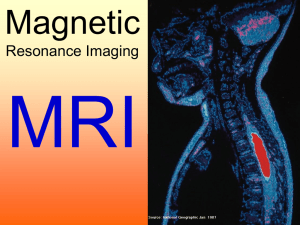
MRI
... Magnetic Resonance Imaging It is energetically more favourable for hydrogen nuclei to return to their original state in the external magnetic field after the RF pulse. As they do so, they re-emit the energy absorbed from the radio wave in about 0.01 to 0.1 seconds. The emitted energy is a radio wav ...
... Magnetic Resonance Imaging It is energetically more favourable for hydrogen nuclei to return to their original state in the external magnetic field after the RF pulse. As they do so, they re-emit the energy absorbed from the radio wave in about 0.01 to 0.1 seconds. The emitted energy is a radio wav ...
22_LectureOutline
... Many materials that are not ferromagnetic are paramagnetic – they will partially align in a strong magnetic field, but the alignment disappears when the external field is gone. ...
... Many materials that are not ferromagnetic are paramagnetic – they will partially align in a strong magnetic field, but the alignment disappears when the external field is gone. ...
What is a magnet? - Northern Highlands
... have a compass with you if you are hiking. Some automobiles now come equipped with a built-in compass, and some even use more sophisticated global positioning system technology, which uses satellites rather than magnetic fields to determine direction. How does a compass work? A simple compass is rea ...
... have a compass with you if you are hiking. Some automobiles now come equipped with a built-in compass, and some even use more sophisticated global positioning system technology, which uses satellites rather than magnetic fields to determine direction. How does a compass work? A simple compass is rea ...
Inquiry Activity
... north pole of the magnet and into the south pole of the magnet. This kind of magnetic field is known as a magnetic dipole. (See diagram on right) Magnets are not the only things that can produce magnetic fields. Moving charged particles such as electrons can also create a magnetic field. A straight ...
... north pole of the magnet and into the south pole of the magnet. This kind of magnetic field is known as a magnetic dipole. (See diagram on right) Magnets are not the only things that can produce magnetic fields. Moving charged particles such as electrons can also create a magnetic field. A straight ...
magnetic-properties
... “magnetite” a natural magnetic material Fe3O4. They discovered that the stone always pointed towards north. ...
... “magnetite” a natural magnetic material Fe3O4. They discovered that the stone always pointed towards north. ...
CHAPTER 27: MAGNETIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC FORCES
... • This chapter focuses on how moving charges and currents respond to magnetic fields. Later we will study how moving charges and currents produce magnetic fields. • A permanent magnet is an object made from a material that is permanently magnetized and thus creates its own persistent magnetic field. ...
... • This chapter focuses on how moving charges and currents respond to magnetic fields. Later we will study how moving charges and currents produce magnetic fields. • A permanent magnet is an object made from a material that is permanently magnetized and thus creates its own persistent magnetic field. ...
I Magnetism in Nature
... because they average out, for example due to the thermal motion of the spins or through some other mechanism. This is called motional narrowing. Why narrowing? When molecules are static the effect of complex coupling to their spin neighbors manifests itself as a broadening of their spectral line. O ...
... because they average out, for example due to the thermal motion of the spins or through some other mechanism. This is called motional narrowing. Why narrowing? When molecules are static the effect of complex coupling to their spin neighbors manifests itself as a broadening of their spectral line. O ...
2-17 Magnetic Field: Causes
... depends on the strength of the magnetic field. This turns the iron rod or bar into a magnet. Remove the rod or bar from the magnetic field and local forces on the domains cause them to revert back toward their original orientations. They do not achieve their original orientations and the iron remain ...
... depends on the strength of the magnetic field. This turns the iron rod or bar into a magnet. Remove the rod or bar from the magnetic field and local forces on the domains cause them to revert back toward their original orientations. They do not achieve their original orientations and the iron remain ...
Physics 6B - UCSB Campus Learning Assistance Services
... Notice that the force is always perpendicular to the velocity. This will yield a circular path. In other words, the magnetic force is a centripetal force. ...
... Notice that the force is always perpendicular to the velocity. This will yield a circular path. In other words, the magnetic force is a centripetal force. ...
Magnets Hold a refrigerator magnet close to your refrigerator door
... In the 1200s, sailors learned how to make a compass that could help them find their way at sea. They made a needle from a thin piece of lodestone or iron. They hung the needle from a string. The needle always pointed north. Because Earth is a big magnet, the south pole of the compass needle always p ...
... In the 1200s, sailors learned how to make a compass that could help them find their way at sea. They made a needle from a thin piece of lodestone or iron. They hung the needle from a string. The needle always pointed north. Because Earth is a big magnet, the south pole of the compass needle always p ...
Compass
A compass is an instrument used for navigation and orientation that shows direction relative to the geographic cardinal directions, or ""points"". Usually, a diagram called a compass rose, shows the directions north, south, east, and west as abbreviated initials marked on the compass. When the compass is used, the rose can be aligned with the corresponding geographic directions, so, for example, the ""N"" mark on the rose really points to the north. Frequently, in addition to the rose or sometimes instead of it, angle markings in degrees are shown on the compass. North corresponds to zero degrees, and the angles increase clockwise, so east is 90 degrees, south is 180, and west is 270. These numbers allow the compass to show azimuths or bearings, which are commonly stated in this notation.The magnetic compass was first invented as a device for divination as early as the Chinese Han Dynasty (since about 206 BC), and later adopted for navigation by the Song Dynasty Chinese during the 11th century. The use of a compass is recorded in Western Europe and in Persia around the early 13th century.