2 as the interference is very sensitive to its alignment. As you translate mirror M1 , you will see fringes appearing and disappearing o ...
science 106
... (a) (7 pts) Above, you see a plane wave passing from air into water at oblique incidence. 1 is the angle of incidence in air and 2 is the angle of refraction in water. Two consecutive wavefronts in air and water are shown. The arrows point along the direction of wave motion in each medium. Use sim ...
... (a) (7 pts) Above, you see a plane wave passing from air into water at oblique incidence. 1 is the angle of incidence in air and 2 is the angle of refraction in water. Two consecutive wavefronts in air and water are shown. The arrows point along the direction of wave motion in each medium. Use sim ...
25.7 The Photon Model of Electromagnetic Waves
... photo. Instead, it is a collection of dots. A few points on the detector have registered the presence of light, but most have not. As the illumination increases, the density of these dots increases until the dots form a full picture. This is not what we might expect. If light is a wave, reducing its ...
... photo. Instead, it is a collection of dots. A few points on the detector have registered the presence of light, but most have not. As the illumination increases, the density of these dots increases until the dots form a full picture. This is not what we might expect. If light is a wave, reducing its ...
Quanta: a new view of the world
... reinforce each other. Fresnel performed the experiment and was entirely vindicated: if the light source is sufficiently point-like (an extended source such as the sun or an ordinary lamp will not work), this diffraction effect is indeed observed. See Paul Falstad's interactive diffraction demo ...
... reinforce each other. Fresnel performed the experiment and was entirely vindicated: if the light source is sufficiently point-like (an extended source such as the sun or an ordinary lamp will not work), this diffraction effect is indeed observed. See Paul Falstad's interactive diffraction demo ...