dekalb reads - GEOCITIES.ws
... 13. Define magnetic poles. 14. Two like poles _______________ each other. 15. The North Pole of one magnet will ________________________________________. 16. It is _____________ to isolate a south magnetic pole from a north magnetic pole. ...
... 13. Define magnetic poles. 14. Two like poles _______________ each other. 15. The North Pole of one magnet will ________________________________________. 16. It is _____________ to isolate a south magnetic pole from a north magnetic pole. ...
L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]
... • how does a compass work • the north pole is really a south pole! • Van Allen radiation belts ...
... • how does a compass work • the north pole is really a south pole! • Van Allen radiation belts ...
chapter24a - Interactive Learning Toolkit
... domains of the material. A magnetic field can force the domains to line up, and the material itself can become magnetic. (Ex: iron, nickel, cobalt, steel) Paramagnetic materials are weakly attracted to magnets. The atoms of these substances contain electrons most of which spin in the same direction, ...
... domains of the material. A magnetic field can force the domains to line up, and the material itself can become magnetic. (Ex: iron, nickel, cobalt, steel) Paramagnetic materials are weakly attracted to magnets. The atoms of these substances contain electrons most of which spin in the same direction, ...
L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]
... Magnetic forces • Magnetic fields exert sidewise forces on charges • A charge is turned around by the magnetic force • There is NO magnetic force if the charge is ...
... Magnetic forces • Magnetic fields exert sidewise forces on charges • A charge is turned around by the magnetic force • There is NO magnetic force if the charge is ...
Magnetic Field
... not coincide with the N geographic pole, there is a correction that needs to be made to compass readings l Not so bad in ...
... not coincide with the N geographic pole, there is a correction that needs to be made to compass readings l Not so bad in ...
Magnetism -the attraction of a magnet for another object
... Magnetism was discovered in Magnesia Greece (which is now Turkey) A mineral in rocks that is magnetic was discovered. This mineral was called magnetite. The name of these rocks are called lodestones. ...
... Magnetism was discovered in Magnesia Greece (which is now Turkey) A mineral in rocks that is magnetic was discovered. This mineral was called magnetite. The name of these rocks are called lodestones. ...
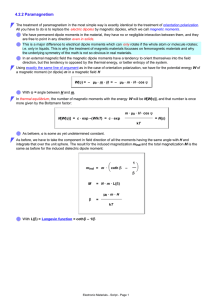
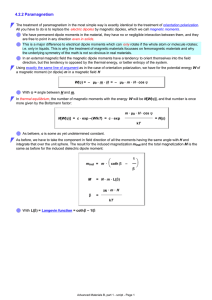
4.2.2 Paramagnetism
... We have permanent dipole moments in the material, they have no or negligible interaction between them, and they are free to point in any direction even in solids. This is a major difference to electrical dipole moments which can only rotate if the whole atom or molecule rotates; i.e. only in liquids ...
... We have permanent dipole moments in the material, they have no or negligible interaction between them, and they are free to point in any direction even in solids. This is a major difference to electrical dipole moments which can only rotate if the whole atom or molecule rotates; i.e. only in liquids ...
conceptutal physics ch.24
... a) In what direction relative to a magnetic field does a charged particle move in order to experience maximum deflecting force? Ans. The charged particle must move at right angles to the field. b) In what direction relative to a magnetic field does a charged particle move in order to experience mimi ...
... a) In what direction relative to a magnetic field does a charged particle move in order to experience maximum deflecting force? Ans. The charged particle must move at right angles to the field. b) In what direction relative to a magnetic field does a charged particle move in order to experience mimi ...
Magnetic Fabric in Granitic Rocks: its Intrusive Origin and
... The anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility (AMS) is one of the most powerful tools of the structural analysis of granitic rocks, because it can efficiently measure the preferred orientation of magnetic minerals (the magnetic fabric) even in massive granites which are isotropic at the first sight. In ...
... The anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility (AMS) is one of the most powerful tools of the structural analysis of granitic rocks, because it can efficiently measure the preferred orientation of magnetic minerals (the magnetic fabric) even in massive granites which are isotropic at the first sight. In ...
Magnetism - Worth County Schools
... - different locations than the earth’s geographic poles ( N magnetic pole – Canada) - the compass – is a freely rotating magnetic needle that responds to the earth’s magnetic poles by pointing North. - Lodestone (magnetite) – a natural magnet was used as the first compass on ships. ...
... - different locations than the earth’s geographic poles ( N magnetic pole – Canada) - the compass – is a freely rotating magnetic needle that responds to the earth’s magnetic poles by pointing North. - Lodestone (magnetite) – a natural magnet was used as the first compass on ships. ...
Worksheet 8.2 - Magnetic Forces on Wires and Charges
... 1. A particle carrying a charge of 0.50 μC enters a magnetic field of strength 0.045 T, with a velocity of 350 m/s. The velocity is perpendicular to the magnetic field. What is the magnetic force acting on the charged particle? 2. A segment of conducting wire 5.0 cm long carrying 5.0 A of current is ...
... 1. A particle carrying a charge of 0.50 μC enters a magnetic field of strength 0.045 T, with a velocity of 350 m/s. The velocity is perpendicular to the magnetic field. What is the magnetic force acting on the charged particle? 2. A segment of conducting wire 5.0 cm long carrying 5.0 A of current is ...
Compass
A compass is an instrument used for navigation and orientation that shows direction relative to the geographic cardinal directions, or ""points"". Usually, a diagram called a compass rose, shows the directions north, south, east, and west as abbreviated initials marked on the compass. When the compass is used, the rose can be aligned with the corresponding geographic directions, so, for example, the ""N"" mark on the rose really points to the north. Frequently, in addition to the rose or sometimes instead of it, angle markings in degrees are shown on the compass. North corresponds to zero degrees, and the angles increase clockwise, so east is 90 degrees, south is 180, and west is 270. These numbers allow the compass to show azimuths or bearings, which are commonly stated in this notation.The magnetic compass was first invented as a device for divination as early as the Chinese Han Dynasty (since about 206 BC), and later adopted for navigation by the Song Dynasty Chinese during the 11th century. The use of a compass is recorded in Western Europe and in Persia around the early 13th century.
![L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001677438_1-6f2ee9f2e116a6ee3a90ac77f126c6b0-300x300.png)

![L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001151145_1-04a797404aa534cecfaa7f9c9c11aff9-300x300.png)














![L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001652997_1-39b0ac23a2b50856ca07ac04d66ac502-300x300.png)
![L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001468655_1-12c2495c0c6eb4c679cede08941ae4d1-300x300.png)