Permanent Magnets
... The poles of the Earth’s magnetic field are not aligned with the Earth’s geographic poles defined as the endpoints of the axis of the Earth’s rotation ...
... The poles of the Earth’s magnetic field are not aligned with the Earth’s geographic poles defined as the endpoints of the axis of the Earth’s rotation ...
The wind from the Sun: an introduction - LESIA
... last the modern solar wind concept was born. Parker’s theory was not only an eminently elegant solution which brought together existing evidences, but it made numerous testable predictions: in particular the wind was to flow at several hundreds of kilometres per second radially away from the Sun. Ir ...
... last the modern solar wind concept was born. Parker’s theory was not only an eminently elegant solution which brought together existing evidences, but it made numerous testable predictions: in particular the wind was to flow at several hundreds of kilometres per second radially away from the Sun. Ir ...
The Earth`s Magnetic Field
... partially blocking it out. However, there is always some part of the plasma and radiation that is able to penetrate through the magnetic field barrier, and this often leads to magnetic disturbances around the Earth. Before humans started seeking out into space, with orbiting satellites and space voy ...
... partially blocking it out. However, there is always some part of the plasma and radiation that is able to penetrate through the magnetic field barrier, and this often leads to magnetic disturbances around the Earth. Before humans started seeking out into space, with orbiting satellites and space voy ...
Physics 122B Electromagnetism
... in which a negative electron orbits a positive nucleus. The electron's motion is that of a current loop. Consequently, an orbiting electron acts as a tiny magnetic dipole, with a north pole and a south pole. However, the atoms of most elements contain many electrons. Unlike the solar system, where a ...
... in which a negative electron orbits a positive nucleus. The electron's motion is that of a current loop. Consequently, an orbiting electron acts as a tiny magnetic dipole, with a north pole and a south pole. However, the atoms of most elements contain many electrons. Unlike the solar system, where a ...
B - University of Utah Physics
... field B. The loop is mounted such that it is free to rotate about a vertical axis through its center. We will consider the forces on each segment and the resulting torque from each. Using RHR-1: The force on segment 3 points down, and that on segment 4 points up. F3 and F4 are also equal in magnitud ...
... field B. The loop is mounted such that it is free to rotate about a vertical axis through its center. We will consider the forces on each segment and the resulting torque from each. Using RHR-1: The force on segment 3 points down, and that on segment 4 points up. F3 and F4 are also equal in magnitud ...
08_LectureOutlines
... The nebular theory states that our solar system formed from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar gas cloud—the solar nebula (Nebula is the Latin word for cloud) ...
... The nebular theory states that our solar system formed from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar gas cloud—the solar nebula (Nebula is the Latin word for cloud) ...
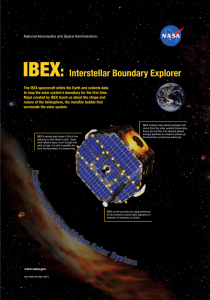
Exploring the Edge of the Solar System
... Neptune. After their planetary observations, both spacecraft continued outward in different directions. The Voyagers were only supposed to last a few years, but they have continued to operate for over 30 years, well past their designed lifetimes. Today, both Voyagers are taking direct measurements o ...
... Neptune. After their planetary observations, both spacecraft continued outward in different directions. The Voyagers were only supposed to last a few years, but they have continued to operate for over 30 years, well past their designed lifetimes. Today, both Voyagers are taking direct measurements o ...
Solar System Formation PPT
... • *Interstellar clouds are vast collections of gases that contain about ___% hydrogen, ___% helium, and traces of the other elements.* • Basic elements (hydrogen, iron, etc.) in the solar nebula _______ into small particles. • Small particles in the solar nebula gradually formed larger particles thr ...
... • *Interstellar clouds are vast collections of gases that contain about ___% hydrogen, ___% helium, and traces of the other elements.* • Basic elements (hydrogen, iron, etc.) in the solar nebula _______ into small particles. • Small particles in the solar nebula gradually formed larger particles thr ...
esa`s magnetic field mission
... of north. Moreover, the strength of the magnetic field constantly changes – and it is currently showing signs of ...
... of north. Moreover, the strength of the magnetic field constantly changes – and it is currently showing signs of ...
Holy Cow Magnet!
... tiny piece of iron to align itself along the lines of magnetic force created by the magnet. You can think of iron filings as thousands of tiny compasses, each under the influence of the strength and direction of the magnetic force. In this activity, instead of using iron filings to visualize magneti ...
... tiny piece of iron to align itself along the lines of magnetic force created by the magnet. You can think of iron filings as thousands of tiny compasses, each under the influence of the strength and direction of the magnetic force. In this activity, instead of using iron filings to visualize magneti ...
Solar Wind-Magnetosphere-Ionosphere Coupling: Dynamics in
... – The magnetosphere-ionosphere is coupled via waves (not necessarily sinesoidal) – Dispersion relation and attenuation rate are derived for the collisional Alfven mode – 1-D self-consistent simulations with continuity, momentum, energy conservation, and Maxwell’s equations and photochemistry have be ...
... – The magnetosphere-ionosphere is coupled via waves (not necessarily sinesoidal) – Dispersion relation and attenuation rate are derived for the collisional Alfven mode – 1-D self-consistent simulations with continuity, momentum, energy conservation, and Maxwell’s equations and photochemistry have be ...
SUPERCONDUCTING MATERIALS
... magnetic field, and the train is levitated by the repulsive force between these magnetic fields. The magnetic field in the train is produced by either electromagnets or by an array of permanent magnets The repulsive force in the track is created by an induced magnetic field in wires or other conduct ...
... magnetic field, and the train is levitated by the repulsive force between these magnetic fields. The magnetic field in the train is produced by either electromagnets or by an array of permanent magnets The repulsive force in the track is created by an induced magnetic field in wires or other conduct ...
The Solar Nebula
... • thermal motions and gas pressure mean that the gas is in motion; • magnetic fields act upon the charged particles in the cloud, making them follow field lines rather than obey gravity; and • rotation gives an outward centrifugal force that keeps the cloud from collapsing. The particles are in moti ...
... • thermal motions and gas pressure mean that the gas is in motion; • magnetic fields act upon the charged particles in the cloud, making them follow field lines rather than obey gravity; and • rotation gives an outward centrifugal force that keeps the cloud from collapsing. The particles are in moti ...
Geomagnetic storm

A geomagnetic storm is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere caused by a solar wind shock wave and/or cloud of magnetic field that interacts with the Earth's magnetic field. The increase in the solar wind pressure initially compresses the magnetosphere. The solar wind's magnetic field interacts with the Earth’s magnetic field and transfers an increased energy into the magnetosphere. Both interactions cause an increase in plasma movement through the magnetosphere (driven by increased electric fields inside the magnetosphere) and an increase in electric current in the magnetosphere and ionosphere.During the main phase of a geomagnetic storm, electric current in the magnetosphere creates a magnetic force that pushes out the boundary between the magnetosphere and the solar wind. The disturbance in the interplanetary medium that drives the storm may be due to a solar coronal mass ejection (CME) or a high speed stream (co-rotating interaction region or CIR) of the solar wind originating from a region of weak magnetic field on the Sun’s surface. The frequency of geomagnetic storms increases and decreases with the sunspot cycle. CME driven storms are more common during the maximum of the solar cycle, while CIR driven storms are more common during the minimum of the solar cycle.Several space weather phenomena tend to be associated with or are caused by a geomagnetic storm. These include: solar energetic Particle (SEP) events, geomagnetically induced currents (GIC), ionospheric disturbances that cause radio and radar scintillation, disruption of navigation by magnetic compass and auroral displays at much lower latitudes than normal. In 1989, a geomagnetic storm energized ground induced currents that disrupted electric power distribution throughout most of the province of Quebec and caused aurorae as far south as Texas.