DEPARTMENT OF ANTHROPOLOGY TEACHER WORKSHOP
... FORENSIC ANTHROPOLOGY AT THE SMITHSONIAN Smithsonian physical anthropologists serve as regular consultants to the FBI and other law enforcement agencies to assist in forensic cases by examining the remains of unidentified deceased persons, especially when the remains have been partially or completel ...
... FORENSIC ANTHROPOLOGY AT THE SMITHSONIAN Smithsonian physical anthropologists serve as regular consultants to the FBI and other law enforcement agencies to assist in forensic cases by examining the remains of unidentified deceased persons, especially when the remains have been partially or completel ...
Geertz and Schneider – USA
... period: the 20 years between the end of world war II until the begin of the new radical movements in the late 1960s (=same time as the previous chapter) focus of this chapter: how new theories of symbolic meanings transformed the subject. USA <-> Britain, although they were cooping with the same pro ...
... period: the 20 years between the end of world war II until the begin of the new radical movements in the late 1960s (=same time as the previous chapter) focus of this chapter: how new theories of symbolic meanings transformed the subject. USA <-> Britain, although they were cooping with the same pro ...
Let us now praise famous women - South African Journal of Science
... For his account, Bank draws on an impressive body of sources, including the women’s scholarship, publications and writing, some of it unpublished field notes and papers, from public and private sources, including correspondence, photographs, interviews and communications with relatives. The chapters ...
... For his account, Bank draws on an impressive body of sources, including the women’s scholarship, publications and writing, some of it unpublished field notes and papers, from public and private sources, including correspondence, photographs, interviews and communications with relatives. The chapters ...
Chapter 4, Studying Culture: Approaches And Methods
... Label theses stages: Savagery, Barbarism, Civilization. Place any new cultures in the classification. Invent an explanation for why the people in one stage developed into the next stage. ...
... Label theses stages: Savagery, Barbarism, Civilization. Place any new cultures in the classification. Invent an explanation for why the people in one stage developed into the next stage. ...
Test No Topics for the Test
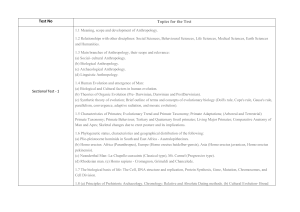
... 5. Religion: Anthropological approaches to the study of religion (evolutionary, psychological and functional); monotheism and polytheism; sacred and profane; myths and rituals; forms of religion in tribal and peasant societies (animism, animatism, fetishism, naturism and totemism); religion, magic a ...
... 5. Religion: Anthropological approaches to the study of religion (evolutionary, psychological and functional); monotheism and polytheism; sacred and profane; myths and rituals; forms of religion in tribal and peasant societies (animism, animatism, fetishism, naturism and totemism); religion, magic a ...
Anthropology 3
... and civilization according to the presence or absence of certain technological features. 1. Lower savagery-from earliest forms of humanity subsisting on fruits and nuts 2. Middle savagery-began with the discovery of fishing technology and the use of fire 3. Upper savagery-began with invention of bow ...
... and civilization according to the presence or absence of certain technological features. 1. Lower savagery-from earliest forms of humanity subsisting on fruits and nuts 2. Middle savagery-began with the discovery of fishing technology and the use of fire 3. Upper savagery-began with invention of bow ...
CULTURAL ANTHROPOLOGY
... and civilization according to the presence or absence of certain technological features. 1. Lower savagery-from earliest forms of humanity subsisting on fruits and nuts 2. Middle savagery-began with the discovery of fishing technology and the use of fire 3. Upper savagery-began with invention of bow ...
... and civilization according to the presence or absence of certain technological features. 1. Lower savagery-from earliest forms of humanity subsisting on fruits and nuts 2. Middle savagery-began with the discovery of fishing technology and the use of fire 3. Upper savagery-began with invention of bow ...
Chapter 1 Introduction
... response to internal or external stimuli. The response of an individual, group, or species to its environment. Such responses may or may not be deliberate and they aren’t necessarily the results of conscious decision making, as in one-celled organisms, insects, and many other species. ...
... response to internal or external stimuli. The response of an individual, group, or species to its environment. Such responses may or may not be deliberate and they aren’t necessarily the results of conscious decision making, as in one-celled organisms, insects, and many other species. ...
Chapter 1 - Cengage Learning
... biology and culture; the concept that biology makes culture possible and that developing culture influences the direction of biological evolution. ...
... biology and culture; the concept that biology makes culture possible and that developing culture influences the direction of biological evolution. ...
Nanda 3e PPTs Chapter 3
... Anthropologists must constantly re-consider the deep connections between cultures Conduct research on one’s own culture- Native anthropology ...
... Anthropologists must constantly re-consider the deep connections between cultures Conduct research on one’s own culture- Native anthropology ...
Neo-Evolutionism and Cultural Ecology
... Postmodernists view: science is itself a culturally determined phenomenon that is affected by class, race and other structural variables Do all food taboos have functional explanations; are such explanations intrinsically more satisfying than symbolic ones ...
... Postmodernists view: science is itself a culturally determined phenomenon that is affected by class, race and other structural variables Do all food taboos have functional explanations; are such explanations intrinsically more satisfying than symbolic ones ...
Visual Anthropology Cassie Wells Proposal for Individually Planned
... importance of the social contexts in which images are made, instead of viewing images as another form of “text”. Visual anthropologists emphasize these findings by analyzing photographic practice as cultural behavior, and by treating vernacular practices, such as snapshots, as ethnographic studies. ...
... importance of the social contexts in which images are made, instead of viewing images as another form of “text”. Visual anthropologists emphasize these findings by analyzing photographic practice as cultural behavior, and by treating vernacular practices, such as snapshots, as ethnographic studies. ...
BA in Anthropology
... Why study anthropology? Through the study of culture, anthropology offers students a set of tools and skills that help make sense of how human difference across both time and space is simultaneously preserved and threatened within an increasingly interconnected and globalized world. Archaeological a ...
... Why study anthropology? Through the study of culture, anthropology offers students a set of tools and skills that help make sense of how human difference across both time and space is simultaneously preserved and threatened within an increasingly interconnected and globalized world. Archaeological a ...
19th Century Anthropology
... natural as well as necessary sequence of progress (Ancient Society, 1877). Other quotations from a Scotsman, John F. MacLennan, or an Englishman, Edward B. Tylor, would take the same position. Cultural anthropology, then, set out to analyze the totality of human culture in time and space. But by ass ...
... natural as well as necessary sequence of progress (Ancient Society, 1877). Other quotations from a Scotsman, John F. MacLennan, or an Englishman, Edward B. Tylor, would take the same position. Cultural anthropology, then, set out to analyze the totality of human culture in time and space. But by ass ...
††††
... The world is shrinking in other ways as well. For better and for worse, satellite television, cellphone networks and the internet have created conditions for instantaneous and friction-free communications. Distance is no longer a decisive hindrance for close contact and new, deterritorialised social ...
... The world is shrinking in other ways as well. For better and for worse, satellite television, cellphone networks and the internet have created conditions for instantaneous and friction-free communications. Distance is no longer a decisive hindrance for close contact and new, deterritorialised social ...
Anthropology and Psychology
... functionnalism and structuralism) are successively presented, illustred and discussed. Each school of thought examined is also viewed like the occasion to examine the contributions to some great authors. For the psychological approach, we shall contrast the current findings concerning the mechanisms ...
... functionnalism and structuralism) are successively presented, illustred and discussed. Each school of thought examined is also viewed like the occasion to examine the contributions to some great authors. For the psychological approach, we shall contrast the current findings concerning the mechanisms ...
anthropology - UPSC Online
... Formalist and Substantivist debate; Principles governing production, distribution and exchange (reciprocity, redistribution and market), in communities, subsisting on hunting and gathering, fishing, swiddening, pastoralism, horticulture, and agriculture; globalization and indigenous economic system ...
... Formalist and Substantivist debate; Principles governing production, distribution and exchange (reciprocity, redistribution and market), in communities, subsisting on hunting and gathering, fishing, swiddening, pastoralism, horticulture, and agriculture; globalization and indigenous economic system ...
Current-Events-Activity-2
... Directions: Using a newspaper, magazine or the internet, please find an article that is related to social studies. (These could be articles about politics, society, economics, anthropology, archeology, culture etc.) Once you have found an article please read it entirely. Then attach it to this page ...
... Directions: Using a newspaper, magazine or the internet, please find an article that is related to social studies. (These could be articles about politics, society, economics, anthropology, archeology, culture etc.) Once you have found an article please read it entirely. Then attach it to this page ...
Chapter 8, Economics
... The worldwide process, dating back to the fall of the Berlin Wall, which involves a revolution in information technology, a dramatic opening of markets, and the privatization of social services. ...
... The worldwide process, dating back to the fall of the Berlin Wall, which involves a revolution in information technology, a dramatic opening of markets, and the privatization of social services. ...
No longer a marginal, or occulted, dimension, writing has emerged
... No longer a marginal, or occulted, dimension, writing has emerged as central to what anthropologist do both in the field and thereafter. The fact that it has not until recently been portrayed or seriously discussed reflects the persistence of an ideology claiming transparency of representation and i ...
... No longer a marginal, or occulted, dimension, writing has emerged as central to what anthropologist do both in the field and thereafter. The fact that it has not until recently been portrayed or seriously discussed reflects the persistence of an ideology claiming transparency of representation and i ...
Chapter 2 - Cengage Learning
... – The degree to which one’s observations and experiments can be reproduced. • Objectivity – The attempt to observe things as they are, without prejudging or falsifying observations in light of some preconceived view of the world. ...
... – The degree to which one’s observations and experiments can be reproduced. • Objectivity – The attempt to observe things as they are, without prejudging or falsifying observations in light of some preconceived view of the world. ...
Anthropology - BCI-SocialScienceSpace
... Physical Anthropology • Mechanisms of biological evolution, genetic inheritance, human adaptability and variation, primatology, and the fossil record of human evolution Cultural Anthropology • Culture, ethnocentrism, cultural aspects of language and communication, subsistence and other economic patt ...
... Physical Anthropology • Mechanisms of biological evolution, genetic inheritance, human adaptability and variation, primatology, and the fossil record of human evolution Cultural Anthropology • Culture, ethnocentrism, cultural aspects of language and communication, subsistence and other economic patt ...
STEM Career Spotlight - Forensic Anthropologist
... anatomy, biology, chemistry, physiology or anthropology as well as a graduate degree in human biology or anthropology. Most forensic anthropologists have a Ph.D. degree. Obtaining the highest level of academic achievement is important as this is not a high demand occupation and there are relatively ...
... anatomy, biology, chemistry, physiology or anthropology as well as a graduate degree in human biology or anthropology. Most forensic anthropologists have a Ph.D. degree. Obtaining the highest level of academic achievement is important as this is not a high demand occupation and there are relatively ...