Nash equilibrium and its proof using Fix Point Theorems
... • Sperner’s lemma claims that there exists at least one small triangle (i.e. not the big triangle we started with) whose vertices are labeled with three different numbers. Sperner’s lemma can be generalized to n-dimensional simplex. Proof: We first proof Sperner’s lemma is correct in 1-dimensional ...
... • Sperner’s lemma claims that there exists at least one small triangle (i.e. not the big triangle we started with) whose vertices are labeled with three different numbers. Sperner’s lemma can be generalized to n-dimensional simplex. Proof: We first proof Sperner’s lemma is correct in 1-dimensional ...
Answers to Practice Questions 10
... JUST TO START 1) Game theory, when applied to an oligopoly situation, a) illustrates the tension between self-interest and cooperation. b) relies on the logic of firms pursing their own self-interests. c) relies on the notion that each firm chooses its best strategy, given the strategies that other ...
... JUST TO START 1) Game theory, when applied to an oligopoly situation, a) illustrates the tension between self-interest and cooperation. b) relies on the logic of firms pursing their own self-interests. c) relies on the notion that each firm chooses its best strategy, given the strategies that other ...
Team-Maxmin Equilibria
... particularly reasonable under a worst-case assumption, since the adversary may even get to know the team’s profile. The same defensive approach may be taken by the adversary of the team. In that case, she uses a minmax strategy by randomizing such that the largest expected payoff Žwhich is her cost. ...
... particularly reasonable under a worst-case assumption, since the adversary may even get to know the team’s profile. The same defensive approach may be taken by the adversary of the team. In that case, she uses a minmax strategy by randomizing such that the largest expected payoff Žwhich is her cost. ...
Game Theory and the Cuban Missile Crisis
... interactions. It applies to situations (games) where there are two or more people (called players) each attempting to choose between two more more ways of acting (called strategies). The possible outcomes of a game depend on the choices made by all players, and can be ranked in order of preference b ...
... interactions. It applies to situations (games) where there are two or more people (called players) each attempting to choose between two more more ways of acting (called strategies). The possible outcomes of a game depend on the choices made by all players, and can be ranked in order of preference b ...
Fast Computing of Restricted Nash Responses by Means of Sampling
... A (p, σf ix ) RNR equilibrium is a pair of strategies (σ1∗ , σ2∗ ) where σ2∗ ∈ BRp,σf ix (σ1∗ ) and σ1∗ ∈ BR(σ2∗ ). In this pair, the strategy σ1∗ is a p-restricted Nash response to σf ix . These are counter-strategies for σf ix , where p provides a balance between exploitation and exploitability. J ...
... A (p, σf ix ) RNR equilibrium is a pair of strategies (σ1∗ , σ2∗ ) where σ2∗ ∈ BRp,σf ix (σ1∗ ) and σ1∗ ∈ BR(σ2∗ ). In this pair, the strategy σ1∗ is a p-restricted Nash response to σf ix . These are counter-strategies for σf ix , where p provides a balance between exploitation and exploitability. J ...
Robust equilibria and ε-dominance
... second seems not to apply well to games with simple structures like centipede or traveler’s dilemma, especially with sophisticated agents,1 the third typically lacks specificity in its predictions, and the fourth depends on the choice both of a type of smoothing function and a diffusion parameter. ...
... second seems not to apply well to games with simple structures like centipede or traveler’s dilemma, especially with sophisticated agents,1 the third typically lacks specificity in its predictions, and the fourth depends on the choice both of a type of smoothing function and a diffusion parameter. ...
Lecture 8 (More on mixed strategies
... • In a two-player game, you might assume other player always does what is worst for you. • Given that assumption, you would choose the strategy such that gives you the best payoff available if the other player always does what is worst for you given your strategy. ...
... • In a two-player game, you might assume other player always does what is worst for you. • Given that assumption, you would choose the strategy such that gives you the best payoff available if the other player always does what is worst for you given your strategy. ...
Game theory and the Cuban missile crisis
... decision-making in social interactions. It applies to situations (games) where there are two or more people (called players) each attempting to choose between two more more ways of acting (called strategies). The possible outcomes of a game depend on the choices made by all players, and can be ranke ...
... decision-making in social interactions. It applies to situations (games) where there are two or more people (called players) each attempting to choose between two more more ways of acting (called strategies). The possible outcomes of a game depend on the choices made by all players, and can be ranke ...
Network Theory - Department of Mathematics
... In applications to chemistry, this quantity is ‘free energy’. Free energy always decreases, and takes its minimum value in equilibrium. This is a way of saying that entropy approaches a maximum subject to certain constraints. In certain evolutionary games, this result is related to Fisher’s Fundame ...
... In applications to chemistry, this quantity is ‘free energy’. Free energy always decreases, and takes its minimum value in equilibrium. This is a way of saying that entropy approaches a maximum subject to certain constraints. In certain evolutionary games, this result is related to Fisher’s Fundame ...
gt2 - Carnegie Mellon School of Computer Science
... • MIP Nash is best at finding optimal equilibria • Lemke-Howson and PNS are good at finding sample equilibria – M-Enum is an algorithm similar to Lemke-Howson for enumerating all equilibria ...
... • MIP Nash is best at finding optimal equilibria • Lemke-Howson and PNS are good at finding sample equilibria – M-Enum is an algorithm similar to Lemke-Howson for enumerating all equilibria ...
Multi-Agent Learning II: Algorithms - Stanford Artificial Intelligence
... Thus after five repetitions of the Rochambeau game in which the opponent played (R, S, P, R, P ), the current model of her mixed strategy is (R = .4, P = .4, S = .2). There exist many variants of the general scheme, for example those in which one does not play the exact best response in step 2. This ...
... Thus after five repetitions of the Rochambeau game in which the opponent played (R, S, P, R, P ), the current model of her mixed strategy is (R = .4, P = .4, S = .2). There exist many variants of the general scheme, for example those in which one does not play the exact best response in step 2. This ...
Topic 7. Market failure and the theory of second best
... behaviour. Strategies are a plan of how players (firms) will behave in particular states of the game (market conditions). Payoffs are the outcomes for each player (firm) that result from the actions of all players (firms). ...
... behaviour. Strategies are a plan of how players (firms) will behave in particular states of the game (market conditions). Payoffs are the outcomes for each player (firm) that result from the actions of all players (firms). ...
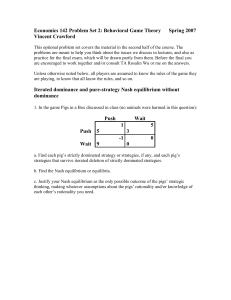
game_2
... as the payoff from for every possible choice of strategies by all of the other players. If the game has chance elements, we say that dominates if the mean payoff to X from (averaged over all choices by Nature) is always at least as great as that from . Two of X's strategies are equivalent ...
... as the payoff from for every possible choice of strategies by all of the other players. If the game has chance elements, we say that dominates if the mean payoff to X from (averaged over all choices by Nature) is always at least as great as that from . Two of X's strategies are equivalent ...
THE APPLICATION OF THE GAME THEORY TO THE
... of the actions of the competitor. As can be seen from the payoff matrix, if company A charges 5€, company B is more profitable if it charges the price of €5 (€50 compared to €35, which they would accrue if they charged €8 for their products). Also, if company B charges €5 for its products, it pays o ...
... of the actions of the competitor. As can be seen from the payoff matrix, if company A charges 5€, company B is more profitable if it charges the price of €5 (€50 compared to €35, which they would accrue if they charged €8 for their products). Also, if company B charges €5 for its products, it pays o ...
PRISM-games: A Model Checker for Stochastic Multi
... whilst adding novel model checking algorithms for stochastic games, as well as functionality to synthesise optimal player strategies, explore or export them, and verify other properties under the specified strategy. ...
... whilst adding novel model checking algorithms for stochastic games, as well as functionality to synthesise optimal player strategies, explore or export them, and verify other properties under the specified strategy. ...
6 The Mixing Problem: Purification and Conjectures
... implementation costs, but in this case they play a critical role in evaluating the relative costs of playing a mixed strategy best response or any of the pure strategies in its support. Hence the mixing problem: why bother ...
... implementation costs, but in this case they play a critical role in evaluating the relative costs of playing a mixed strategy best response or any of the pure strategies in its support. Hence the mixing problem: why bother ...
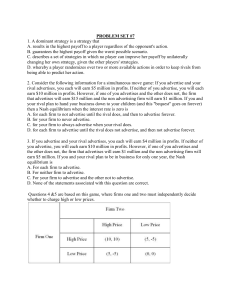
gameproblems
... costs associated with waterbed production are the initial costs of building a plant. This company has already invested in a plant capable of producing up to 25,000 beds and this is a sunk cost (and therefore irrelevant for current pricing decisions). (a) suppose a would-be entrant to this industry c ...
... costs associated with waterbed production are the initial costs of building a plant. This company has already invested in a plant capable of producing up to 25,000 beds and this is a sunk cost (and therefore irrelevant for current pricing decisions). (a) suppose a would-be entrant to this industry c ...
A Framework for Reasoning about Rational Agents
... to model and reason about rational behavior of agents. In our approach, some strategies (or rather strategy profiles) can be assumed plausible, and one can reason about what can be plausibly achieved by agents under such an assumption. This idea has been inspired by the way in which games are analyz ...
... to model and reason about rational behavior of agents. In our approach, some strategies (or rather strategy profiles) can be assumed plausible, and one can reason about what can be plausibly achieved by agents under such an assumption. This idea has been inspired by the way in which games are analyz ...