
Permanent magnets - KCPE-KCSE
... exerts a constant force over a region. Such a field will consist of parallel equally spaced magnetic field lines. This type of field can almost be found between a north and south magnetic pole. ...
... exerts a constant force over a region. Such a field will consist of parallel equally spaced magnetic field lines. This type of field can almost be found between a north and south magnetic pole. ...
Magnetism and Electromagnetism
... • The right-hand rule can be used to establish the direction of the electromagnetic lines of force around a conductor. • An electromagnet is basically a coil of wire around a magnetic core. • When a conductor moves within a magnetic field, or when a magnetic field moves relative to a conductor, a vo ...
... • The right-hand rule can be used to establish the direction of the electromagnetic lines of force around a conductor. • An electromagnet is basically a coil of wire around a magnetic core. • When a conductor moves within a magnetic field, or when a magnetic field moves relative to a conductor, a vo ...
Class Notes - Ms. Shevlin`s Website
... • Three metals are attracted to magnets and can be made into magnets themselves. • These metals are iron, cobalt and nickel. • Other metals that are mixtures of these metals or alloys are also attracted to magnets. • Find out which materials you have contain one or more of these metals. ...
... • Three metals are attracted to magnets and can be made into magnets themselves. • These metals are iron, cobalt and nickel. • Other metals that are mixtures of these metals or alloys are also attracted to magnets. • Find out which materials you have contain one or more of these metals. ...
magnetism - scienceathawthorn
... A wire carrying an electric current also shows magnetic field lines around it. They obey the same rules as magnetic fields. The closer the lines are together the stronger the force. But does this attract or repel a magnet? That depends on which way the current is flowing. ...
... A wire carrying an electric current also shows magnetic field lines around it. They obey the same rules as magnetic fields. The closer the lines are together the stronger the force. But does this attract or repel a magnet? That depends on which way the current is flowing. ...
Magnet Lab - Warren County Schools
... the plastic bag, is not affected either. A magnetic field is strongest at the magnet's poles (the ends of a bar magnet). Each pole of a bar magnet has a different charge. You can see this by the different colors and the markings on the end: "S" for south and "N" for north. In magnets, opposite charg ...
... the plastic bag, is not affected either. A magnetic field is strongest at the magnet's poles (the ends of a bar magnet). Each pole of a bar magnet has a different charge. You can see this by the different colors and the markings on the end: "S" for south and "N" for north. In magnets, opposite charg ...
The Earth`s B-Field
... approximately 11.3° from the planet's axis of rotation. The cause of the field can be explained by dynamo theory. Dynamo theory describes the process through which a rotating, convecting, and electrically conducting fluid acts to maintain a magnetic field. In the case of the Earth, the magnetic fiel ...
... approximately 11.3° from the planet's axis of rotation. The cause of the field can be explained by dynamo theory. Dynamo theory describes the process through which a rotating, convecting, and electrically conducting fluid acts to maintain a magnetic field. In the case of the Earth, the magnetic fiel ...
Document
... 2. We demonstrate that the relative strength or weakness of the vertical flow asymmetry characteristic of stratified convection is uncorrelated with the net transport of magnetic flux into the lower half of a vertically closed, horizontally periodic Cartesian domain. Given an initially horizontal, u ...
... 2. We demonstrate that the relative strength or weakness of the vertical flow asymmetry characteristic of stratified convection is uncorrelated with the net transport of magnetic flux into the lower half of a vertically closed, horizontally periodic Cartesian domain. Given an initially horizontal, u ...
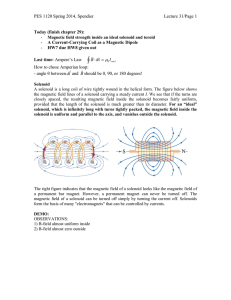
PES 1120 Spring 2014, Spendier Lecture 31/Page 1 Today (finish
... We turn now to the other aspect of a current-carrying coil as a magnetic dipole. What magnetic field does it produce at a point in the surrounding space? The problem does not have enough symmetry to make Ampere’s law useful; so we must turn to the law of Biot and Savart. For simplicity, we first con ...
... We turn now to the other aspect of a current-carrying coil as a magnetic dipole. What magnetic field does it produce at a point in the surrounding space? The problem does not have enough symmetry to make Ampere’s law useful; so we must turn to the law of Biot and Savart. For simplicity, we first con ...
Level 4 - PO 417-1-A
... Unfortunately, the magnetic poles do not coincide with the geographic poles. Furthermore, magnetic north changes position a little every year. Averaged over thousands of years, the position of magnetic north will roughly correspond with true north, but at any given time the two poles can be very far ...
... Unfortunately, the magnetic poles do not coincide with the geographic poles. Furthermore, magnetic north changes position a little every year. Averaged over thousands of years, the position of magnetic north will roughly correspond with true north, but at any given time the two poles can be very far ...
B - Fort Bend ISD
... where they were found. The Chinese used them for navigating ships in the 12th century. We know they contained iron ore which is called magnetite. ...
... where they were found. The Chinese used them for navigating ships in the 12th century. We know they contained iron ore which is called magnetite. ...
magnetics_intro
... Ferromagnetic and Ferrimagnetic materials generally made up of domains with uniform magnetic direction Within domains the magnetic moments of atoms are aligned The domains form when cooled below the Curie Temperature Magnetic domains (bands) visible in Microcystalline grains of NdFeB ...
... Ferromagnetic and Ferrimagnetic materials generally made up of domains with uniform magnetic direction Within domains the magnetic moments of atoms are aligned The domains form when cooled below the Curie Temperature Magnetic domains (bands) visible in Microcystalline grains of NdFeB ...
Geomagnetism. - Brock University
... North and south poles are the points of intersection of the axis of the magnetic field and the surface of the Earth. The axis of the magnetic field is at a small angle to the axis of rotation: termed the magnetic declination. The magnetic poles moves about the geographic poles: termed secular varia ...
... North and south poles are the points of intersection of the axis of the magnetic field and the surface of the Earth. The axis of the magnetic field is at a small angle to the axis of rotation: termed the magnetic declination. The magnetic poles moves about the geographic poles: termed secular varia ...
aurora_meeting - School of GeoSciences
... Kathy Whaler ([email protected]), School of GeoSciences, University of Edinburgh Mike Purucker, Planetary Geodynamics Laboratory, NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center, Maryland, USA ...
... Kathy Whaler ([email protected]), School of GeoSciences, University of Edinburgh Mike Purucker, Planetary Geodynamics Laboratory, NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center, Maryland, USA ...
ch-6 [Magnetism]
... • Ancient Greek and Chinese used stones exist in nature that have “magical” attractive properties later known as lodestone and magnetite (iron oxide Fe203) • These stones used in navigation • Today we know that iron, cobalt, and nickel are magnetic materials. They are magnets due to special arrangem ...
... • Ancient Greek and Chinese used stones exist in nature that have “magical” attractive properties later known as lodestone and magnetite (iron oxide Fe203) • These stones used in navigation • Today we know that iron, cobalt, and nickel are magnetic materials. They are magnets due to special arrangem ...
Liquid Magnets Worksheet – Answers
... Individual nanoparticles align with magnetic field. Result is a three dimensional depiction of magnetic field directions and varying strengths. KEY: Single domain arrow is characteristic of the nanoparticle because of the particle size can only contain one domain. 5. Why do ferrofluid materials beha ...
... Individual nanoparticles align with magnetic field. Result is a three dimensional depiction of magnetic field directions and varying strengths. KEY: Single domain arrow is characteristic of the nanoparticle because of the particle size can only contain one domain. 5. Why do ferrofluid materials beha ...
Chapter 12: Magnetism and Magnetic Circuits
... The Nature of a Magnetic Field • Magnetism – Force of attraction or repulsion that acts between magnets and other magnetic materials ...
... The Nature of a Magnetic Field • Magnetism – Force of attraction or repulsion that acts between magnets and other magnetic materials ...
Magnetosphere of Jupiter
The magnetosphere of Jupiter is the cavity created in the solar wind by the planet's magnetic field. Extending up to seven million kilometers in the Sun's direction and almost to the orbit of Saturn in the opposite direction, Jupiter's magnetosphere is the largest and most powerful of any planetary magnetosphere in the Solar System, and by volume the largest known continuous structure in the Solar System after the heliosphere. Wider and flatter than the Earth's magnetosphere, Jupiter's is stronger by an order of magnitude, while its magnetic moment is roughly 18,000 times larger. The existence of Jupiter's magnetic field was first inferred from observations of radio emissions at the end of the 1950s and was directly observed by the Pioneer 10 spacecraft in 1973.Jupiter's internal magnetic field is generated by electrical currents in the planet's outer core, which is composed of liquid metallic hydrogen. Volcanic eruptions on Jupiter's moon Io eject large amounts of sulfur dioxide gas into space, forming a large torus around the planet. Jupiter's magnetic field forces the torus to rotate with the same angular velocity and direction as the planet. The torus in turn loads the magnetic field with plasma, in the process stretching it into a pancake-like structure called a magnetodisk. In effect, Jupiter's magnetosphere is shaped by Io's plasma and its own rotation, rather than by the solar wind like Earth's magnetosphere. Strong currents in the magnetosphere generate permanent aurorae around the planet's poles and intense variable radio emissions, which means that Jupiter can be thought of as a very weak radio pulsar. Jupiter's aurorae have been observed in almost all parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, including infrared, visible, ultraviolet and soft X-rays.The action of the magnetosphere traps and accelerates particles, producing intense belts of radiation similar to Earth's Van Allen belts, but thousands of times stronger. The interaction of energetic particles with the surfaces of Jupiter's largest moons markedly affects their chemical and physical properties. Those same particles also affect and are affected by the motions of the particles within Jupiter's tenuous planetary ring system. Radiation belts present a significant hazard for spacecraft and potentially to human space travellers.




















![ch-6 [Magnetism]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004366853_1-cbc1ce7a74752c20e1a6e456bd1e46ed-300x300.png)

