Magnetism - Cloudfront.net
... If you cut a permanent magnet in half, each will have a north and south pole. You can separate + and – charges but not N and S ...
... If you cut a permanent magnet in half, each will have a north and south pole. You can separate + and – charges but not N and S ...
Tracing the release sites of the energy stored in the twisted coronal
... the energy stored in the twisted coronal structure in X-class flares ...
... the energy stored in the twisted coronal structure in X-class flares ...
A general rule for how a pickup coil will respond to a magnetic field
... opposite end of the battery to switch the magnetic field. A) What happens to the magnetic field if the direction of current in the wire loop is reversed? B) What happens to the strength of the magnetic field as more electrons move (as current increases)? (Use the slider bar to increase voltage.) A. ...
... opposite end of the battery to switch the magnetic field. A) What happens to the magnetic field if the direction of current in the wire loop is reversed? B) What happens to the strength of the magnetic field as more electrons move (as current increases)? (Use the slider bar to increase voltage.) A. ...
B - Fort Bend ISD
... However, the north and south poles are not located exactly at the locations we call the north and south poles. ...
... However, the north and south poles are not located exactly at the locations we call the north and south poles. ...
A three-dimensional magnetic field and electromagnetic force
... 800 segments (801 mesh points) and each of them carries a current of 1 A. The outer solenoid extends from z = 0.2 cm to z = 0.8 cm. In the simulations presented below, the position of the inner solenoid is varied along the z − axis. The magnetic force between the two solenoids is represented as a fu ...
... 800 segments (801 mesh points) and each of them carries a current of 1 A. The outer solenoid extends from z = 0.2 cm to z = 0.8 cm. In the simulations presented below, the position of the inner solenoid is varied along the z − axis. The magnetic force between the two solenoids is represented as a fu ...
Level 4 - PO 417-1-A
... Unfortunately, the magnetic poles do not coincide with the geographic poles. Furthermore, magnetic north changes position a little every year. Averaged over thousands of years, the position of magnetic north will roughly correspond with true north, but at any given time the two poles can be very far ...
... Unfortunately, the magnetic poles do not coincide with the geographic poles. Furthermore, magnetic north changes position a little every year. Averaged over thousands of years, the position of magnetic north will roughly correspond with true north, but at any given time the two poles can be very far ...
Magnet Lab - Warren County Schools
... A magnet is a solid object, usually a rock or piece of metal, that can push or pull objects made of iron. Go on a magnet hunt around your house to find out what types of objects are magnetic. Look around and make of a list of objects you see that you think will be attracted to a magnet and another l ...
... A magnet is a solid object, usually a rock or piece of metal, that can push or pull objects made of iron. Go on a magnet hunt around your house to find out what types of objects are magnetic. Look around and make of a list of objects you see that you think will be attracted to a magnet and another l ...
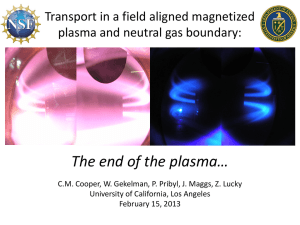
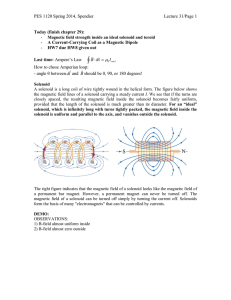
Magnetic Confinement Demonstration
... The circular motion produced by a magnetic force on a charged particle can be understood by using Newton’s Second Law, F = ma. The force exerted by a magnetic field, B, on a moving particle of electrical charge, q, with velocity, v, is F = qvB whenever v and B are perpendicular. Setting this equal t ...
... The circular motion produced by a magnetic force on a charged particle can be understood by using Newton’s Second Law, F = ma. The force exerted by a magnetic field, B, on a moving particle of electrical charge, q, with velocity, v, is F = qvB whenever v and B are perpendicular. Setting this equal t ...
Magnetosphere of Saturn

The magnetosphere of Saturn is the cavity created in the flow of the solar wind by the planet's internally generated magnetic field. Discovered in 1979 by the Pioneer 11 spacecraft, Saturn's magnetosphere is the second largest of any planet in the Solar System after Jupiter. The magnetopause, the boundary between Saturn's magnetosphere and the solar wind, is located at a distance of about 20 Saturn radii from the planet's center, while its magnetotail stretches hundreds of radii behind it.Saturn's magnetosphere is filled with plasmas originating from both the planet and its moons. The main source is the small moon Enceladus, which ejects as much as 1,000 kg/s of water vapor from the geysers on its south pole, a portion of which is ionized and forced to co-rotate with the Saturn’s magnetic field. This loads the field with as much as 100 kg of water group ions per second. This plasma gradually moves out from the inner magnetosphere via the interchange instability mechanism and then escapes through the magnetotail.The interaction between Saturn's magnetosphere and the solar wind generates bright oval aurorae around the planet's poles observed in visible, infrared and ultraviolet light. The aurorae are related to the powerful saturnian kilometric radiation (SKR), which spans the frequency interval between 100 kHz to 1300 kHz and was once thought to modulate with a period equal to the planet's rotation. However, later measurements showed that the periodicity of the SKR's modulation varies by as much as 1%, and so probably does not exactly coincide with Saturn’s true rotational period, which as of 2010 remains unknown. Inside the magnetosphere there are radiation belts, which house particles with energy as high as tens of megaelectronvolts. The energetic particles have significant influence on the surfaces of inner icy moons of Saturn.In 1980–1981 the magnetosphere of Saturn was studied by the Voyager spacecraft. As of 2010 it is a subject of the ongoing investigation by Cassini mission, which arrived in 2004.