
L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]
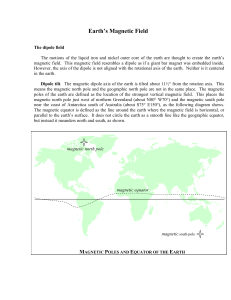
... due to currents flowing in The magnetic north pole is its molten core (not entirely inclined about 14° from the understood!) geographic north pole, or by about 600 miles. ...
... due to currents flowing in The magnetic north pole is its molten core (not entirely inclined about 14° from the understood!) geographic north pole, or by about 600 miles. ...
Chapter 1 Earth`s Magnetic Field
... Dipole offset. The magnetic dipole of the earth is not centered on the earth’s core, but instead is offset by about 700 kilometers towards the direction of southeastern Asia. This creates two features in the magnetic field at the earth’s surface. The South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA). The point on the e ...
... Dipole offset. The magnetic dipole of the earth is not centered on the earth’s core, but instead is offset by about 700 kilometers towards the direction of southeastern Asia. This creates two features in the magnetic field at the earth’s surface. The South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA). The point on the e ...
Unit 07 Magnetic Fields
... we call them “north” and “south.” However, unlike electric charges, magnetic charges never appear by themselves – they only appear together. If you take a bar magnet and break it in half, you don’t end up with one north pole and one south pole; rather, you end up with two smaller magnets! Today, the ...
... we call them “north” and “south.” However, unlike electric charges, magnetic charges never appear by themselves – they only appear together. If you take a bar magnet and break it in half, you don’t end up with one north pole and one south pole; rather, you end up with two smaller magnets! Today, the ...
Magnetic Jeopardy
... magnetic field is due north at this point and has a strength of 0.14 104 T. What is the direction of the force on the wire? ...
... magnetic field is due north at this point and has a strength of 0.14 104 T. What is the direction of the force on the wire? ...
F = BIL (f=force, b=magnetic field, i=current, l
... -Armature- is the power producing part of a motor -Domain- is a region in which the magnetic field of atoms are grouped together and aligned -Electric Motor- converts electrical energy into mechanical energy -Electromagnet- is a type of magnet whose magnetic field is produced by an electric current ...
... -Armature- is the power producing part of a motor -Domain- is a region in which the magnetic field of atoms are grouped together and aligned -Electric Motor- converts electrical energy into mechanical energy -Electromagnet- is a type of magnet whose magnetic field is produced by an electric current ...
chapter24a - Interactive Learning Toolkit
... domains of the material. A magnetic field can force the domains to line up, and the material itself can become magnetic. (Ex: iron, nickel, cobalt, steel) Paramagnetic materials are weakly attracted to magnets. The atoms of these substances contain electrons most of which spin in the same direction, ...
... domains of the material. A magnetic field can force the domains to line up, and the material itself can become magnetic. (Ex: iron, nickel, cobalt, steel) Paramagnetic materials are weakly attracted to magnets. The atoms of these substances contain electrons most of which spin in the same direction, ...
Magnetic Forces Practice
... to the plane formed by the field and the moving charge, and is greatest when the magnetic field and current are perpendicular to each other. The force on the current carrying wire shown above is therefore into the plane of the page and is determined by using the left-hand finger rule. ...
... to the plane formed by the field and the moving charge, and is greatest when the magnetic field and current are perpendicular to each other. The force on the current carrying wire shown above is therefore into the plane of the page and is determined by using the left-hand finger rule. ...
JRoo (sercle)`s Epic Test Regarding the Field of Magnetism The test
... with neighboring spins pointing in the same direction, i.e. permanent magnetism (Cobalt) ...
... with neighboring spins pointing in the same direction, i.e. permanent magnetism (Cobalt) ...
Lecture 13 - UConn Physics
... • Cosmic rays (atomic nuclei stripped bare of their electrons) would continuously bombard Earth’s surface if most of them were not deflected by Earth’s magnetic field. Given that Earth is, to an excellent approximation, a magnetic dipole, the intensity of cosmic rays bombarding its surface is greate ...
... • Cosmic rays (atomic nuclei stripped bare of their electrons) would continuously bombard Earth’s surface if most of them were not deflected by Earth’s magnetic field. Given that Earth is, to an excellent approximation, a magnetic dipole, the intensity of cosmic rays bombarding its surface is greate ...
Magnetosphere of Saturn

The magnetosphere of Saturn is the cavity created in the flow of the solar wind by the planet's internally generated magnetic field. Discovered in 1979 by the Pioneer 11 spacecraft, Saturn's magnetosphere is the second largest of any planet in the Solar System after Jupiter. The magnetopause, the boundary between Saturn's magnetosphere and the solar wind, is located at a distance of about 20 Saturn radii from the planet's center, while its magnetotail stretches hundreds of radii behind it.Saturn's magnetosphere is filled with plasmas originating from both the planet and its moons. The main source is the small moon Enceladus, which ejects as much as 1,000 kg/s of water vapor from the geysers on its south pole, a portion of which is ionized and forced to co-rotate with the Saturn’s magnetic field. This loads the field with as much as 100 kg of water group ions per second. This plasma gradually moves out from the inner magnetosphere via the interchange instability mechanism and then escapes through the magnetotail.The interaction between Saturn's magnetosphere and the solar wind generates bright oval aurorae around the planet's poles observed in visible, infrared and ultraviolet light. The aurorae are related to the powerful saturnian kilometric radiation (SKR), which spans the frequency interval between 100 kHz to 1300 kHz and was once thought to modulate with a period equal to the planet's rotation. However, later measurements showed that the periodicity of the SKR's modulation varies by as much as 1%, and so probably does not exactly coincide with Saturn’s true rotational period, which as of 2010 remains unknown. Inside the magnetosphere there are radiation belts, which house particles with energy as high as tens of megaelectronvolts. The energetic particles have significant influence on the surfaces of inner icy moons of Saturn.In 1980–1981 the magnetosphere of Saturn was studied by the Voyager spacecraft. As of 2010 it is a subject of the ongoing investigation by Cassini mission, which arrived in 2004.



![L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001652997_1-39b0ac23a2b50856ca07ac04d66ac502-300x300.png)


![L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001468655_1-12c2495c0c6eb4c679cede08941ae4d1-300x300.png)












![L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008057814_1-60bd3a273eeadb9e6de7a28a98376c5d-300x300.png)


