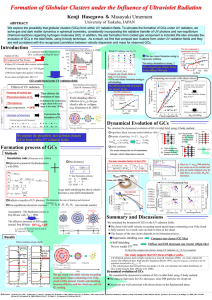
Full Text Report
... model. Dielectronic recombination processes involving autoionization states of Ne-like ions and higher are treated explicitly, with electron capture rates determined from detailed balance with their corresponding autoionization rates. For lower ionization stages, autoionization states are not explic ...
... model. Dielectronic recombination processes involving autoionization states of Ne-like ions and higher are treated explicitly, with electron capture rates determined from detailed balance with their corresponding autoionization rates. For lower ionization stages, autoionization states are not explic ...
wavelength
... systems always seek the lowest available energy state. • This means that atoms with electrons in excited levels will rapidly `de-excite’ and spit out a photon to conserve energy. ...
... systems always seek the lowest available energy state. • This means that atoms with electrons in excited levels will rapidly `de-excite’ and spit out a photon to conserve energy. ...
PH607 The Physics of Stars
... In the cool outer layers of a star, the gas is only partially ionized, much of the heat used to raise the temperature of the gas goes into ...
... In the cool outer layers of a star, the gas is only partially ionized, much of the heat used to raise the temperature of the gas goes into ...
solutions
... dark energy is a hypothetical form of energy that permeates all of space and tends to increase the rate of expansion of the universe. The idea of dark energy was invented to explain recent observations that the Universe appears to be expanding at an accelerating rate. In the standard model of cosmol ...
... dark energy is a hypothetical form of energy that permeates all of space and tends to increase the rate of expansion of the universe. The idea of dark energy was invented to explain recent observations that the Universe appears to be expanding at an accelerating rate. In the standard model of cosmol ...
2006ph607chapterone
... In the cool outer layers of a star, the gas is only partially ionized, much of the heat used to raise the temperature of the gas goes into ionization and hence cv and cp are nearly same ~1. A star can have an outer convective layer ...
... In the cool outer layers of a star, the gas is only partially ionized, much of the heat used to raise the temperature of the gas goes into ionization and hence cv and cp are nearly same ~1. A star can have an outer convective layer ...
HEA_Pulsars
... superconducting (s and both very large) Neutron stars very dense and zero-T energy supports star and prevents collapse. ...
... superconducting (s and both very large) Neutron stars very dense and zero-T energy supports star and prevents collapse. ...
COSMIC RAY ACCELERATION and TRANSPORT LECTURE I
... From the previous plot we see that at low energies P/S ~ 0.1 which implies X(E) ~ 5 g cm-2 As a function of energy: ...
... From the previous plot we see that at low energies P/S ~ 0.1 which implies X(E) ~ 5 g cm-2 As a function of energy: ...
Section I. SpuItering of ices ASTROPHYSICAL IMPLICATIONS OF
... because of the preferential erosion of NH, compared to H,O [44]. The magnetosphere particles decrease in intensity at the edge of the major A ring, so that there do not appear to be significant effects by the particles on the principal rings of Saturn. However, galactic cosmic rays do strike these r ...
... because of the preferential erosion of NH, compared to H,O [44]. The magnetosphere particles decrease in intensity at the edge of the major A ring, so that there do not appear to be significant effects by the particles on the principal rings of Saturn. However, galactic cosmic rays do strike these r ...
Neutron Stars and Black Holes
... evolution of stars with magnetic fields. b)! Supernova of a massive star, leaving a neutron core mass of 1.4 to 3 solar masses. c)! By evolution from a supergiant to a compact, hot, but pulsing star. d)! Through the evolution of a binary system. e)! They are ET communication encoders, emitting faste ...
... evolution of stars with magnetic fields. b)! Supernova of a massive star, leaving a neutron core mass of 1.4 to 3 solar masses. c)! By evolution from a supergiant to a compact, hot, but pulsing star. d)! Through the evolution of a binary system. e)! They are ET communication encoders, emitting faste ...
5 April 2012—Gravitational waves 12 Apr 2012 Radiation from a source
... The behavior P ∂ P-53 will be discussed the next class. Q: Simplicio: If a system loses energy, it should slow down, not speed up. What is wrong with Simplicio's thinking when applied to the binary pulsar? dPdt ...
... The behavior P ∂ P-53 will be discussed the next class. Q: Simplicio: If a system loses energy, it should slow down, not speed up. What is wrong with Simplicio's thinking when applied to the binary pulsar? dPdt ...
Document
... • visual pollution • dependency on wind speed • appropriate space and position needed. ...
... • visual pollution • dependency on wind speed • appropriate space and position needed. ...
Hygienic bases layout and building of settlements
... Conduct data collection, analysis and synthesis, ...
... Conduct data collection, analysis and synthesis, ...
Nuclear reactions in the Sun
... • The knowledge of M, R, L and age immediately determines the physical scales (T, P, r) of the solar interior and shows that nuclear reactions are the only sufficient source of solar power. • Helioseismology provides an accurate picture of the solar interior. It measures sound speed, not temperature ...
... • The knowledge of M, R, L and age immediately determines the physical scales (T, P, r) of the solar interior and shows that nuclear reactions are the only sufficient source of solar power. • Helioseismology provides an accurate picture of the solar interior. It measures sound speed, not temperature ...
Magnetic Monopoles
... Experiments are conducted to measure a flux of magnetic monopoles that hit the earth as cosmic rays ...
... Experiments are conducted to measure a flux of magnetic monopoles that hit the earth as cosmic rays ...
Dec. 6 - UF Physics
... • All the solutions to E’s equations which give Hubbard’s law have singularities • Einstein thought that singularities such as these indicated that there were important physical effects not accounted for in his equations. He also thought that the right answer would involve static behavior: large-sca ...
... • All the solutions to E’s equations which give Hubbard’s law have singularities • Einstein thought that singularities such as these indicated that there were important physical effects not accounted for in his equations. He also thought that the right answer would involve static behavior: large-sca ...
Coupling and Collapse
... thermalization since there is no exchange of energy between the photons and the electrons. 3. Generally scattering with exchange of energy is called Compton scattering. 4. Compton scattering however does not change the number of photons as it could be done, for instance, by free – free transitions. ...
... thermalization since there is no exchange of energy between the photons and the electrons. 3. Generally scattering with exchange of energy is called Compton scattering. 4. Compton scattering however does not change the number of photons as it could be done, for instance, by free – free transitions. ...
The Quadrupole Cusp: A Universal Accelerator, or From Radiation
... Details of Injection (#1&5) • They have a 24-48 hour typical rise time from a SW disturbance (shock, Dst storm, etc.) But can be as short as 8 hr (Jan 97) or as long as 72 hours. • The intensity roughly follows a solar cycle dependence but can vary by 3 orders of magnitude • The spectral hardness g ...
... Details of Injection (#1&5) • They have a 24-48 hour typical rise time from a SW disturbance (shock, Dst storm, etc.) But can be as short as 8 hr (Jan 97) or as long as 72 hours. • The intensity roughly follows a solar cycle dependence but can vary by 3 orders of magnitude • The spectral hardness g ...
Radiation Processes in High Energy Astrophysics
... down to the temperature of the thermal background gas (plasma) power-law spectrum of positrons E+ ...
... down to the temperature of the thermal background gas (plasma) power-law spectrum of positrons E+ ...
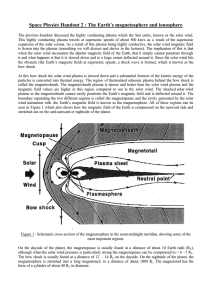
Space Physics Handout 2 : The Earth`s magnetosphere and
... the Sun; ionisation increases in the sunlit atmosphere and decreases on the shadowed side. The ionosphere extends to rather high altitudes and at low and mid-latitudes gradually merges into the plasmasphere which was mentioned above. At high latitudes plasma sheet electrons can precipitate along mag ...
... the Sun; ionisation increases in the sunlit atmosphere and decreases on the shadowed side. The ionosphere extends to rather high altitudes and at low and mid-latitudes gradually merges into the plasmasphere which was mentioned above. At high latitudes plasma sheet electrons can precipitate along mag ...
Health threat from cosmic rays

The health threat from cosmic rays is the danger posed by galactic cosmic rays and solar energetic particles to astronauts on interplanetary missions. Galactic cosmic rays (GCRs) consist of high energy protons (85%), helium (14%) and other high energy nuclei (HZE ions). Solar energetic particles consist primarily of protons accelerated by the Sun to high energies via proximity to solar flares and coronal mass ejections. They are one of the most important barriers standing in the way of plans for interplanetary travel by crewed spacecraft.