Flag Antenna Construction
... The Flag Antenna is in the family of terminated loops that can yield a cardioid (heartshaped, single-direction null) pick-up pattern. Its name comes from its horizontal rectangular shape. Length of the upper and lower horizontal wire members is typically about 2 to 3 times the height of the two vert ...
... The Flag Antenna is in the family of terminated loops that can yield a cardioid (heartshaped, single-direction null) pick-up pattern. Its name comes from its horizontal rectangular shape. Length of the upper and lower horizontal wire members is typically about 2 to 3 times the height of the two vert ...
The Tenna-Tune
... The circuit is shown in Figure 1, and the parts list is shown in Table 1. This is just a resistive 50-ohm bridge coupled with an IC-706MKIIG “tune” interface. The bridge is the same I used in my previous article “Add an absorptive SWR indicator to the MFJ-902 antenna tuner” in the October 2005 QST. ...
... The circuit is shown in Figure 1, and the parts list is shown in Table 1. This is just a resistive 50-ohm bridge coupled with an IC-706MKIIG “tune” interface. The bridge is the same I used in my previous article “Add an absorptive SWR indicator to the MFJ-902 antenna tuner” in the October 2005 QST. ...
Chapter 10 - Electrical, Antenna and RF Safety
... • Confine antenna radiation to the radiating elements. Provide a single, good station ground, and eliminate radiation from transmission lines. Use good coaxial cable, not open-wire lines or end-fed antennas that come directly into the transmitter area. • No person should near any transmitting antenn ...
... • Confine antenna radiation to the radiating elements. Provide a single, good station ground, and eliminate radiation from transmission lines. Use good coaxial cable, not open-wire lines or end-fed antennas that come directly into the transmitter area. • No person should near any transmitting antenn ...
k18v2. fm transmitter
... problem with this type of circuit is that any external load (antenna) will change the operating frequency. This is normal. If the antenna load is heavy then the transmitter could be moved off frequency by 1MHz, or perhaps even more. The tuned coil, L1, has two output tappings for the antenna connect ...
... problem with this type of circuit is that any external load (antenna) will change the operating frequency. This is normal. If the antenna load is heavy then the transmitter could be moved off frequency by 1MHz, or perhaps even more. The tuned coil, L1, has two output tappings for the antenna connect ...
Communications
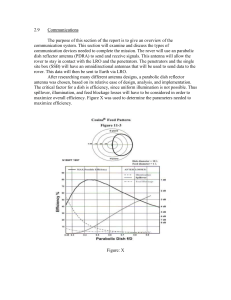
... dish reflector antenna (PDRA) to send and receive signals. This antenna will allow the rover to stay in contact with the LRO and the penetrators. The penetrators and the single site box (SSB) will have an omnidirectional antennas that will be used to send data to the rover. This data will then be se ...
... dish reflector antenna (PDRA) to send and receive signals. This antenna will allow the rover to stay in contact with the LRO and the penetrators. The penetrators and the single site box (SSB) will have an omnidirectional antennas that will be used to send data to the rover. This data will then be se ...
COST 286 – Joint technical action 1 (JTA1)
... In this work, NEC is used to calculate the currents for different cable-antenna setups. The termination resistance is realized by adding a single wire connecting cable and ground. This wire was set to 150 Ohm resistance (i.e. loaded) via LD NEC card. The basic principle of obtaining a voltage drop o ...
... In this work, NEC is used to calculate the currents for different cable-antenna setups. The termination resistance is realized by adding a single wire connecting cable and ground. This wire was set to 150 Ohm resistance (i.e. loaded) via LD NEC card. The basic principle of obtaining a voltage drop o ...
Radio Communications Principles
... • Antenna gain is defined as the power output, in a particular direction compared to that produced in any direction by a perfect isotropic omnidirectional antenna • If an antenna has a gain of 3dB, that antenna improves on the isotropic antenna in that direction by 3dB, or a factor of 2 (100.3) • Th ...
... • Antenna gain is defined as the power output, in a particular direction compared to that produced in any direction by a perfect isotropic omnidirectional antenna • If an antenna has a gain of 3dB, that antenna improves on the isotropic antenna in that direction by 3dB, or a factor of 2 (100.3) • Th ...
Exam-Prep Jepperdee
... Each numeric point value on either game board is a hyperlink which reveals a question. Advancing the game one slide past a question (by clicking the screen) displays its answer. Clicking “Back” on the answer slide returns you to the game board. “SFJ” stands for “semi-final jepperdee” and “FJ” means ...
... Each numeric point value on either game board is a hyperlink which reveals a question. Advancing the game one slide past a question (by clicking the screen) displays its answer. Clicking “Back” on the answer slide returns you to the game board. “SFJ” stands for “semi-final jepperdee” and “FJ” means ...
Wireless Media
... Measure of directionality of antenna Defined as the output power in particular direction compared to that produced by an isotropic antenna The antenna gain is related to the effective area of an antenna: ...
... Measure of directionality of antenna Defined as the output power in particular direction compared to that produced by an isotropic antenna The antenna gain is related to the effective area of an antenna: ...
Exam-Prep Jepperdee: Technician Edition
... To reduce high voltage discharge from the tip of the antenna back ...
... To reduce high voltage discharge from the tip of the antenna back ...
Document
... vice versa. It is usually used with a radio transmitter or radio receiver. In transmission a radio transmitter supplies an oscillating radio frequency electric current to the antenna's terminals, and the antenna radiates the energy from the current as electromagnet waves (radio waves). In reception, ...
... vice versa. It is usually used with a radio transmitter or radio receiver. In transmission a radio transmitter supplies an oscillating radio frequency electric current to the antenna's terminals, and the antenna radiates the energy from the current as electromagnet waves (radio waves). In reception, ...
– BGB719N7ESD Radio Without Limits
... High input impedance, high gain, low noise amplifiers with small footprints and high robustness against electrostatic discharge (ESD) are key success factors in active antenna designs. Infineon’s latest generation LNA, the BGB719N7ESD, meets today’s embedded active FM and mobile TV antenna design ch ...
... High input impedance, high gain, low noise amplifiers with small footprints and high robustness against electrostatic discharge (ESD) are key success factors in active antenna designs. Infineon’s latest generation LNA, the BGB719N7ESD, meets today’s embedded active FM and mobile TV antenna design ch ...
Spring10E1
... 9. If the frequency of a sine wave is 830 kHz determine the Wave length. λ = v/f = 3(108m/s)/830(103c/s) = 361.45m 10. What kind of antenna, dipole or vertical, is used for AM antennas? Vertical 11. Determine the VSWR if Emax = 100V and Emin = 80V. VSWR = 100/80 = 1.25:1 ...
... 9. If the frequency of a sine wave is 830 kHz determine the Wave length. λ = v/f = 3(108m/s)/830(103c/s) = 361.45m 10. What kind of antenna, dipole or vertical, is used for AM antennas? Vertical 11. Determine the VSWR if Emax = 100V and Emin = 80V. VSWR = 100/80 = 1.25:1 ...
Antenna (radio)

An antenna (plural antennae or antennas), or aerial, is an electrical device which converts electric power into radio waves, and vice versa. It is usually used with a radio transmitter or radio receiver. In transmission, a radio transmitter supplies an electric current oscillating at radio frequency (i.e. a high frequency alternating current (AC)) to the antenna's terminals, and the antenna radiates the energy from the current as electromagnetic waves (radio waves). In reception, an antenna intercepts some of the power of an electromagnetic wave in order to produce a tiny voltage at its terminals, that is applied to a receiver to be amplified.Antennas are essential components of all equipment that uses radio. They are used in systems such as radio broadcasting, broadcast television, two-way radio, communications receivers, radar, cell phones, and satellite communications, as well as other devices such as garage door openers, wireless microphones, Bluetooth-enabled devices, wireless computer networks, baby monitors, and RFID tags on merchandise.Typically an antenna consists of an arrangement of metallic conductors (elements), electrically connected (often through a transmission line) to the receiver or transmitter. An oscillating current of electrons forced through the antenna by a transmitter will create an oscillating magnetic field around the antenna elements, while the charge of the electrons also creates an oscillating electric field along the elements. These time-varying fields radiate away from the antenna into space as a moving transverse electromagnetic field wave. Conversely, during reception, the oscillating electric and magnetic fields of an incoming radio wave exert force on the electrons in the antenna elements, causing them to move back and forth, creating oscillating currents in the antenna.Antennas can be designed to transmit and receive radio waves in all horizontal directions equally (omnidirectional antennas), or preferentially in a particular direction (directional or high gain antennas). In the latter case, an antenna may also include additional elements or surfaces with no electrical connection to the transmitter or receiver, such as parasitic elements, parabolic reflectors or horns, which serve to direct the radio waves into a beam or other desired radiation pattern.The first antennas were built in 1888 by German physicist Heinrich Hertz in his pioneering experiments to prove the existence of electromagnetic waves predicted by the theory of James Clerk Maxwell. Hertz placed dipole antennas at the focal point of parabolic reflectors for both transmitting and receiving. He published his work in Annalen der Physik und Chemie (vol. 36, 1889).