Managerial Economics
... The relative cost of organising transaction through different forms of governance determined by: • Extent to which complete contracts are possible. Where contract refers to agreement between two parties which could be explicit or not. • Extent to which there is a threat of opportunism by parties in ...
... The relative cost of organising transaction through different forms of governance determined by: • Extent to which complete contracts are possible. Where contract refers to agreement between two parties which could be explicit or not. • Extent to which there is a threat of opportunism by parties in ...
Practice Problems II Answers
... (If both drive a hard bargain, there’s no deal, so there’s zero change relative to the baseline. If both drive an easy bargain, Hector pays $700 for a $1000 gain, and Menelaus receives $700 for accepting a $400 loss, yielding net $300 each. If Hector drives an easy bargain and Menelaus a hard barga ...
... (If both drive a hard bargain, there’s no deal, so there’s zero change relative to the baseline. If both drive an easy bargain, Hector pays $700 for a $1000 gain, and Menelaus receives $700 for accepting a $400 loss, yielding net $300 each. If Hector drives an easy bargain and Menelaus a hard barga ...
CUR 412: Game Theory and its Applications Final
... Q2. (24 pts) Consider two firms that play a Cournot duopoly game with inverse demand p = 100 − q and costs for each firm given by ci (qi ) = 10qi . Suppose that before the Cournot duopoly game, Firm 1 can choose to invest in cost reduction. If Firm 1 does, then it must pay a one-time cost of F , an ...
... Q2. (24 pts) Consider two firms that play a Cournot duopoly game with inverse demand p = 100 − q and costs for each firm given by ci (qi ) = 10qi . Suppose that before the Cournot duopoly game, Firm 1 can choose to invest in cost reduction. If Firm 1 does, then it must pay a one-time cost of F , an ...
Emergence of cooperation and evolutionary stability in finite
... ESS concept is neither necessary nor sufficient; for large populations, it is necessary but not sufficient (Fig 3). If we consider a game with many different strategies, then the two conditions must hold in paiwise comparison with every other strategy. Summing up, (i) in finite populations, natural ...
... ESS concept is neither necessary nor sufficient; for large populations, it is necessary but not sufficient (Fig 3). If we consider a game with many different strategies, then the two conditions must hold in paiwise comparison with every other strategy. Summing up, (i) in finite populations, natural ...
Prcpt04.pdf
... But it is risky - if Row has misunderstood the game, or his hand trembles when he is making the choice, then Right may get Column a very bad payoff. So many Column players might choose the safer Left. This can be justified as a Nash equilibrium of a richer game where the possibility of Row making an ...
... But it is risky - if Row has misunderstood the game, or his hand trembles when he is making the choice, then Right may get Column a very bad payoff. So many Column players might choose the safer Left. This can be justified as a Nash equilibrium of a richer game where the possibility of Row making an ...
Game Theory and Strategic Behaviour
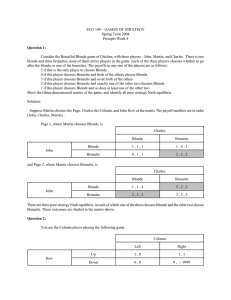
... Payoffs: The cost/benefit that each player gets from each possible outcome of the game (the prison sentences entered in each cell of the matrix) ...
... Payoffs: The cost/benefit that each player gets from each possible outcome of the game (the prison sentences entered in each cell of the matrix) ...
Mixed Nash Equilibria 1 Normal Form Game 2 Pure Nash Equilibrium
... Proof of Theorem 2.11. Consider a finite normal form game. Without loss of generality let N = {1, . . . , n}, Si = {1, . . . , mi }. So the set of mixed states X can be considered a subset of P Rm with m = ni=1 mi . Exercise: Show that X is convex and compact. We will define a function f : X → X tha ...
... Proof of Theorem 2.11. Consider a finite normal form game. Without loss of generality let N = {1, . . . , n}, Si = {1, . . . , mi }. So the set of mixed states X can be considered a subset of P Rm with m = ni=1 mi . Exercise: Show that X is convex and compact. We will define a function f : X → X tha ...
gs2.aamas07 - Carnegie Mellon School of Computer Science
... • Sequence form: More compact representation based on sequences of moves rather than pure strategies [Romanovskii 62, Koller & Megiddo 92, von Stengel 96] – Two-person zero-sum games can be solved in time polynomial in size of game tree – Doesn’t scale to Rhode Island Hold’em (3.1 billion nodes) or ...
... • Sequence form: More compact representation based on sequences of moves rather than pure strategies [Romanovskii 62, Koller & Megiddo 92, von Stengel 96] – Two-person zero-sum games can be solved in time polynomial in size of game tree – Doesn’t scale to Rhode Island Hold’em (3.1 billion nodes) or ...
Salop Model of Product Differentiation Consumers are located
... So far, we have assumed that players’ randomisations (when they play mixed strategies) are independent. In the 2×2 coordination games considered earlier, for instance, we can describe the mixed strategy equilibrium as follows: ...
... So far, we have assumed that players’ randomisations (when they play mixed strategies) are independent. In the 2×2 coordination games considered earlier, for instance, we can describe the mixed strategy equilibrium as follows: ...
Game Theory - Department of computing science
... King-cobra males try to push each-other’s heads to the ground rather than biting Stags have roaring matches, walk parallel, and sometimes lock horns and push rather than trying to kill each-other When cats fight they scream more than they actually fight The more dangerous the species, the more ritua ...
... King-cobra males try to push each-other’s heads to the ground rather than biting Stags have roaring matches, walk parallel, and sometimes lock horns and push rather than trying to kill each-other When cats fight they scream more than they actually fight The more dangerous the species, the more ritua ...
Chapter 29
... since we have actually seen some types of equilibria last time. • Game theory is concerned with the general analysis of strategic interaction. It can be used to study parlor games, political negotiation, and economic behaviors. ...
... since we have actually seen some types of equilibria last time. • Game theory is concerned with the general analysis of strategic interaction. It can be used to study parlor games, political negotiation, and economic behaviors. ...
Repeated Games - UCSB Economics
... of the game, it does not seem empirically plausible – why? Under the enter/accommodate equilibrium, the incumbent earns a payoff of 2x20 =40. But perhaps he can do better, for instance, suppose the incumbent chooses to fight the first 15 rivals and accommodate the last 5. If this strategy this is co ...
... of the game, it does not seem empirically plausible – why? Under the enter/accommodate equilibrium, the incumbent earns a payoff of 2x20 =40. But perhaps he can do better, for instance, suppose the incumbent chooses to fight the first 15 rivals and accommodate the last 5. If this strategy this is co ...