Imagine-self perspective-taking promotes Nash choices in - E-SGH
... As already mentioned, the row players may choose non-Nash equilibrium strategy because of rational expectations that (i) the column player is not fully rational or (ii) is motivated to act in a not self-interested manner. The latter can be at least partially explained by social value orientation (S ...
... As already mentioned, the row players may choose non-Nash equilibrium strategy because of rational expectations that (i) the column player is not fully rational or (ii) is motivated to act in a not self-interested manner. The latter can be at least partially explained by social value orientation (S ...
updated version for the 2015 Superbowl
... Definition: A combination of strategies is a Nash (non-cooperative) equilibrium if each player’s strategy is best, given the strategies chosen by the other players. The Nash equilibrium is a “mutual best response” in the sense that each player is correctly assessing the strategies of all other playe ...
... Definition: A combination of strategies is a Nash (non-cooperative) equilibrium if each player’s strategy is best, given the strategies chosen by the other players. The Nash equilibrium is a “mutual best response” in the sense that each player is correctly assessing the strategies of all other playe ...
10/(1+ δ)
... Cooperation is sustained if the expected value of cooperation exceeds the expected value of defection: 3 / (1 – δ) > (10 - 9δ) / (1 – δ), or 3 > 10 - 9δ, or 7 < 9δ δ > or equal to 7 / 9, then cooperation can be sustained. Strategy is: Play C as long as opponent played C in all previous rounds; if op ...
... Cooperation is sustained if the expected value of cooperation exceeds the expected value of defection: 3 / (1 – δ) > (10 - 9δ) / (1 – δ), or 3 > 10 - 9δ, or 7 < 9δ δ > or equal to 7 / 9, then cooperation can be sustained. Strategy is: Play C as long as opponent played C in all previous rounds; if op ...
Evolutionary Game Theory: The Game of Life
... limiting resources (e.g. food, water, space, mates, safety, etc.). You may have previously considered adaptations due to the physical phenotype of the organisms. This unit will look specifically at behavioral choices made to obtain the resources organisms need for survival and for reproduction. You ...
... limiting resources (e.g. food, water, space, mates, safety, etc.). You may have previously considered adaptations due to the physical phenotype of the organisms. This unit will look specifically at behavioral choices made to obtain the resources organisms need for survival and for reproduction. You ...
Slides - The collected game design rants of Marc LeBlanc
... Mechanics vs. Dynamics • There’s a grey area Some behaviors are direct consequences of rules. Others are indirect. “Dynamics” usually means the latter. ...
... Mechanics vs. Dynamics • There’s a grey area Some behaviors are direct consequences of rules. Others are indirect. “Dynamics” usually means the latter. ...
Social Decision Making Strategies in Internet Poker Playing
... devotes plenty of time on a regular basis to poker will have more hands and actions in memory. It will be easier for this particular player to refer to past events and experience and make new decisions in line with these memories. The participants also showed a frequent use of social information cue ...
... devotes plenty of time on a regular basis to poker will have more hands and actions in memory. It will be easier for this particular player to refer to past events and experience and make new decisions in line with these memories. The participants also showed a frequent use of social information cue ...
Robust equilibria and ε-dominance
... and similarly for the total global regret R(s). Since Rε and R are continuous on E, they attain minima, say at profiles s∗ and t∗ respectively. Then s∗ is an ε-robust equilibrium and t∗ is a globally ε-robust equilibrium. Definition 6. For a game G, let εG = inf{ε ≥ 0|Ai ⊆ Ei (ε) for all i ∈ I}. εG ...
... and similarly for the total global regret R(s). Since Rε and R are continuous on E, they attain minima, say at profiles s∗ and t∗ respectively. Then s∗ is an ε-robust equilibrium and t∗ is a globally ε-robust equilibrium. Definition 6. For a game G, let εG = inf{ε ≥ 0|Ai ⊆ Ei (ε) for all i ∈ I}. εG ...
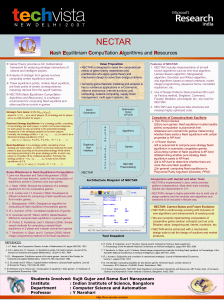
NECTAR: Nash Equilibrium Computation Algorithms
... other equilibrium points in games. Strategic Form Game: G=(N,(Si)iЄN,(ui)iЄN), where N = {1,2,…,n} is set of players, Si is strategy set for player i and ui is utility function for player i. Dominant Strategy Equilibrium: It is a strategy profile, consisting of one strategy per each player, in which ...
... other equilibrium points in games. Strategic Form Game: G=(N,(Si)iЄN,(ui)iЄN), where N = {1,2,…,n} is set of players, Si is strategy set for player i and ui is utility function for player i. Dominant Strategy Equilibrium: It is a strategy profile, consisting of one strategy per each player, in which ...
Evolutionary game theory

Evolutionary game theory (EGT) is the application of game theory to evolving populations of lifeforms in biology. EGT is useful in this context by defining a framework of contests, strategies, and analytics into which Darwinian competition can be modelled. EGT originated in 1973 with John Maynard Smith and George R. Price's formalisation of the way in which such contests can be analysed as ""strategies"" and the mathematical criteria that can be used to predict the resulting prevalence of such competing strategies.Evolutionary game theory differs from classical game theory by focusing more on the dynamics of strategy change as influenced not solely by the quality of the various competing strategies, but by the effect of the frequency with which those various competing strategies are found in the population.Evolutionary game theory has proven itself to be invaluable in helping to explain many complex and challenging aspects of biology. It has been particularly helpful in establishing the basis of altruistic behaviours within the context of Darwinian process. Despite its origin and original purpose, evolutionary game theory has become of increasing interest to economists, sociologists, anthropologists, and philosophers.