ppt
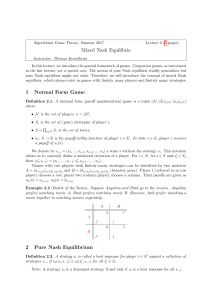
... Gain Floor, Loss Ceiling, Saddle Point, Value of Game The Gain Floor of a two-player zero-sum game A, written (A), is the worst outcome for player 1 if he picks his best strategy i*: (A) =min j A i*,j The Loss Ceiling (likewise) is the best outcome for player 1 (hence worst for player 2) if playe ...
... Gain Floor, Loss Ceiling, Saddle Point, Value of Game The Gain Floor of a two-player zero-sum game A, written (A), is the worst outcome for player 1 if he picks his best strategy i*: (A) =min j A i*,j The Loss Ceiling (likewise) is the best outcome for player 1 (hence worst for player 2) if playe ...
state based potential games
... - We provide a systematic methodology for localizing the agents’ objective functions while ensuing that the resulting equilibria are optimal with regards to the system level objective function. - It is proved that the learning algorithm gradient play guarantees convergence to a stationary state NE i ...
... - We provide a systematic methodology for localizing the agents’ objective functions while ensuing that the resulting equilibria are optimal with regards to the system level objective function. - It is proved that the learning algorithm gradient play guarantees convergence to a stationary state NE i ...
Game Balancing Theory
... Any successful strategy for one side can be used by both sides Success is derived from execution, not strategy Or success is derived from fine details (a pawn in Chess) ...
... Any successful strategy for one side can be used by both sides Success is derived from execution, not strategy Or success is derived from fine details (a pawn in Chess) ...
Proofs_A4_Review - Kelvin-2011-2012-Sem02
... number dimensions will always be an odd number. Search for a counterexample to his claim. ...
... number dimensions will always be an odd number. Search for a counterexample to his claim. ...
OPEC Debrief - Faculty Directory | Berkeley-Haas
... 1. What is the prescription for successful cooperation in OPEC? Successful cooperation requires incorporating several of the elements we highlighted in class: clarity in what the price targets are and what happens if they’re not met, clear statement and actual enforcement of punishment strategies (t ...
... 1. What is the prescription for successful cooperation in OPEC? Successful cooperation requires incorporating several of the elements we highlighted in class: clarity in what the price targets are and what happens if they’re not met, clear statement and actual enforcement of punishment strategies (t ...
1 - contentextra
... actions) based on the predicted behavior of their competitors. If a large firm competing with other large firms understands the various ‘payoffs’ (referring to the profits or losses that will result from a particular economic decision made by itself and its competitors) then it will be better able t ...
... actions) based on the predicted behavior of their competitors. If a large firm competing with other large firms understands the various ‘payoffs’ (referring to the profits or losses that will result from a particular economic decision made by itself and its competitors) then it will be better able t ...
Game Theory - Department of computing science
... These describe the evolution of the frequencies with which different strategies occur in the population Assume we have n types in the population with frequencies x1 to xn. As above, the fitness fi will be a function of the state x = (x1, x2, . . . , xn). We assume that the population is large enough ...
... These describe the evolution of the frequencies with which different strategies occur in the population Assume we have n types in the population with frequencies x1 to xn. As above, the fitness fi will be a function of the state x = (x1, x2, . . . , xn). We assume that the population is large enough ...
States as Game Players The Example of Russia, China and
... Then, how to model this multi-polarization of relations between states? The issue is even more complex than, according to circumstances the States are mutually sometimes partners and sometimes opponents (Evans, Graham and Newnham, Jeffrey (1998)). Facing with these developments, the States both have ...
... Then, how to model this multi-polarization of relations between states? The issue is even more complex than, according to circumstances the States are mutually sometimes partners and sometimes opponents (Evans, Graham and Newnham, Jeffrey (1998)). Facing with these developments, the States both have ...
a ppt file
... • Players can reach Nash equilibrium only by rational reasoning in some games, e.g., Prisoners’ dilemma. • However, rationality alone is often insufficient to lead to NE. (see Battle of the sexes, Hawk-Dove game, etc.) • A common (and correct) belief about future actions combined with rationality is ...
... • Players can reach Nash equilibrium only by rational reasoning in some games, e.g., Prisoners’ dilemma. • However, rationality alone is often insufficient to lead to NE. (see Battle of the sexes, Hawk-Dove game, etc.) • A common (and correct) belief about future actions combined with rationality is ...
Evolutionary game theory

Evolutionary game theory (EGT) is the application of game theory to evolving populations of lifeforms in biology. EGT is useful in this context by defining a framework of contests, strategies, and analytics into which Darwinian competition can be modelled. EGT originated in 1973 with John Maynard Smith and George R. Price's formalisation of the way in which such contests can be analysed as ""strategies"" and the mathematical criteria that can be used to predict the resulting prevalence of such competing strategies.Evolutionary game theory differs from classical game theory by focusing more on the dynamics of strategy change as influenced not solely by the quality of the various competing strategies, but by the effect of the frequency with which those various competing strategies are found in the population.Evolutionary game theory has proven itself to be invaluable in helping to explain many complex and challenging aspects of biology. It has been particularly helpful in establishing the basis of altruistic behaviours within the context of Darwinian process. Despite its origin and original purpose, evolutionary game theory has become of increasing interest to economists, sociologists, anthropologists, and philosophers.